
Give the biological terms for ‘the repeating components of each DNA strand lengthwise’.
Answer
578.4k+ views
Hint: Nucleotides are organic molecules which consist of a phosphate and a nucleoside. They act as monomeric units of deoxyribonucleic acid and ribonucleic acid nucleic acid polymers, both of which are important biomolecules in all life forms on Earth.
Complete answer:
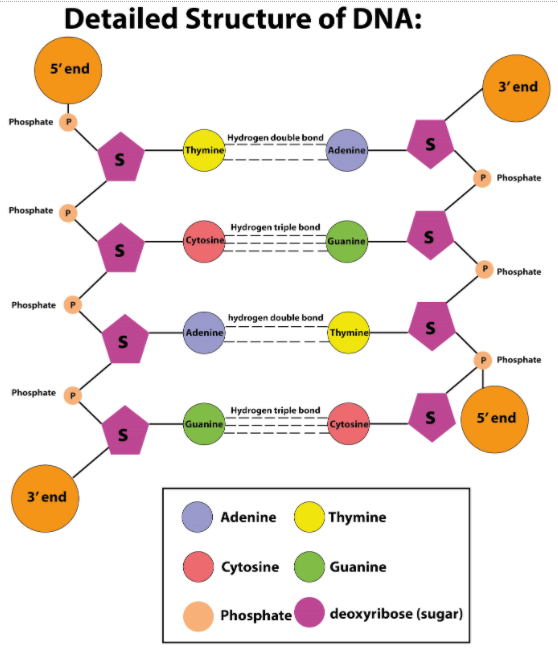
A sugar, a base (adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine/uracil), and a phosphate unit make up the nucleotide. Nucleic acids, RNA, and DNA are nucleotide polymers linked together by phosphodiester bonds.
Adenine is one of the two nucleobases of purine (the other being guanine) used in the nucleotide production of nucleic acids. In DNA, adenine binds via two hydrogen bonds to thymine to help stabilize the structures of the nucleic acid. Adenine binds to uracil in RNA, which is used for protein synthesis.
Guanine is one of the four key nucleobases present in DNA and RNA nucleic acids, with adenine, cytosine, and thymine being the others. Guanine is combined with cytosine in DNA. The nucleoside of guanine is called guanosine.
Cytosine is, along with adenine, guanine, and thymine, one of the four major bases present in DNA and RNA. It is a derivative of pyrimidine with a heterocyclic aromatic ring and two attached substituents. The cytosine nucleoside is cytidine. It forms three hydrogen bonds with guanine during Watson-Crick base pairing.
Thymine One of the four nucleobases represented by the letters G-C-A-T in the nucleic acid of DNA is thymine. Adenine, Guanine, and Cytosine are the others. 5-methyluracil, a pyrimidine nucleobase, is also known as thymine. In RNA, the nucleobase uracil is substituted for thymine.
Additional Information: Uracil is one of the four nucleobases identified by the letters A, G, C, and U in the nucleic acid RNA. The others are adenine, guanine, and cytosine. In RNA, through two hydrogen bonds, uracil binds to adenine. In DNA, thymine replaces the uracil nucleobase. Uracil is a type of thymine that is demethylated.
5-Methylcytosine is a DNA base cytosine methylated variant that controls the transcription of genes and takes on many other biological roles. The DNA retains the same sequence when cytosine is methylated, but the expression of methylated genes can be changed.
Note: An organic molecule that is the building block of DNA and RNA is a nucleotide. They also have cell signaling, metabolism, and enzyme reactions-related functions. There are three parts of a nucleotide: a phosphate group, a 5-carbon sugar, and a nitrogen base.
Complete answer:
A sugar, a base (adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine/uracil), and a phosphate unit make up the nucleotide. Nucleic acids, RNA, and DNA are nucleotide polymers linked together by phosphodiester bonds.
Adenine is one of the two nucleobases of purine (the other being guanine) used in the nucleotide production of nucleic acids. In DNA, adenine binds via two hydrogen bonds to thymine to help stabilize the structures of the nucleic acid. Adenine binds to uracil in RNA, which is used for protein synthesis.
Guanine is one of the four key nucleobases present in DNA and RNA nucleic acids, with adenine, cytosine, and thymine being the others. Guanine is combined with cytosine in DNA. The nucleoside of guanine is called guanosine.
Cytosine is, along with adenine, guanine, and thymine, one of the four major bases present in DNA and RNA. It is a derivative of pyrimidine with a heterocyclic aromatic ring and two attached substituents. The cytosine nucleoside is cytidine. It forms three hydrogen bonds with guanine during Watson-Crick base pairing.
Thymine One of the four nucleobases represented by the letters G-C-A-T in the nucleic acid of DNA is thymine. Adenine, Guanine, and Cytosine are the others. 5-methyluracil, a pyrimidine nucleobase, is also known as thymine. In RNA, the nucleobase uracil is substituted for thymine.

Additional Information: Uracil is one of the four nucleobases identified by the letters A, G, C, and U in the nucleic acid RNA. The others are adenine, guanine, and cytosine. In RNA, through two hydrogen bonds, uracil binds to adenine. In DNA, thymine replaces the uracil nucleobase. Uracil is a type of thymine that is demethylated.
5-Methylcytosine is a DNA base cytosine methylated variant that controls the transcription of genes and takes on many other biological roles. The DNA retains the same sequence when cytosine is methylated, but the expression of methylated genes can be changed.
Note: An organic molecule that is the building block of DNA and RNA is a nucleotide. They also have cell signaling, metabolism, and enzyme reactions-related functions. There are three parts of a nucleotide: a phosphate group, a 5-carbon sugar, and a nitrogen base.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




