
What can gel electrophoresis be used for?
Answer
481.5k+ views
Hint: Gel electrophoresis is a scientific technique used in research laboratories used in the separation of charged molecules like DNA, proteins and RNA through charge, and molecular size. In this technique, the molecules to be separated are pushed by an electrical field, via a gel, containing small pores. Molecules travel through gel pores at a speed, which is inversely proportional to their respective lengths.
Complete answer
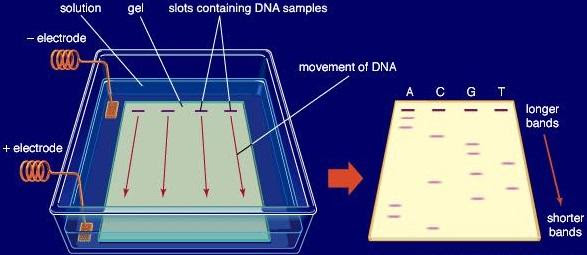
Fig: Parts of an Electrophoresis Apparatus
Gel electrophoresis is used in various fields like molecular biology, genetic engineering, microbiology, forensics, and biochemistry. It is used by DNA fingerprinting to differentiate between samples of genetic materials.
Some of the key applications of gel electrophoresis are given below:
1. In the study of evolutionary relationships through the analysis of genetic similarity among species or populations.
2. In blotting techniques for the analytical purpose of macromolecules.
3. In the analysis of resistance towards antibiotics.
4. In the study of function and structure of proteins.
5. In paternity testing via DNA fingerprinting.
6. In DNA profiling for the taxonomy studies for the differentiation of different specie.s
7. For the analysis of genes associated with a particular illness.
8. For analyzing results of polymerase chain reaction.
9. For the separation of DNA fragments for the use in DNA fingerprinting to investigate crime scenes.
10. Used in immunoelectrophoresis.
11. Used in the separation of different types of proteins and nucleic acids.
12. Quantification of proteins.
13. Checking the purity of proteins.
14. Identification of disulfide bonds between proteins.
15. Purification of isolated proteins.
16. Estimation of molecular weight of proteins.
Note:
Gel electrophoresis is classified into agarose gel electrophoresis, starch electrophoresis, polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and denatured or sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). The native variant is run on non-denaturing conditions, leading to preservation of the molecule's native structure. Denaturing conditions unfold the proteins, losing secondary and tertiary structures.
Complete answer

Fig: Parts of an Electrophoresis Apparatus
Gel electrophoresis is used in various fields like molecular biology, genetic engineering, microbiology, forensics, and biochemistry. It is used by DNA fingerprinting to differentiate between samples of genetic materials.
Some of the key applications of gel electrophoresis are given below:
1. In the study of evolutionary relationships through the analysis of genetic similarity among species or populations.
2. In blotting techniques for the analytical purpose of macromolecules.
3. In the analysis of resistance towards antibiotics.
4. In the study of function and structure of proteins.
5. In paternity testing via DNA fingerprinting.
6. In DNA profiling for the taxonomy studies for the differentiation of different specie.s
7. For the analysis of genes associated with a particular illness.
8. For analyzing results of polymerase chain reaction.
9. For the separation of DNA fragments for the use in DNA fingerprinting to investigate crime scenes.
10. Used in immunoelectrophoresis.
11. Used in the separation of different types of proteins and nucleic acids.
12. Quantification of proteins.
13. Checking the purity of proteins.
14. Identification of disulfide bonds between proteins.
15. Purification of isolated proteins.
16. Estimation of molecular weight of proteins.
Note:
Gel electrophoresis is classified into agarose gel electrophoresis, starch electrophoresis, polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and denatured or sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). The native variant is run on non-denaturing conditions, leading to preservation of the molecule's native structure. Denaturing conditions unfold the proteins, losing secondary and tertiary structures.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




