
What function do ribosomes serve in polypeptide synthesis?
Answer
491.7k+ views
Hint:Ribosomes are ribonucleoprotein granular organelles without covering membrane. They were first observed by Claude and named microsomes. Palade saw them in animal cells and named them ribosomes. Ribosomes are a universal component of cells being present in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. They are absent in mature erythrocytes. They have a diameter of approx 18 nm. E. coli has about 10,000-30,000 ribosomes. There are upto 10 million ribosomes in cultured mammalian cells
Complete answer:
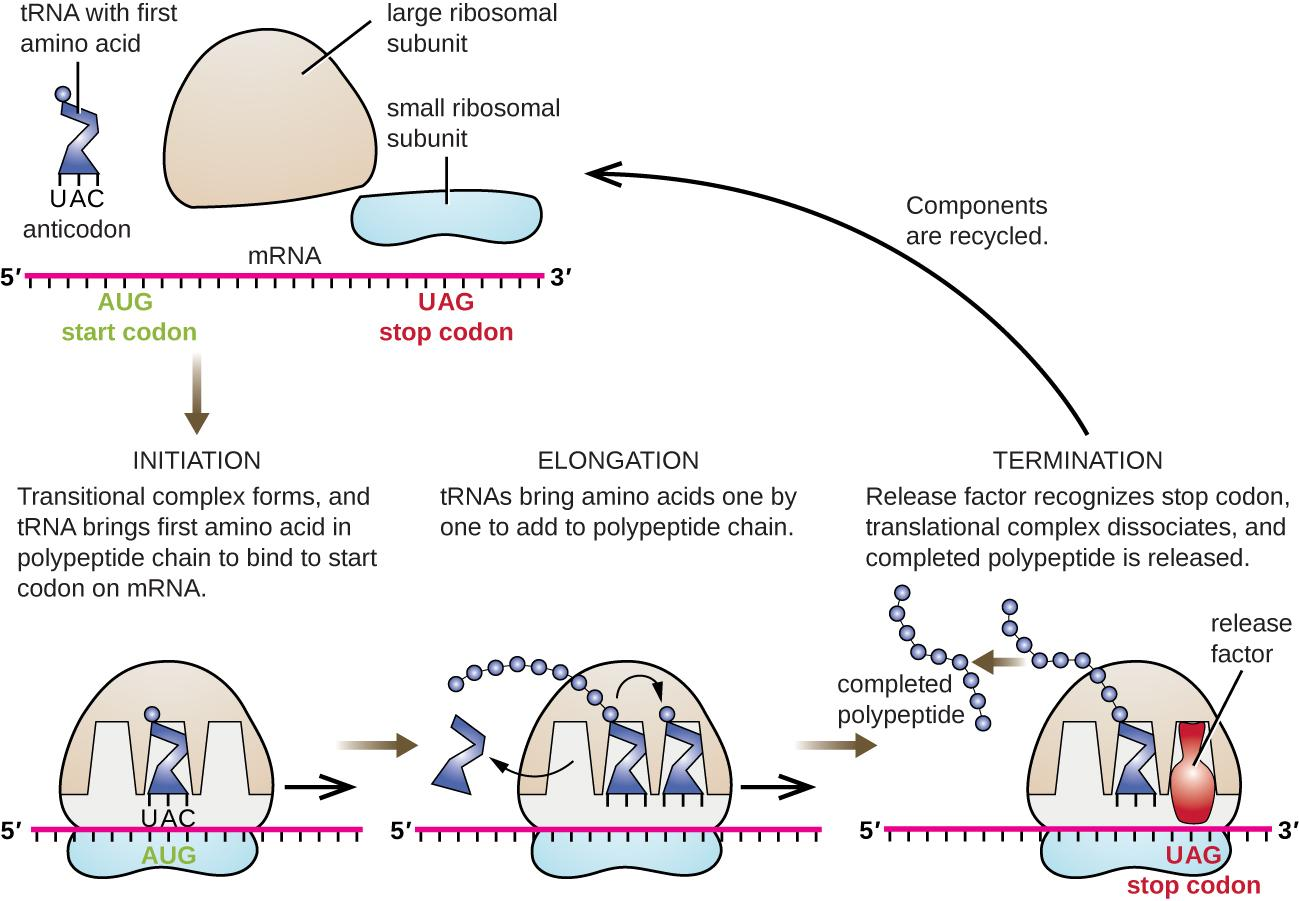
Cells performing active Protein synthesis like pancreatic and liver cells contain a very large number of ribosomes. Ribosomes serve as a framework on which Protein synthesis occurs. The initiation complex is formed by binding of mRNA to the 30S subunit of ribosome. Ribosomes have the ability to catalyze the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids leading to the incorporation of amino acids into protein. This is the main role of ribosomes.
Ribosome is made up of two unequal subunits, smaller and larger. Prokaryotic ribosomes are composed of 30 S and 50 S subunits. S stands for sedimentation coefficient or Svedberg coefficient. Both 30 S and 50 S subunits have a combined coefficient of 70 S. Eukaryotic ribosomes are larger than prokaryotic ribosomes. They have two subunits of 40 S and 60 S, having a combined coefficient of 80 S.
Prokaryotes have the ribosome binding site near the 5’ end of mRNA upstream of start codon AUG. There are many bases between 5’ end of mRNA and AUG codon. There is a sequence of 5’-AGGAGGU-3’, which is called the Shine-Dalgarno sequence. The 3’-end region of 16 S rRNA has a complementary sequence of 3’-AUUCCUUCCA-5’. This sequence binds mRNA to the ribosome.
Ribosome has two channels. One channel has a decoding centre, linear mRNA enters and escapes through this channel and it is also accessible to the charged tRNAs. The newly synthesized polypeptide chain escapes through the other channel. Charged tRNAs decode the codons of mRNA in the small subunit of ribosomes which contain the decoding centre. Peptidyl transferase centre is present in a large subunit which forms peptide bonds between successive amino acids. The mRNA binds to the 3’-end of 16sRNA. The mRNA, 30 S subunit and charged tRNA combine to form a preinitiation complex along with initiation factors and GTP. Later 50S ribosomal subunits also join to form 70 S initiation complexes.
Note:
There are two types of ribosomes in eukaryotic cells, cytoplasmic ribosomes and organelle ribosomes. Cytoplasmic ribosomes also called cyto ribosomes may occur free in the cytosol or may be bound to the endoplasmic reticulum and outer surface of the nuclear envelope. Organelle ribosomes occur in semi-autonomous organelles- in the matrix of ribosomes and inside the matrix or stroma of plastids. Prokaryotic cells do not have mitochondria and plastids therefore, only cytoplasmic ribosomes are present in them.
Complete answer:
Cells performing active Protein synthesis like pancreatic and liver cells contain a very large number of ribosomes. Ribosomes serve as a framework on which Protein synthesis occurs. The initiation complex is formed by binding of mRNA to the 30S subunit of ribosome. Ribosomes have the ability to catalyze the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids leading to the incorporation of amino acids into protein. This is the main role of ribosomes.
Ribosome is made up of two unequal subunits, smaller and larger. Prokaryotic ribosomes are composed of 30 S and 50 S subunits. S stands for sedimentation coefficient or Svedberg coefficient. Both 30 S and 50 S subunits have a combined coefficient of 70 S. Eukaryotic ribosomes are larger than prokaryotic ribosomes. They have two subunits of 40 S and 60 S, having a combined coefficient of 80 S.
Prokaryotes have the ribosome binding site near the 5’ end of mRNA upstream of start codon AUG. There are many bases between 5’ end of mRNA and AUG codon. There is a sequence of 5’-AGGAGGU-3’, which is called the Shine-Dalgarno sequence. The 3’-end region of 16 S rRNA has a complementary sequence of 3’-AUUCCUUCCA-5’. This sequence binds mRNA to the ribosome.
Ribosome has two channels. One channel has a decoding centre, linear mRNA enters and escapes through this channel and it is also accessible to the charged tRNAs. The newly synthesized polypeptide chain escapes through the other channel. Charged tRNAs decode the codons of mRNA in the small subunit of ribosomes which contain the decoding centre. Peptidyl transferase centre is present in a large subunit which forms peptide bonds between successive amino acids. The mRNA binds to the 3’-end of 16sRNA. The mRNA, 30 S subunit and charged tRNA combine to form a preinitiation complex along with initiation factors and GTP. Later 50S ribosomal subunits also join to form 70 S initiation complexes.

Note:
There are two types of ribosomes in eukaryotic cells, cytoplasmic ribosomes and organelle ribosomes. Cytoplasmic ribosomes also called cyto ribosomes may occur free in the cytosol or may be bound to the endoplasmic reticulum and outer surface of the nuclear envelope. Organelle ribosomes occur in semi-autonomous organelles- in the matrix of ribosomes and inside the matrix or stroma of plastids. Prokaryotic cells do not have mitochondria and plastids therefore, only cytoplasmic ribosomes are present in them.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




