
What is Germination, explain with a diagram?
Answer
502.8k+ views
Hint: The process of an organism growing from a seed or spore is known as germination. The term refers to the growth of a seedling from an angiosperm or gymnosperm seed, the growth of sprout from a spore, such as fungi, ferns, or bacteria, and the growth of the pollen tube from a seed plant's pollen grain.
Complete answer:
Germination is a fundamental process that all higher plants go through. A seed is allowed to mature, germinate, and produce new plantlets during this process. The entire germination process in seeds takes place in the presence of certain favorable conditions, such as air, water, light, and temperature.
Process of Germination in Seeds:
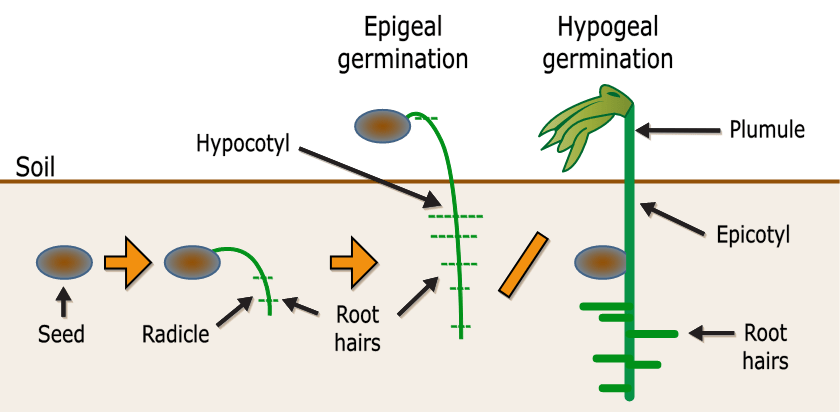
The seeds rapidly absorb water during the early stages of germination, resulting in swelling and softening of the seed coat at an optimal temperature. Imbibition is the name for this stage. The activation of enzymes kicks off the growth process. The seed's internal physiology is activated, and it begins to respire, produce proteins, and metabolize the stored food. This is the lag phase of the process.
Radicles emerge from the seed coat and form a primary root. The seed begins to absorb water from the ground. The shoot begins to grow upwards after the radicle and plumule emerge.
The seedling is formed when the seed cell becomes metabolically active, elongates, and divides in the final stage of seed germination.
Note:
Seed Germination Affecting Factors:
Seed germination is influenced by several major factors. These are some of them:
Water: Seed germination is affected by a lack of or additional supply of water.
The temperature has an impact on the seed's growth rate as well as its metabolism.
Oxygen: As seeds germinate, they take in a lot of oxygen and release the energy they need to grow. As a result, a lack of oxygen affects seed germination.
Dormancy of Seeds: This is a condition in which seeds are unable to germinate, even when the conditions are ideal.
Complete answer:
Germination is a fundamental process that all higher plants go through. A seed is allowed to mature, germinate, and produce new plantlets during this process. The entire germination process in seeds takes place in the presence of certain favorable conditions, such as air, water, light, and temperature.
Process of Germination in Seeds:

The seeds rapidly absorb water during the early stages of germination, resulting in swelling and softening of the seed coat at an optimal temperature. Imbibition is the name for this stage. The activation of enzymes kicks off the growth process. The seed's internal physiology is activated, and it begins to respire, produce proteins, and metabolize the stored food. This is the lag phase of the process.
Radicles emerge from the seed coat and form a primary root. The seed begins to absorb water from the ground. The shoot begins to grow upwards after the radicle and plumule emerge.
The seedling is formed when the seed cell becomes metabolically active, elongates, and divides in the final stage of seed germination.
Note:
Seed Germination Affecting Factors:
Seed germination is influenced by several major factors. These are some of them:
Water: Seed germination is affected by a lack of or additional supply of water.
The temperature has an impact on the seed's growth rate as well as its metabolism.
Oxygen: As seeds germinate, they take in a lot of oxygen and release the energy they need to grow. As a result, a lack of oxygen affects seed germination.
Dormancy of Seeds: This is a condition in which seeds are unable to germinate, even when the conditions are ideal.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




