
Give a test to differentiate ${ 1,1-dichloroethane }$ and ${ 1,2-dichloroethane }$:
A) ${ 2,4-DNP }$ and then aq. KOH
B) aq. KOH and then ${ 2,4-DNP }$
C) ${ NaHSO }_{ 3 }$
D) Lucas reagent
Answer
592.2k+ views
Hint: The only difference between 1,1-dichloroethane and 1,2-dichloroethane is that the two chlorine atoms are present on the same carbon atom in case of 1,1-dichloroethane, they are present in the adjacent carbon atoms in case of 1,2-dichloroethane. So we can oxidize both the compounds and 1,1-dichloroethane will form acetaldehyde while 1,2-dichloroethane will form ethan-1,2-diol. There is a particular reagent which can be used to distinguish between these two and it gives a yellow precipitate in presence of aldehydes.
Complete answer:
> Lucas reagent: It is a solution of anhydrous zinc chloride in concentrated hydrochloric acid. This solution is used to differentiate between primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols of low molecular weight. This is a replacement wherein the chloride replaces a hydroxyl group.
> ${ NaHSO }_{ 3 }$ It is known as Sodium bisulfite is a weakly acidic compound. It is usually used as a mild reducing agent, so typically used as an aqueous solution.
> The reaction of ${ 1,1-dichloroethane }$ and ${ 1,2-dichloroethane }$ with ${ 2,4-DNP }$ firstly, and then aqueous KOH won’t occur as ${ 2,4-DNP }$ is used to differentiate between an aldehyde and a ketone, so firstly when aqueous KOH reacts with these compounds then geminal diol will be formed. Hence, this is not the correct option.
> When ${ 1,1-dichloroethane }$ reacts with aq. KOH then ethanal will be produced which is a pungent-smelling aldehyde which when further reacts with ${ 2,4-DNP }$ then ${ 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine }$ will be produced which is insoluble and yellow colored precipitate.
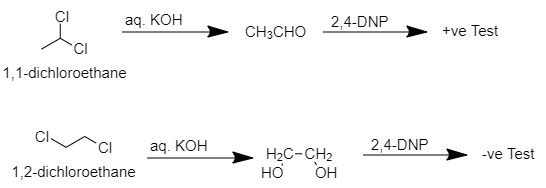
When ${ 1,2-dichloroethane }$ reacts with aq. KOH then ${ ethan-1,2diol }$ will be produced which is odorless and when it reacts with ${ 2,4-DNP }$ then no precipitate formation occurs.
Therefore, we can say that we can differentiate ${ 1,1-dichloroethane }$ and ${ 1,2-dichloroethane }$ from aq. KOH and then ${ 2,4-DNP }$.
So, The correct option is B.
Note: The possibility to make a mistake is that you may choose option A. But to differentiate 1,1-dichloroethane and 1,2-dichloroethane we have to add aq. KOH and then 2,4-DNP will be used. Do not make a mistake by thinking that adding 2,4-DNP first and then aq. KOH will yield the same result. The 2,4-DNP gives yellow precipitate only for aldehydes. So we need to oxidize the compounds by aq. KOH first then we have to use 2,4-DNP for getting the result.
Complete answer:
> Lucas reagent: It is a solution of anhydrous zinc chloride in concentrated hydrochloric acid. This solution is used to differentiate between primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols of low molecular weight. This is a replacement wherein the chloride replaces a hydroxyl group.
> ${ NaHSO }_{ 3 }$ It is known as Sodium bisulfite is a weakly acidic compound. It is usually used as a mild reducing agent, so typically used as an aqueous solution.
> The reaction of ${ 1,1-dichloroethane }$ and ${ 1,2-dichloroethane }$ with ${ 2,4-DNP }$ firstly, and then aqueous KOH won’t occur as ${ 2,4-DNP }$ is used to differentiate between an aldehyde and a ketone, so firstly when aqueous KOH reacts with these compounds then geminal diol will be formed. Hence, this is not the correct option.
> When ${ 1,1-dichloroethane }$ reacts with aq. KOH then ethanal will be produced which is a pungent-smelling aldehyde which when further reacts with ${ 2,4-DNP }$ then ${ 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine }$ will be produced which is insoluble and yellow colored precipitate.

When ${ 1,2-dichloroethane }$ reacts with aq. KOH then ${ ethan-1,2diol }$ will be produced which is odorless and when it reacts with ${ 2,4-DNP }$ then no precipitate formation occurs.
Therefore, we can say that we can differentiate ${ 1,1-dichloroethane }$ and ${ 1,2-dichloroethane }$ from aq. KOH and then ${ 2,4-DNP }$.
So, The correct option is B.
Note: The possibility to make a mistake is that you may choose option A. But to differentiate 1,1-dichloroethane and 1,2-dichloroethane we have to add aq. KOH and then 2,4-DNP will be used. Do not make a mistake by thinking that adding 2,4-DNP first and then aq. KOH will yield the same result. The 2,4-DNP gives yellow precipitate only for aldehydes. So we need to oxidize the compounds by aq. KOH first then we have to use 2,4-DNP for getting the result.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




