
What is Gatterman aldehyde synthesis?
Answer
582.6k+ views
Hint: The reaction involving carbon compounds and the derivatives of carbon are known as organic reactions. Gatterman aldehyde synthesis is an organic reaction which is used to synthesize aromatic aldehydes.
Complete step by step answer:
Carbon and derivatives of carbon are considered as organic compounds and the reactions involving organic compounds are known as organic reactions. Gatterman aldehyde synthesis is an organic reaction and as we can see in its name that it is used to make aldehydes. It is mostly used for aromatic compounds because stable products are available only for aromatic compounds. The aromatic compounds are converted into aldehydes using hydrogen cyanide, hydrogen chloride and a Lewis acid such as aluminium chloride.
The reaction is as follows:
Step1.
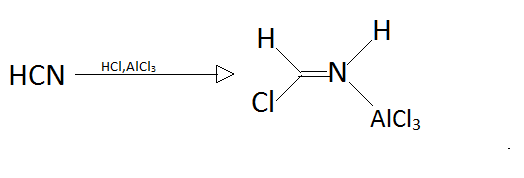
Step2.
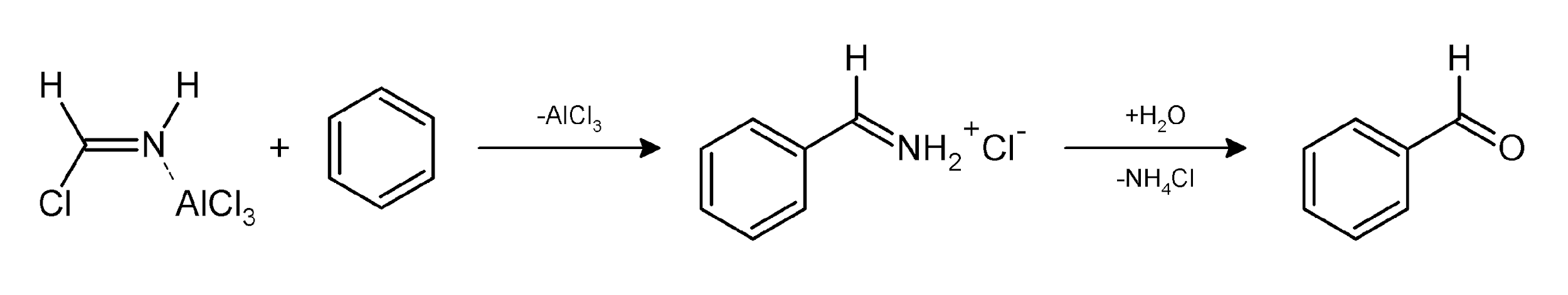
In step one as we can see that hydrogen cyanide reacts with hydrochloric acid and aluminium chloride to produce a new better nucleophile that can attack on aromatic compound benzene.
In step two the reagent attacks on benzene forms a product releasing aluminium chloride and on further reacting with water it again releases ammonium chloride and hence our final product benzaldehyde is produced.
So this is the overall Gatterman aldehyde synthesis.
Gatterman aldehyde synthesis is similar to the friedel craft reaction. When an alkyl group is added to a benzene ring via electrophilic substitution reaction, it is called a friedel craft alkylation and the same is happening here but the group attached is different, we are adding an aldehyde group on the benzene ring.
Note:
A reaction similar to Gatterman aldehyde synthesis also exists in organic chemistry which is known as Gatterman Koch synthesis. The functionality of both the reactions is the same but reagents are different. Carbon monoxide is used in Gatterman Koch synthesis.
Complete step by step answer:
Carbon and derivatives of carbon are considered as organic compounds and the reactions involving organic compounds are known as organic reactions. Gatterman aldehyde synthesis is an organic reaction and as we can see in its name that it is used to make aldehydes. It is mostly used for aromatic compounds because stable products are available only for aromatic compounds. The aromatic compounds are converted into aldehydes using hydrogen cyanide, hydrogen chloride and a Lewis acid such as aluminium chloride.
The reaction is as follows:
Step1.

Step2.

In step one as we can see that hydrogen cyanide reacts with hydrochloric acid and aluminium chloride to produce a new better nucleophile that can attack on aromatic compound benzene.
In step two the reagent attacks on benzene forms a product releasing aluminium chloride and on further reacting with water it again releases ammonium chloride and hence our final product benzaldehyde is produced.
So this is the overall Gatterman aldehyde synthesis.
Gatterman aldehyde synthesis is similar to the friedel craft reaction. When an alkyl group is added to a benzene ring via electrophilic substitution reaction, it is called a friedel craft alkylation and the same is happening here but the group attached is different, we are adding an aldehyde group on the benzene ring.
Note:
A reaction similar to Gatterman aldehyde synthesis also exists in organic chemistry which is known as Gatterman Koch synthesis. The functionality of both the reactions is the same but reagents are different. Carbon monoxide is used in Gatterman Koch synthesis.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




