
Give some examples of electric dipoles with their explanation.
Answer
518.4k+ views
Hint:In electrostatics, when two charges equal in magnitude but have opposite sign in nature are placed at some distance, this forms an arrangement which is known as electric dipole and its moment is known as electric dipole moment whose direction is always from negative charge to the positive charge side.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first understand the electric dipole in brief. Since electric dipole moment is defined as the product of charge and the distance between them and has a SI unit of $Cm$ . It’s denoted as: $p = q \times 2a$ where $2a$ is the distance between two charges. One of the most common examples of Electric dipole is to find electric field intensity at equatorial point which is calculated as: let us first draw the diagram.
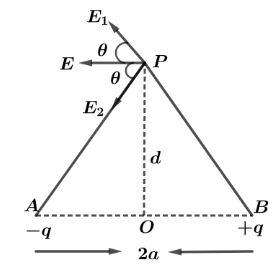
Dipole moment $\vec P = q \times 2a$, { $q$ is charge and $2a$ is half distance of dipole}
Electric field intensity $E = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}} \times \dfrac{q}{{{r^2}}}$ { $q$ is charge and r is distance of given point}
From the diagram we can see, Net electric field intensity will only have horizontal components of $E\cos \theta $. And Now,
In triangle AOP and POB,
${(AP)^2} = {(BP)^2} = ({d^2} + {a^2})$
And, $ < PAO = \theta $ {by vertically opposite angle}
So, $\cos \theta = \dfrac{1}{{{{({d^2} + {a^2})}^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}}}$
Now, we will calculate electric field intensity due to both charges at point P
Electric field ${E_1}$ at point P due to $ - q$ along $AP$ is given by,
${E_1} = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\dfrac{q}{{{{(AP)}^2}}}$
$\Rightarrow {E_1} = k \times \dfrac{q}{{{{({d^2} + {a^2})}^2}}}$,
where {$k = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}$} $ \to (i)$
Similarly, Electric field along PB is given by,
${E_2} = k \times \dfrac{q}{{{{(PB)}^2}}}$
$\Rightarrow {E_2} = k \times \dfrac{q}{{{{({d^2} + {a^2})}^2}}}$...........$ \to (ii)$
Since, ${E_1} = {E_2}$ say $E$
Net electric field at point $P$ will be the sum of $E\sin \theta $ components and $E\cos \theta $ components but as we see from the diagram, vertical components will be cancelled, only horizontal components will be added. Hence, net electric field intensity at point $P$ is given by,
${E_p} = 2E\cos \theta $
As, $\cos \theta = \dfrac{1}{{{{({d^2} + {l^2})}^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}}}$
$\Rightarrow {E_p} = 2 \times k \times \dfrac{q}{{{{({d^2} + {a^2})}^2}}} \times \dfrac{1}{{{{({d^2} + {a^2})}^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}}}$
For small dipole where, $a < < < d$
Hence, electric field intensity at equatorial point is given by,
${E_p} = - \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\dfrac{{\vec P}}{{{d^3}}}$.
And the direction of the electric field is always opposite to that of the electric dipole.Another example of an electric dipole may be considered as $C{O_2}$ and $C{H_4}$ are the molecules whose dipole moment is zero but when placed in an electric field they produced a significant dipole moment in the direction of opposite to that of electric field.
Note: Many chemical molecules have their own electric dipole moment due to the presence of positive and negative charges inside them and they get polarized easily in the presence of an electric field and such molecules are called polar molecules ${H_2}O$ is an example of polar molecule.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first understand the electric dipole in brief. Since electric dipole moment is defined as the product of charge and the distance between them and has a SI unit of $Cm$ . It’s denoted as: $p = q \times 2a$ where $2a$ is the distance between two charges. One of the most common examples of Electric dipole is to find electric field intensity at equatorial point which is calculated as: let us first draw the diagram.

Dipole moment $\vec P = q \times 2a$, { $q$ is charge and $2a$ is half distance of dipole}
Electric field intensity $E = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}} \times \dfrac{q}{{{r^2}}}$ { $q$ is charge and r is distance of given point}
From the diagram we can see, Net electric field intensity will only have horizontal components of $E\cos \theta $. And Now,
In triangle AOP and POB,
${(AP)^2} = {(BP)^2} = ({d^2} + {a^2})$
And, $ < PAO = \theta $ {by vertically opposite angle}
So, $\cos \theta = \dfrac{1}{{{{({d^2} + {a^2})}^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}}}$
Now, we will calculate electric field intensity due to both charges at point P
Electric field ${E_1}$ at point P due to $ - q$ along $AP$ is given by,
${E_1} = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\dfrac{q}{{{{(AP)}^2}}}$
$\Rightarrow {E_1} = k \times \dfrac{q}{{{{({d^2} + {a^2})}^2}}}$,
where {$k = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}$} $ \to (i)$
Similarly, Electric field along PB is given by,
${E_2} = k \times \dfrac{q}{{{{(PB)}^2}}}$
$\Rightarrow {E_2} = k \times \dfrac{q}{{{{({d^2} + {a^2})}^2}}}$...........$ \to (ii)$
Since, ${E_1} = {E_2}$ say $E$
Net electric field at point $P$ will be the sum of $E\sin \theta $ components and $E\cos \theta $ components but as we see from the diagram, vertical components will be cancelled, only horizontal components will be added. Hence, net electric field intensity at point $P$ is given by,
${E_p} = 2E\cos \theta $
As, $\cos \theta = \dfrac{1}{{{{({d^2} + {l^2})}^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}}}$
$\Rightarrow {E_p} = 2 \times k \times \dfrac{q}{{{{({d^2} + {a^2})}^2}}} \times \dfrac{1}{{{{({d^2} + {a^2})}^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}}}$
For small dipole where, $a < < < d$
Hence, electric field intensity at equatorial point is given by,
${E_p} = - \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\dfrac{{\vec P}}{{{d^3}}}$.
And the direction of the electric field is always opposite to that of the electric dipole.Another example of an electric dipole may be considered as $C{O_2}$ and $C{H_4}$ are the molecules whose dipole moment is zero but when placed in an electric field they produced a significant dipole moment in the direction of opposite to that of electric field.
Note: Many chemical molecules have their own electric dipole moment due to the presence of positive and negative charges inside them and they get polarized easily in the presence of an electric field and such molecules are called polar molecules ${H_2}O$ is an example of polar molecule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




