
Give advantages and disadvantages of series and parallel connection of resistors.
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: Recall how we group resistors and what the types are. One must know how the intensity of current and voltage changes in each type. Then we will move to their advantages and disadvantages and where shall we use a specific type of grouping.
Formula Used:
For series grouping of resistors,
\[R = {R_1} + {R_2} + {R_3} + ...\]
Where $R$ is the equivalent resistance of the individual resistances ${R_1},{R_2},{R_3}...$ in series connection
For parallel grouping of resistances,
$R = \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_3}}} + ...$
Where $R$ is the equivalent resistance of the individual resistances ${R_1},{R_2},{R_3}...$ in parallel connection.
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s start by what we mean by grouping of resistors. Replacing a number of resistors by a single equivalent resistor is known as grouping of resistors. Resistors are grouped either in series or in parallel or mixed combination. In series grouping of resistors, a number of resistances are connected such that we can proceed from one terminal to another terminal of a battery only along a single path.
In series grouping the current flowing through each resistance is the same and the potential difference across each resistor is different which is directly proportional to each individual resistance.
In case of parallel grouping of resistors, a number of resistances are connected such that we can proceed from one terminal to another of the battery in multiple path across resistors. In parallel grouping we see that potential difference of each resistor is same that is, the potential difference of the battery. And the current flowing through each resistance is different that is inversely proportional to the resistace.
Look at the following diagram.
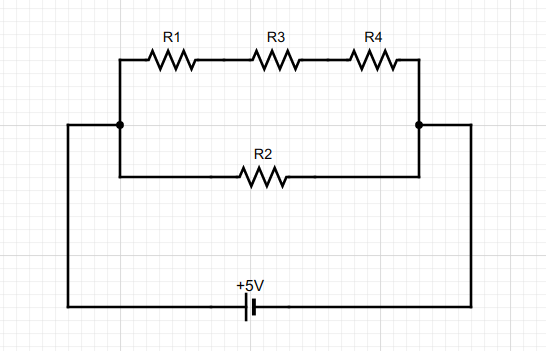
Here the circuit is connected to a battery of emf $5V$. And the resistances ${R_1},{R_2},{R_3}$ are connected in series. Their equivalent resistance is connected in parallel to the resistor ${R_2}$.
Let’s now discuss the advantages and disadvantages of series grouping.
To control the current in a circuit series connection is useful because on connecting the resistors in series the total circuit resistance increases and the current decreases. Series circuits have a single path that connects the electric source to the output devices. These circuits have limited uses because if a fault occurs in one appliance, the current does not flow in the circuit and all the other components in the circuit stop working. If the electrical appliance is connected in series, the applied voltage is divided and the efficiency of the appliance decreases.
To get maximum resistance we use series connection.
For parallel grouping,
Parallel circuits provide the same voltage to every source and appliance in the circuit, thus all appliances can work at their full efficiency. If there occurs a short circuit in the circuit, parallel connections handle it properly as the current flow does not stop. To get minimum resistance we use parallel connection.
Note: Concept of grouping of resistance is important to answer this question. Also there can be questions like how do we group/ connect an ammeter or voltmeter. Keep in mind that an ammeter is always connected in parallel and an ideal ammeter has infinite resistance and a voltmeter is connected in parallel to the circuit and an ideal voltmeter has zero resistance offering.
Formula Used:
For series grouping of resistors,
\[R = {R_1} + {R_2} + {R_3} + ...\]
Where $R$ is the equivalent resistance of the individual resistances ${R_1},{R_2},{R_3}...$ in series connection
For parallel grouping of resistances,
$R = \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_3}}} + ...$
Where $R$ is the equivalent resistance of the individual resistances ${R_1},{R_2},{R_3}...$ in parallel connection.
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s start by what we mean by grouping of resistors. Replacing a number of resistors by a single equivalent resistor is known as grouping of resistors. Resistors are grouped either in series or in parallel or mixed combination. In series grouping of resistors, a number of resistances are connected such that we can proceed from one terminal to another terminal of a battery only along a single path.
In series grouping the current flowing through each resistance is the same and the potential difference across each resistor is different which is directly proportional to each individual resistance.
In case of parallel grouping of resistors, a number of resistances are connected such that we can proceed from one terminal to another of the battery in multiple path across resistors. In parallel grouping we see that potential difference of each resistor is same that is, the potential difference of the battery. And the current flowing through each resistance is different that is inversely proportional to the resistace.
Look at the following diagram.

Here the circuit is connected to a battery of emf $5V$. And the resistances ${R_1},{R_2},{R_3}$ are connected in series. Their equivalent resistance is connected in parallel to the resistor ${R_2}$.
Let’s now discuss the advantages and disadvantages of series grouping.
To control the current in a circuit series connection is useful because on connecting the resistors in series the total circuit resistance increases and the current decreases. Series circuits have a single path that connects the electric source to the output devices. These circuits have limited uses because if a fault occurs in one appliance, the current does not flow in the circuit and all the other components in the circuit stop working. If the electrical appliance is connected in series, the applied voltage is divided and the efficiency of the appliance decreases.
To get maximum resistance we use series connection.
For parallel grouping,
Parallel circuits provide the same voltage to every source and appliance in the circuit, thus all appliances can work at their full efficiency. If there occurs a short circuit in the circuit, parallel connections handle it properly as the current flow does not stop. To get minimum resistance we use parallel connection.
Note: Concept of grouping of resistance is important to answer this question. Also there can be questions like how do we group/ connect an ammeter or voltmeter. Keep in mind that an ammeter is always connected in parallel and an ideal ammeter has infinite resistance and a voltmeter is connected in parallel to the circuit and an ideal voltmeter has zero resistance offering.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




