
Give a few examples of kinetic energy.
Answer
524.7k+ views
Hint: First, we will look at the meaning of the word "energy" and the various forms of energy, then we will look at the definition of kinetic energy and its example.
Complete step by step solution:
The energy associated with an object's motion is called kinetic energy. Objects in motion have the ability to make a shift or perform work.
Examples of Kinetic energy:
Consider a wrecking ball to better grasp. A wrecking ball in motion is used for destruction of houses, bricks, and other materials. And a slow-moving wrecking ball can do a lot of harm to a stationary target like an empty building. A wrecking ball that is not in motion, on the other hand, does not do any work.
The energy associated with the continuous, spontaneous bouncing of atoms or molecules is another example of kinetic energy. Thermal energy is another name for this. Temperature refers to the average thermal energy of a group of molecules, and heat refers to the transfer of thermal energy between two objects.
Additional information:
Life and all living things need energy to function. All of the energy on Earth comes from the sun, either directly or indirectly. Energy is a quantitative property in physics that must be passed to an object for it to conduct work. As a result, we can describe energy as the ability to perform some physical activity. As a result, they say that energy is the capacity to do work.
Energy is a conserved quantity, and the law of conservation of energy states that it cannot be formed or killed, only transformed from one form to another. Joule is the SI unit of energy.
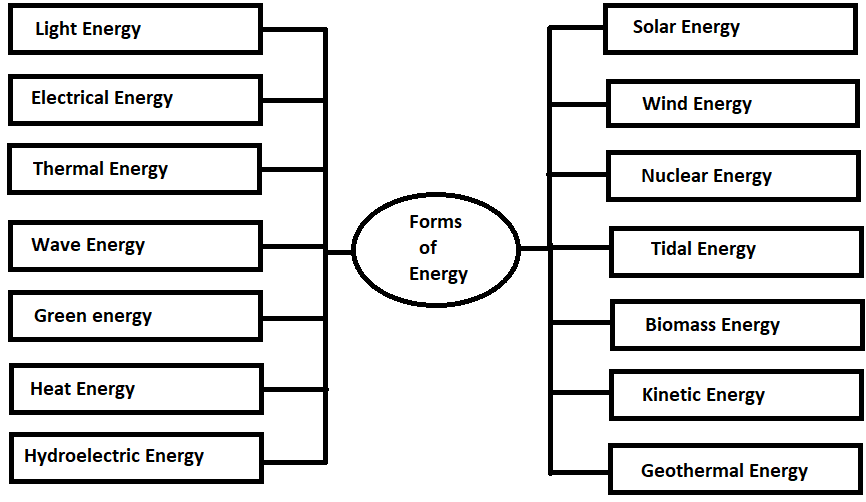
Below shown picture represents forms of energy:
Note:
Radiant energy, thermal energy, sound energy, electrical energy, and mechanical energy are all types of kinetic energy. The following formula is used to calculate kinetic energy:
\[K.E=\dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}}\].
Where, $m$ is the mass of the object and
$v$ is the velocity of the object.
Complete step by step solution:
The energy associated with an object's motion is called kinetic energy. Objects in motion have the ability to make a shift or perform work.
Examples of Kinetic energy:
Consider a wrecking ball to better grasp. A wrecking ball in motion is used for destruction of houses, bricks, and other materials. And a slow-moving wrecking ball can do a lot of harm to a stationary target like an empty building. A wrecking ball that is not in motion, on the other hand, does not do any work.
The energy associated with the continuous, spontaneous bouncing of atoms or molecules is another example of kinetic energy. Thermal energy is another name for this. Temperature refers to the average thermal energy of a group of molecules, and heat refers to the transfer of thermal energy between two objects.
Additional information:
Life and all living things need energy to function. All of the energy on Earth comes from the sun, either directly or indirectly. Energy is a quantitative property in physics that must be passed to an object for it to conduct work. As a result, we can describe energy as the ability to perform some physical activity. As a result, they say that energy is the capacity to do work.
Energy is a conserved quantity, and the law of conservation of energy states that it cannot be formed or killed, only transformed from one form to another. Joule is the SI unit of energy.
Below shown picture represents forms of energy:

Note:
Radiant energy, thermal energy, sound energy, electrical energy, and mechanical energy are all types of kinetic energy. The following formula is used to calculate kinetic energy:
\[K.E=\dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}}\].
Where, $m$ is the mass of the object and
$v$ is the velocity of the object.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




