
Give reasons for the following: Split rings are used instead of slip rings to construct dc dynamo.
Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint: We need to look into the construction part of D.C. machines. There is the induction of alternating voltage in the rotor of the machine, be it of alternate (A.C.) nature or direct (D.C.) nature. It depends upon the commutator used which decides the nature of the output.
Complete step-by-step solution:
The E.M.F. produced in the rotating rotor is always A.C., be it an A.C. machine or D.C. machine. It is the commutator that decides whether we will get A.C. in the output or we will get D.C. in the output.
Hence, the commutator holds the utmost importance in deciding the nature of the electrical output we receive.
In the case of slip rings, two brushes are used to get the electrical output. These brushes are always in direct contact with the rings with which the rotor windings are attached. As soon as the polarity of induced e.m.f. changes, due to the A.C. nature of the induced voltage, the polarity in the output also changes. Thus, this gives rise to Alternating Current or A.C. in the output.
In the case of split rings, the brushes are again in direct contact with the rings. But the ring is now divided into two equal parts and hence split rings. As soon as the polarity of the voltage induced in the rotor reverses or the induced e.m.f. reverses, the brushes also change the part of the ring with which they were in contact with. This changes the terminals of the output and hence the polarity of the output remains the same. This gives rise to the D.C. current.
The following diagram shows the difference between a split and slip ring for A.C and D.C. generator:
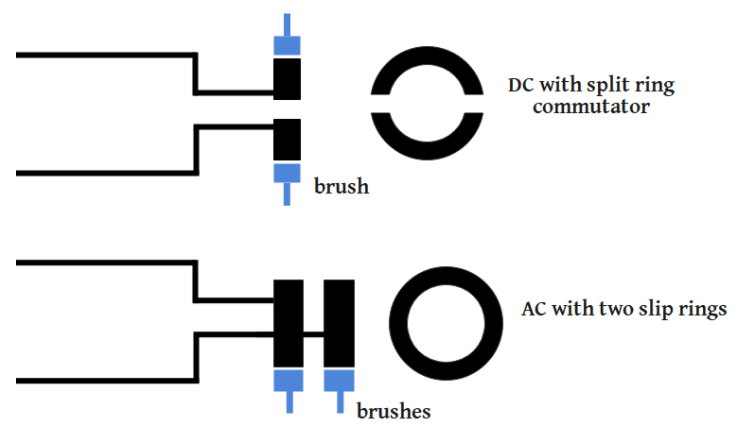
Thus, this is the reason that split rings are used instead of slip rings to construct the D.C. dynamo.
Note: Split rings are, on the basis of construction, the same rings like that as the slip rings. The only change in split rings is that they are cut into two parts, with one part electrically isolated from the other. The rest of the basic working remains the same for both of them.
Complete step-by-step solution:
The E.M.F. produced in the rotating rotor is always A.C., be it an A.C. machine or D.C. machine. It is the commutator that decides whether we will get A.C. in the output or we will get D.C. in the output.
Hence, the commutator holds the utmost importance in deciding the nature of the electrical output we receive.
In the case of slip rings, two brushes are used to get the electrical output. These brushes are always in direct contact with the rings with which the rotor windings are attached. As soon as the polarity of induced e.m.f. changes, due to the A.C. nature of the induced voltage, the polarity in the output also changes. Thus, this gives rise to Alternating Current or A.C. in the output.
In the case of split rings, the brushes are again in direct contact with the rings. But the ring is now divided into two equal parts and hence split rings. As soon as the polarity of the voltage induced in the rotor reverses or the induced e.m.f. reverses, the brushes also change the part of the ring with which they were in contact with. This changes the terminals of the output and hence the polarity of the output remains the same. This gives rise to the D.C. current.
The following diagram shows the difference between a split and slip ring for A.C and D.C. generator:

Thus, this is the reason that split rings are used instead of slip rings to construct the D.C. dynamo.
Note: Split rings are, on the basis of construction, the same rings like that as the slip rings. The only change in split rings is that they are cut into two parts, with one part electrically isolated from the other. The rest of the basic working remains the same for both of them.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




