
Give an account of somatic structure and life cycle of an acellular slime mould that you have studied.
Answer
537.9k+ views
Hint: Slime moulds are of two types: cellular and acellular. In their life cycles, acellular slime moulds have a "plasmodium" period. Plasmodium consists of millions of nuclei that share a single, gigantic cell to differentiate them without any membranes.
Complete answer:
1) Plasmodium is the name of the somatic structure of the acellular slime mould. It is inherently diploid. It consists of a protoplasm multinucleate. In the protoplasm, it has many diploid nuclei which continue to divide by mitosis. It has no definite form at all. With the help of finger-like projection, the movement is called pseudopodia. It also includes moving strands for locomotion, called phaneroplasmodium.
2) In nature, it is saprophytic. It relies for growth and nourishment on dead and rotting matter. For food, it also consumes bacteria, protozoa, etc.
3) Prior to entering the reproductive process, plasmodium exceeds a certain size. The slime dries during this process. The diploid protoplasm concentrates, creating a cushion-like mass at a few stages. This structure-like mould grows into a stalked sporangium.
4) The diploid protoplas divides into several young spores each having a diploid nucleus.
5) To form a meiospore, the diploid nucleus of the spore undergoes meiosis.
6)The Meiospore is released and dispersed by wind after maturation. It falls on a substratum.
7) Then it germinates to release swarm cells under the favorable state of moisture, temperature and pH. These act in pairs like gametes and fuse to form the zygote.
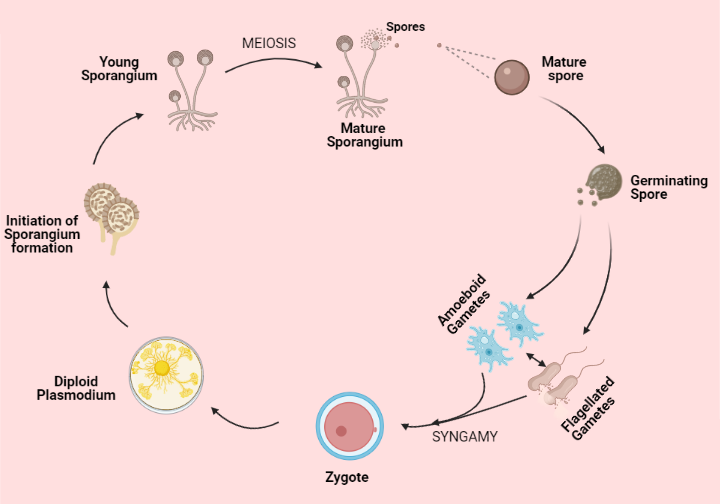
Note: 1) Acellular slime mould can reach 1ft. In diameter.
2) They reproduce asexually in absence of food and moisture.
3) Examples include Physarum, Cribaria, etc.
Complete answer:
1) Plasmodium is the name of the somatic structure of the acellular slime mould. It is inherently diploid. It consists of a protoplasm multinucleate. In the protoplasm, it has many diploid nuclei which continue to divide by mitosis. It has no definite form at all. With the help of finger-like projection, the movement is called pseudopodia. It also includes moving strands for locomotion, called phaneroplasmodium.
2) In nature, it is saprophytic. It relies for growth and nourishment on dead and rotting matter. For food, it also consumes bacteria, protozoa, etc.
3) Prior to entering the reproductive process, plasmodium exceeds a certain size. The slime dries during this process. The diploid protoplasm concentrates, creating a cushion-like mass at a few stages. This structure-like mould grows into a stalked sporangium.
4) The diploid protoplas divides into several young spores each having a diploid nucleus.
5) To form a meiospore, the diploid nucleus of the spore undergoes meiosis.
6)The Meiospore is released and dispersed by wind after maturation. It falls on a substratum.
7) Then it germinates to release swarm cells under the favorable state of moisture, temperature and pH. These act in pairs like gametes and fuse to form the zygote.

Note: 1) Acellular slime mould can reach 1ft. In diameter.
2) They reproduce asexually in absence of food and moisture.
3) Examples include Physarum, Cribaria, etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




