
Give Arrhenius an equation. How will you determine the activation energy of a reaction by graph method?
Answer
565.2k+ views
Hint: Arrhenius equation is useful for calculating the energy of activation of a reaction having rate constant “k” at temperature “T”
Activation energy is the excess energy that the reacting molecules whose energy is less than threshold energy must acquire to react to give the products.
Activation energy can be obtained graphically by the slope of lnK vs \[\dfrac{1}{T}\]
Complete step by step answer:
Arrhenius equation for calculating the energy of activation of a reaction having rate constant “k” at temperature “T” can be written as follows,
\[k = A{e^{\dfrac{{ - {E_a}}}{{RT}}}}......(1)\]
Where,
k- Rate constant
A- Frequency factor
${E_a}$- Arrhenius activation energy
R-Gas constant
T-Temperature
Taking the natural logarithm of equation (1) on both sides,
\[(1) \Rightarrow \ln k = \ln A + \left( {\dfrac{{ - {E_a}}}{{RT}}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \ln k = \left( {\dfrac{{ - {E_a}}}{{RT}}} \right) + \ln A.......(2)\]
Equation (2) depicts the \[y = mx + c\] equation where
\[y = ln{{ }}k\]
\[m = \dfrac{{ - {E_a}}}{R}\]
\[x = \dfrac{1}{T}\]
\[c = ln{{ }}A\]
Thus, the plot $lnK\;{{ }}\;vs{{ }}\;\dfrac{1}{T}$ can be drawn as,
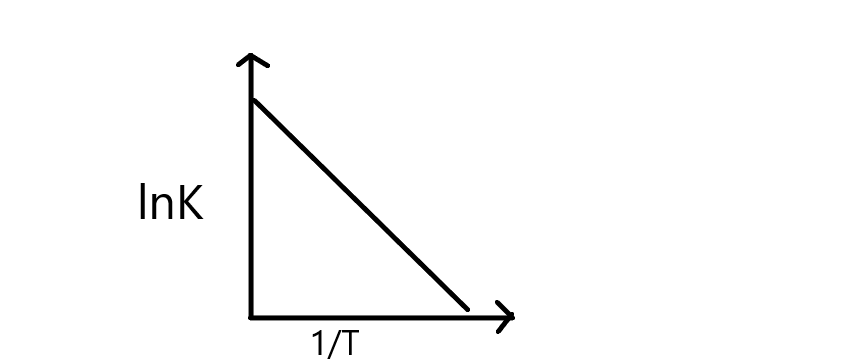
From the graph, it depicts that rate constant decreases with increase in $\dfrac{1}{T}$ resulting in a straight line, and its slope can be equal to \[\dfrac{{ - {E_a}}}{R}\]
Thus, from the slope \[\ln Kvs\dfrac{1}{T}\], we can calculate the activation energy of a reaction.
Note: The slope of the natural logarithm of the Arrhenius equation is negative. \[m = \dfrac{{ - {E_a}}}{R}\] Where \[R = 8.314J{K^{ - 1}}mo{l^{ - 1}}\]
The rate constant is affected by temperature whereas activation energy is independent of temperature. The activation energy is affected by the use of catalysts. . Generally, activation energy is the excess energy required by the molecules to react to yield a product. When a catalyst is used, the activation energy barrier gets decreased and it makes the reaction happen faster.
When the temperature increases, more molecules are undergoing collision and temperature cannot change the activation barrier of a reaction.
Activation energy is the excess energy that the reacting molecules whose energy is less than threshold energy must acquire to react to give the products.
Activation energy can be obtained graphically by the slope of lnK vs \[\dfrac{1}{T}\]
Complete step by step answer:
Arrhenius equation for calculating the energy of activation of a reaction having rate constant “k” at temperature “T” can be written as follows,
\[k = A{e^{\dfrac{{ - {E_a}}}{{RT}}}}......(1)\]
Where,
k- Rate constant
A- Frequency factor
${E_a}$- Arrhenius activation energy
R-Gas constant
T-Temperature
Taking the natural logarithm of equation (1) on both sides,
\[(1) \Rightarrow \ln k = \ln A + \left( {\dfrac{{ - {E_a}}}{{RT}}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \ln k = \left( {\dfrac{{ - {E_a}}}{{RT}}} \right) + \ln A.......(2)\]
Equation (2) depicts the \[y = mx + c\] equation where
\[y = ln{{ }}k\]
\[m = \dfrac{{ - {E_a}}}{R}\]
\[x = \dfrac{1}{T}\]
\[c = ln{{ }}A\]
Thus, the plot $lnK\;{{ }}\;vs{{ }}\;\dfrac{1}{T}$ can be drawn as,

From the graph, it depicts that rate constant decreases with increase in $\dfrac{1}{T}$ resulting in a straight line, and its slope can be equal to \[\dfrac{{ - {E_a}}}{R}\]
Thus, from the slope \[\ln Kvs\dfrac{1}{T}\], we can calculate the activation energy of a reaction.
Note: The slope of the natural logarithm of the Arrhenius equation is negative. \[m = \dfrac{{ - {E_a}}}{R}\] Where \[R = 8.314J{K^{ - 1}}mo{l^{ - 1}}\]
The rate constant is affected by temperature whereas activation energy is independent of temperature. The activation energy is affected by the use of catalysts. . Generally, activation energy is the excess energy required by the molecules to react to yield a product. When a catalyst is used, the activation energy barrier gets decreased and it makes the reaction happen faster.
When the temperature increases, more molecules are undergoing collision and temperature cannot change the activation barrier of a reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




