
Give an example of a seed with endosperm, perisperm and caruncle is
(a) Castor
(b) Coffee
(c) Lily
(d) Cotton
Answer
583.8k+ views
Hint: A species which bears perennial flowering in the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae. It belongs to the sole species in the monotypic genus, Ricinus. This species reproduces with a mixed pollination system. It favors selfing by geitonogamy but at the same time can be an out-crosser by anemophily (wind pollination) or entomophily (insect pollination).
Complete step by step answer:
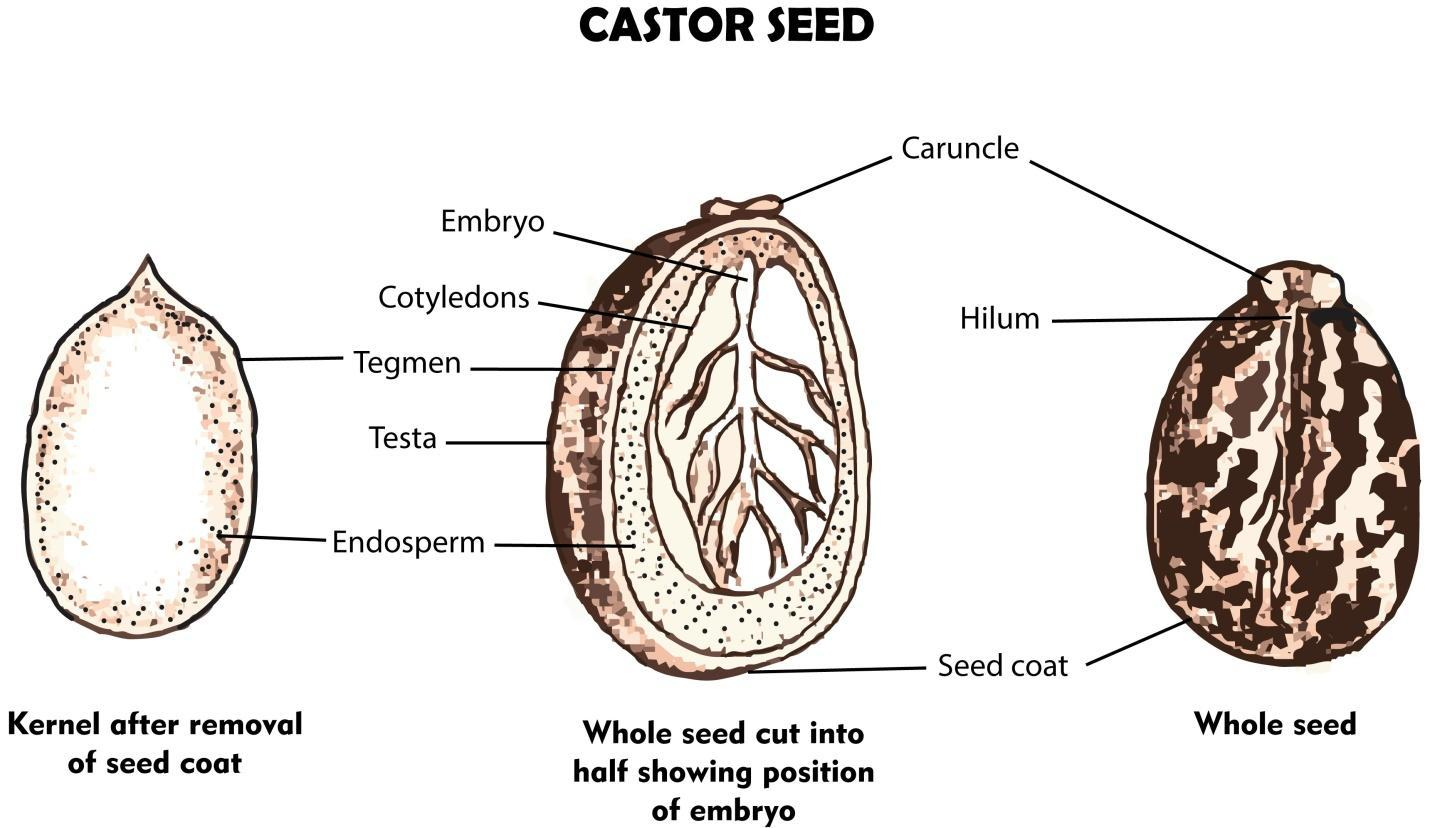
The endosperm is formed when the two sperm nuclei inside a pollen grain reach the inside of an ovule or embryo sac. The egg is fertilized by one sperm nucleus, which forms a zygote, while the other sperm nucleus usually fuses with the two polar nuclei at the center of the embryo sac.
The perisperm is the nutritive tissue of a seed derived from the nucellus and deposited externally to the embryo sac —distinguished from the endosperm.
Euphorbiaceae seeds possess a structure called the caruncle which is present in the micropylar region. This shows the ecological function of promoting seed dispersal by ants (myrmecochory), but it is debated whether it also has. agronomic importance influencing seed germination.
The castor-oil seed is dicotyledonous (having two cotyledons). Near the narrow end of the seed, a white spongy bilobed outgrowth present which partially covers the hilum (dark scar) and completely covers the micropyle (small pore). The water absorbed percolates through the micropyle into the seed.
Additional information:
1) Castor seed is the source of castor oil, which has a wide variety of uses. The castor seeds contain almost between 40% to 60% oil that is rich in triglycerides, mainly ricinolein.
2) Some examples of perisperm seeds are Sugar beet, coffee, and black pepper.
3) The endosperm is seen to be completely absorbed in maturity in some seeds (e.g., pea and bean) , and the fleshy food-storing cotyledons nourish the embryo as it germinates. The endosperms are present until germination in some other species (e.g., wheat, castor bean) , and the cotyledons are typically thin and membranous and serve to absorb the stored food from the endosperm upon germination.
4) The seed also contains ricin, a water-soluble toxin, which is also present in lower concentrations throughout the plant.
So, the correct answer is, 'Castor (Ricinus communis)'.
Note: In the laboratory, scientists tested an alcoholic extract of the leaf to protect the liver from damage from certain poisons. In antimicrobial testing, methanolic extracts of the leaves of Ricinus communis were used against eight pathogenic bacteria in rats and showed antimicrobial properties. At low doses, the pericarp of Ricinus showed central nervous system effects in mice but at high doses mice quickly died. Moreover, the water extract of the root bark showed analgesic activity in rats. Antihistamine and anti-inflammatory properties were found in the ethanolic extract of Ricinus communis root bark.
Complete step by step answer:
The endosperm is formed when the two sperm nuclei inside a pollen grain reach the inside of an ovule or embryo sac. The egg is fertilized by one sperm nucleus, which forms a zygote, while the other sperm nucleus usually fuses with the two polar nuclei at the center of the embryo sac.
The perisperm is the nutritive tissue of a seed derived from the nucellus and deposited externally to the embryo sac —distinguished from the endosperm.
Euphorbiaceae seeds possess a structure called the caruncle which is present in the micropylar region. This shows the ecological function of promoting seed dispersal by ants (myrmecochory), but it is debated whether it also has. agronomic importance influencing seed germination.
The castor-oil seed is dicotyledonous (having two cotyledons). Near the narrow end of the seed, a white spongy bilobed outgrowth present which partially covers the hilum (dark scar) and completely covers the micropyle (small pore). The water absorbed percolates through the micropyle into the seed.

Additional information:
1) Castor seed is the source of castor oil, which has a wide variety of uses. The castor seeds contain almost between 40% to 60% oil that is rich in triglycerides, mainly ricinolein.
2) Some examples of perisperm seeds are Sugar beet, coffee, and black pepper.
3) The endosperm is seen to be completely absorbed in maturity in some seeds (e.g., pea and bean) , and the fleshy food-storing cotyledons nourish the embryo as it germinates. The endosperms are present until germination in some other species (e.g., wheat, castor bean) , and the cotyledons are typically thin and membranous and serve to absorb the stored food from the endosperm upon germination.
4) The seed also contains ricin, a water-soluble toxin, which is also present in lower concentrations throughout the plant.
So, the correct answer is, 'Castor (Ricinus communis)'.
Note: In the laboratory, scientists tested an alcoholic extract of the leaf to protect the liver from damage from certain poisons. In antimicrobial testing, methanolic extracts of the leaves of Ricinus communis were used against eight pathogenic bacteria in rats and showed antimicrobial properties. At low doses, the pericarp of Ricinus showed central nervous system effects in mice but at high doses mice quickly died. Moreover, the water extract of the root bark showed analgesic activity in rats. Antihistamine and anti-inflammatory properties were found in the ethanolic extract of Ricinus communis root bark.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




