
Gabriel phthalimide reaction is used for the preparation of:
A) Primary aromatic amines
B) Secondary amines
C) Primary aliphatic amines
D) Tertiary amines
Answer
596.7k+ views
Hint: in this reaction phthalimide is treated with ethanolic potassium hydroxide. The product obtained is then heated with alkyl halide, followed by alkaline hydrolysis producing the final product. Now try and put together the reaction.
Complete step by step solution:
-This reaction is used for transforming primary alkyl halide into primary amines.
-Secondary and tertiary amines are not formed by this synthesis, so pure primary amines are formed which is the reason why this reaction is preferred for formation of primary amine.
-This is a 3 step reaction:
Step 1: Phthalimide is treated with potassium hydroxide ($KOH$) initiating an acid-base reaction. Imide is deprotonated by the hydroxide ion. This forms a potassium salt of phthalimide (imide ion) which is nucleophilic in nature.
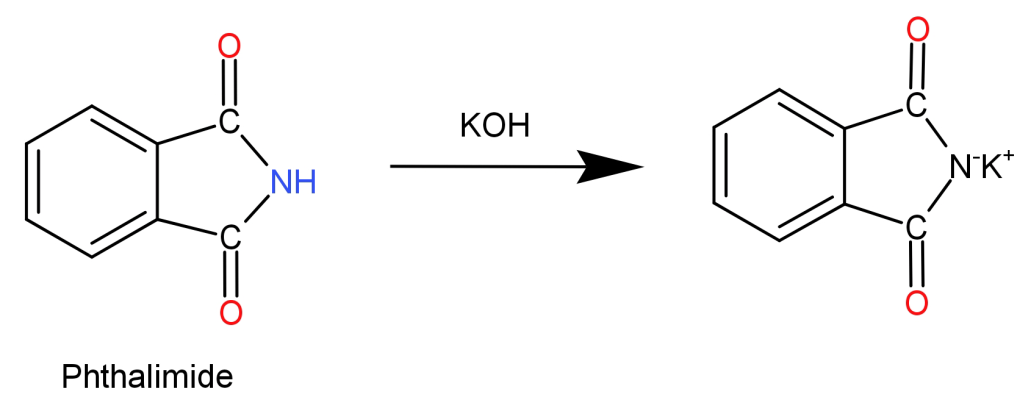
Step 2: Now, the obtained imide ion is treated with alkyl halide ($R - X$). The electrophilic carbon of the alkyl halide is attacked by the nucleophilic imide. Halogen atom of the alkyl halide is removed and replaced by the nitrogen atom which bonds with the carbon itself. This results in the formation of N-Alkyl Phthalimide.

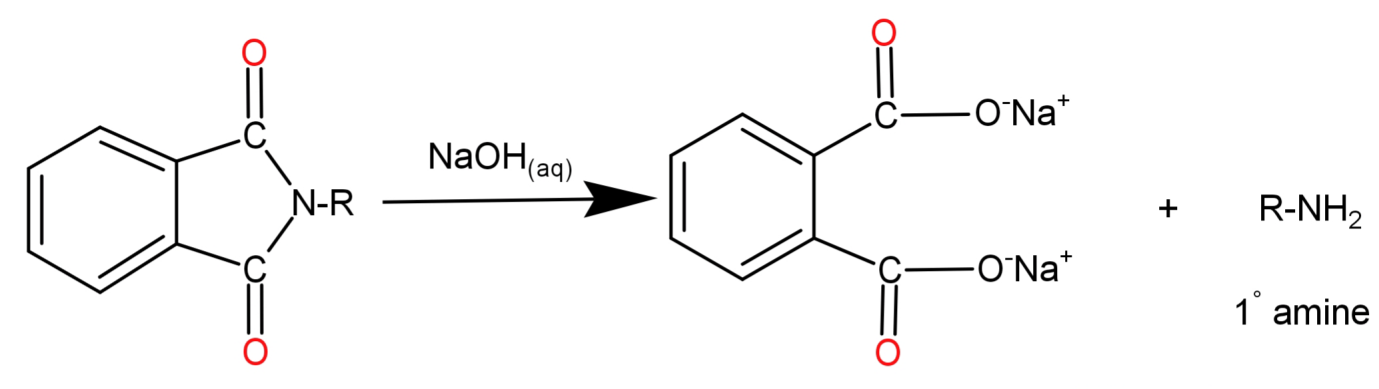
Step 3: N-Alkyl Phthalimide then undergoes alkaline hydrolysis by reaction with aqueous Sodium Hydroxide ($NaO{N_{(aq)}}$). The hydroxide ion from Sodium hydroxide reacts with the carbon atom from the alkyl group causing the cleavage of N-Alkyl Phthalimide and the cation attaches itself to the oxygen atom. When the oxygen atom replaces the nitrogen in phthalimide the ejected hydrogen ions get attached to the nitrogen which was already attached to the alkyl (R) group.
-Only aliphatic primary amines are formed and not aromatic because aryl halides do not undergo the nucleophilic substitution reaction with the anion formed by phthalimide.
So, the correct option is, (C) Primary aliphatic amines
Note: Do not confuse yourself between options (A) Aromatic Primary amines and (C) Primary aliphatic amines because aromatic primary amines cannot be formed since aryl halides do not undergo nucleophilic substitution reaction with the phthalimide anion.
Complete step by step solution:
-This reaction is used for transforming primary alkyl halide into primary amines.
-Secondary and tertiary amines are not formed by this synthesis, so pure primary amines are formed which is the reason why this reaction is preferred for formation of primary amine.
-This is a 3 step reaction:
Step 1: Phthalimide is treated with potassium hydroxide ($KOH$) initiating an acid-base reaction. Imide is deprotonated by the hydroxide ion. This forms a potassium salt of phthalimide (imide ion) which is nucleophilic in nature.

Step 2: Now, the obtained imide ion is treated with alkyl halide ($R - X$). The electrophilic carbon of the alkyl halide is attacked by the nucleophilic imide. Halogen atom of the alkyl halide is removed and replaced by the nitrogen atom which bonds with the carbon itself. This results in the formation of N-Alkyl Phthalimide.

Step 3: N-Alkyl Phthalimide then undergoes alkaline hydrolysis by reaction with aqueous Sodium Hydroxide ($NaO{N_{(aq)}}$). The hydroxide ion from Sodium hydroxide reacts with the carbon atom from the alkyl group causing the cleavage of N-Alkyl Phthalimide and the cation attaches itself to the oxygen atom. When the oxygen atom replaces the nitrogen in phthalimide the ejected hydrogen ions get attached to the nitrogen which was already attached to the alkyl (R) group.
-Only aliphatic primary amines are formed and not aromatic because aryl halides do not undergo the nucleophilic substitution reaction with the anion formed by phthalimide.
So, the correct option is, (C) Primary aliphatic amines

Note: Do not confuse yourself between options (A) Aromatic Primary amines and (C) Primary aliphatic amines because aromatic primary amines cannot be formed since aryl halides do not undergo nucleophilic substitution reaction with the phthalimide anion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




