
What is the genetic code? Write its four salient features. Draw a diagram of t-RNA
Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint: The genetic code was given by two scientists named Nirenberg and Matthaei. Genetic code is a triplet and this concept was given by George Gamow. With the discovery of genetic code, the idea of transcription and translation was more clearly understood.
Complete answer:
The genetic code describes a relationship of the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain and sequences of nucleotides in mRNA or DNA. 64 genetic codons code for 20 amino acids present in our body. The term genetic code was coined by George Gamow.
The salient features of genetic code are as follows:
-The genetic code is non-ambiguous: This means the codons are specific for each amino acid and therefore one codon cannot account for more than one amino acid.
-Codons are non-overlapping as each nitrogenous base is a constituent of one codon only, a single nitrogenous base is not shared between two codons.
-Codons are Universal: All the codons account for the same amino acids in all organisms starting from the simplest to most complex forms.
-Commaless: The genetic code can be read continuously. On the addition or deletion of a single nucleotide, the whole genetic code will read differently.
The other features of genetic code are as follows:
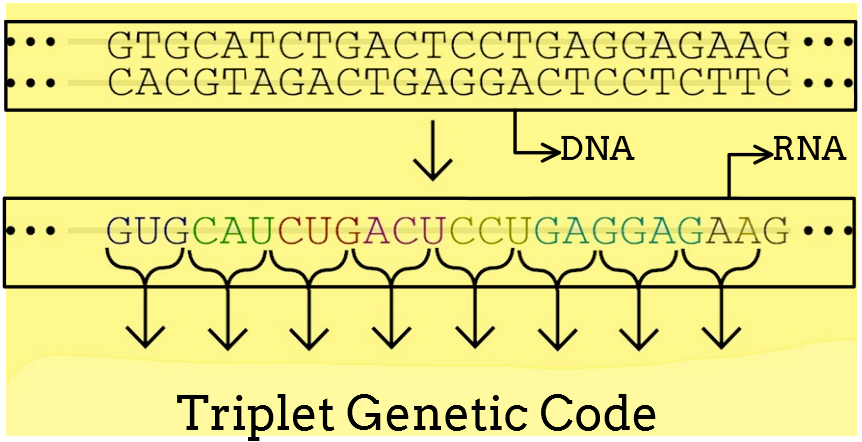
- The genetic code has three adjacent nitrogenous bases and therefore known as a triplet.
- Each sequence of three nucleotides known as codon specifies an amino acid.
- Collinearity: The sequence of codons present on a DNA or mRNA will determine the sequence of amino acids on the polypeptide chain after translation.
-Multiple codons can define a single amino acid but multiple amino acids cannot be accounted for by a single codon.
Note:
It should be noted that the amino acid methionine can be expressed by only one codon AUG. It is also known as the start or initiation codon as it signals the beginning of the chain initiation step. But in prokaryotes GUG and UUG code for methionine but in humans, GUG codes for valine and UUG codes for leucine and this is an exception to the universality of genetic code. UAA, UAG, and UGA all these codons signal termination of the polypeptide chain and hence are known as a stop codon.
Complete answer:
The genetic code describes a relationship of the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain and sequences of nucleotides in mRNA or DNA. 64 genetic codons code for 20 amino acids present in our body. The term genetic code was coined by George Gamow.
The salient features of genetic code are as follows:
-The genetic code is non-ambiguous: This means the codons are specific for each amino acid and therefore one codon cannot account for more than one amino acid.
-Codons are non-overlapping as each nitrogenous base is a constituent of one codon only, a single nitrogenous base is not shared between two codons.
-Codons are Universal: All the codons account for the same amino acids in all organisms starting from the simplest to most complex forms.
-Commaless: The genetic code can be read continuously. On the addition or deletion of a single nucleotide, the whole genetic code will read differently.
The other features of genetic code are as follows:
- The genetic code has three adjacent nitrogenous bases and therefore known as a triplet.
- Each sequence of three nucleotides known as codon specifies an amino acid.
- Collinearity: The sequence of codons present on a DNA or mRNA will determine the sequence of amino acids on the polypeptide chain after translation.
-Multiple codons can define a single amino acid but multiple amino acids cannot be accounted for by a single codon.

Note:
It should be noted that the amino acid methionine can be expressed by only one codon AUG. It is also known as the start or initiation codon as it signals the beginning of the chain initiation step. But in prokaryotes GUG and UUG code for methionine but in humans, GUG codes for valine and UUG codes for leucine and this is an exception to the universality of genetic code. UAA, UAG, and UGA all these codons signal termination of the polypeptide chain and hence are known as a stop codon.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




