
What is genetic drift? Explain genetic drift citing the example of founder effect.
Answer
568.5k+ views
Hint: Biological evolution can be defined as the process of change in the population or species of organisms over time. One of the theories of evolution is Natural Selection which states that change in organisms is brought over time as a result of changes in the heritable physical traits. The change in gene frequencies is brought about by genetic drift and gene flow.
Complete answer:
Genetic drift is the change in the frequencies of an existing gene in a population due to random sampling of organisms. It may help or harm the organism and affect its survival. The effect of change caused due to change in gene frequencies is dependent on the sample size. In smaller populations, changes in gene frequencies lead to visible effects on the survival of the organisms. However, in larger samples, the survival of organisms may not be affected. This is because the affected allele may not vary the fitness of the organism and thus Natural selection does not play a role in it. For example, in a large sample size, if an allele ‘a’ in a species ‘X’ is lost, the survival of many organisms needs to be affected to understand the effect of allele ‘a’ on species ‘X’.
Two types of effects of genetic drift are known – the bottleneck effect and the founder effect.
In the founder effect, a small group of individuals breaks off from a larger population to form a new colony. The individuals in this new population may have a genetic composition that may not be identical to the original population. Thus we can say that the alleles in this founding population may be present at a different frequency than the original population.
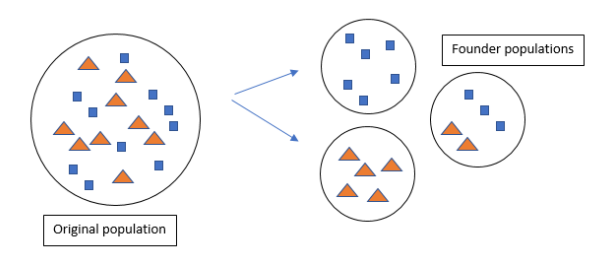
Note: Allele frequencies vary depending on the effect of genetic drift. The population size plays an important role in determining the allele frequencies. Genetic drift plays an important role in the evolution and development of a new population of species.
Complete answer:
Genetic drift is the change in the frequencies of an existing gene in a population due to random sampling of organisms. It may help or harm the organism and affect its survival. The effect of change caused due to change in gene frequencies is dependent on the sample size. In smaller populations, changes in gene frequencies lead to visible effects on the survival of the organisms. However, in larger samples, the survival of organisms may not be affected. This is because the affected allele may not vary the fitness of the organism and thus Natural selection does not play a role in it. For example, in a large sample size, if an allele ‘a’ in a species ‘X’ is lost, the survival of many organisms needs to be affected to understand the effect of allele ‘a’ on species ‘X’.
Two types of effects of genetic drift are known – the bottleneck effect and the founder effect.
In the founder effect, a small group of individuals breaks off from a larger population to form a new colony. The individuals in this new population may have a genetic composition that may not be identical to the original population. Thus we can say that the alleles in this founding population may be present at a different frequency than the original population.

Note: Allele frequencies vary depending on the effect of genetic drift. The population size plays an important role in determining the allele frequencies. Genetic drift plays an important role in the evolution and development of a new population of species.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




