
Give the action of the Clemmensen reduction on 2-butenal?
Answer
492k+ views
Hint: To answer the question we need to discuss the Clemmensen reaction in detail. Clemmensen reaction is the process by which aldehydes and ketones are reduced to alkanes. The reagent which is used is zinc amalgam $ \left( {Zn - Hg} \right) $ in the presence of concentrated Hydrochloric acid $ \left( {HCl} \right) $ . This reaction takes place in an acidic medium.
Complete answer:
The Clemmensen reduction has got its name after Danish chemist, Erik Christian Clemmensen. The general Clemmensen reduction is given as under-
$ {R_1}CO{R_2}\xrightarrow[{HCl}]{{Zn - Hg}}{R_1}C{H_2}{R_2} $
The reactant or substrate must be tolerant to the strongly acidic conditions of the reaction. The mechanism of Clemmensen reduction is not clearly understood however there are 2 approaches- The carbanionic mechanism and the carbenoid mechanism.
In this question, we are asked to perform Clemmensen reduction of 2-butenal. 2-butenal is an example of $ \alpha ,\beta $ unsaturated aldehyde.
The reaction is expected to produce the following desired product of 2-butene.
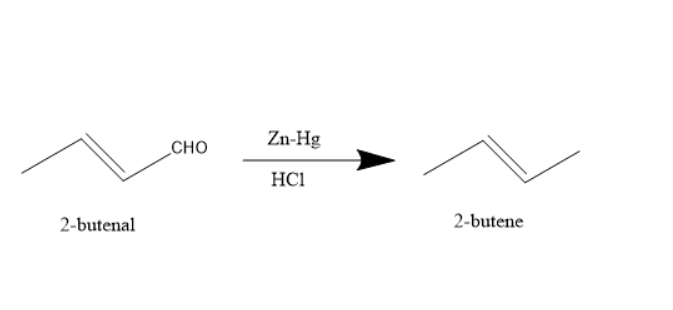
However in this case 2-butene is a minor product.
Since the reaction occurs in the acidic medium it will react with the double bond present, protonate it, hydrochlorination reaction occurs and forms the following chlorinated product-
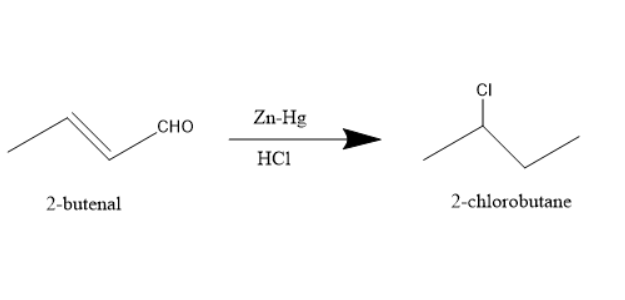
Thus 2-chlorobutane is the major product of the reaction.
Note:
It is interesting to note that if we want that the product must have only its carbonyl oxygen removed and double bond should remain as it is then we must perform the reaction in the basic medium. One example of such a reaction is the Wolf-Kishner reaction (In the presence of hydrazine $ N{H_2} - N{H_2} $ and a strong base $ NaOH $ ). So if we perform the Wolf-Kishner reaction on 2-butenal it will produce 2-butene as a major product.
Complete answer:
The Clemmensen reduction has got its name after Danish chemist, Erik Christian Clemmensen. The general Clemmensen reduction is given as under-
$ {R_1}CO{R_2}\xrightarrow[{HCl}]{{Zn - Hg}}{R_1}C{H_2}{R_2} $
The reactant or substrate must be tolerant to the strongly acidic conditions of the reaction. The mechanism of Clemmensen reduction is not clearly understood however there are 2 approaches- The carbanionic mechanism and the carbenoid mechanism.
In this question, we are asked to perform Clemmensen reduction of 2-butenal. 2-butenal is an example of $ \alpha ,\beta $ unsaturated aldehyde.
The reaction is expected to produce the following desired product of 2-butene.

However in this case 2-butene is a minor product.
Since the reaction occurs in the acidic medium it will react with the double bond present, protonate it, hydrochlorination reaction occurs and forms the following chlorinated product-

Thus 2-chlorobutane is the major product of the reaction.
Note:
It is interesting to note that if we want that the product must have only its carbonyl oxygen removed and double bond should remain as it is then we must perform the reaction in the basic medium. One example of such a reaction is the Wolf-Kishner reaction (In the presence of hydrazine $ N{H_2} - N{H_2} $ and a strong base $ NaOH $ ). So if we perform the Wolf-Kishner reaction on 2-butenal it will produce 2-butene as a major product.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




