
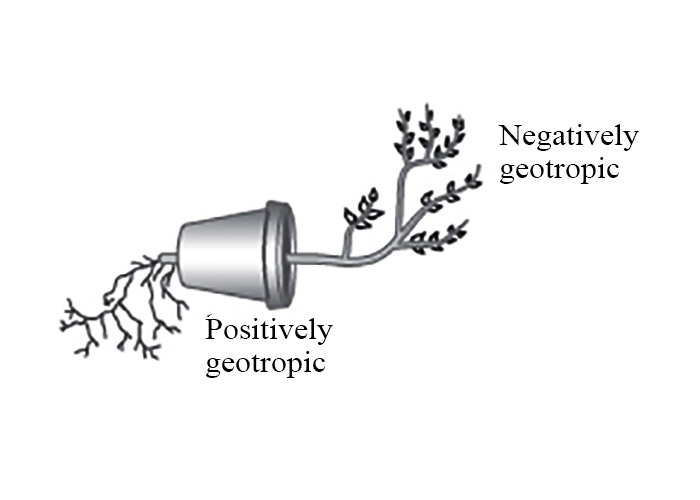
What is geotropism? Draw a labeled diagram of a potted plant showing positive geotropism and negative geotropism.
Answer
607.2k+ views
Hint: It is the growth of plant parts concerning the force of gravity.
Complete answer:
Geotropism is also known as gravitropism is a coordinated process of plant growth in response to gravity pulling on it. It generally occurs in all higher and many lower plants.
Charles Darwin was one of the first scientists to demonstrate that roots show positive geotropism while stem shows negative geotropism. This means that roots grow in the direction of gravitational pull (downward) while stems grow in the opposite direction (upward).
Geotropism is of two types:
- The ability of roots to grow downwards is known as positive geotropism, it is seen in mostly all kinds of plants. Example: roots.
- The upward growth of plant parts against gravity is called negative geotropism, which occurs against the gravitational pull. Example: stem or aerial roots (pneumatophores).
Experiment to demonstrate:
- Take a potted plant, lay it on its side in a horizontal position for some time.
- The stem and roots will grow parallel to the ground. After a few days the potted plant bent towards the earth.
- The growing part of the stem to display negative geotropism, it will grow upwards against the gravitational pull.
- The roots will grow in the direction of gravitational pull in a downward position resulting in positive geotropism.
Note: Plants sometimes may grow in response to gravity called geotropism along with phototropism which involves light in the growth and development of plants.
Complete answer:
Geotropism is also known as gravitropism is a coordinated process of plant growth in response to gravity pulling on it. It generally occurs in all higher and many lower plants.
Charles Darwin was one of the first scientists to demonstrate that roots show positive geotropism while stem shows negative geotropism. This means that roots grow in the direction of gravitational pull (downward) while stems grow in the opposite direction (upward).
Geotropism is of two types:
- The ability of roots to grow downwards is known as positive geotropism, it is seen in mostly all kinds of plants. Example: roots.
- The upward growth of plant parts against gravity is called negative geotropism, which occurs against the gravitational pull. Example: stem or aerial roots (pneumatophores).
Experiment to demonstrate:
- Take a potted plant, lay it on its side in a horizontal position for some time.
- The stem and roots will grow parallel to the ground. After a few days the potted plant bent towards the earth.
- The growing part of the stem to display negative geotropism, it will grow upwards against the gravitational pull.
- The roots will grow in the direction of gravitational pull in a downward position resulting in positive geotropism.

Note: Plants sometimes may grow in response to gravity called geotropism along with phototropism which involves light in the growth and development of plants.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




