
Give the IUPAC name of
a)
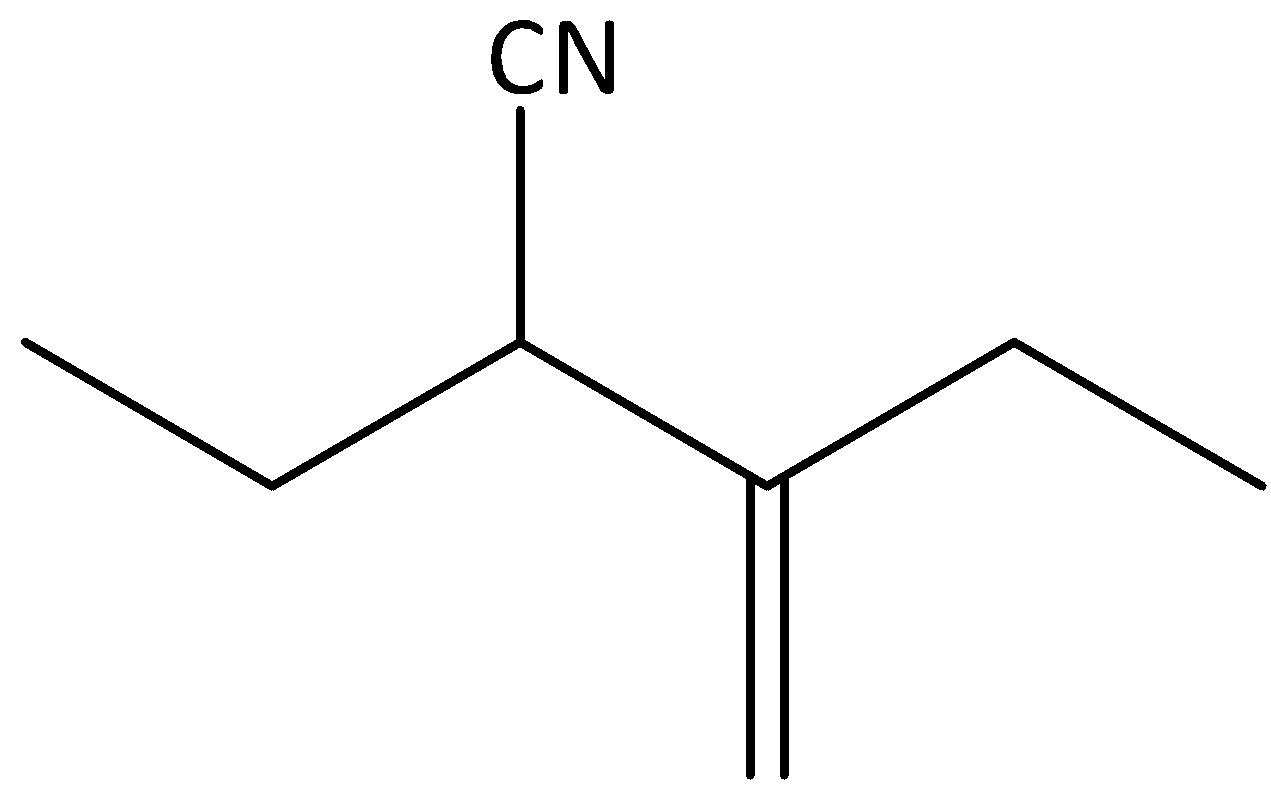
b)
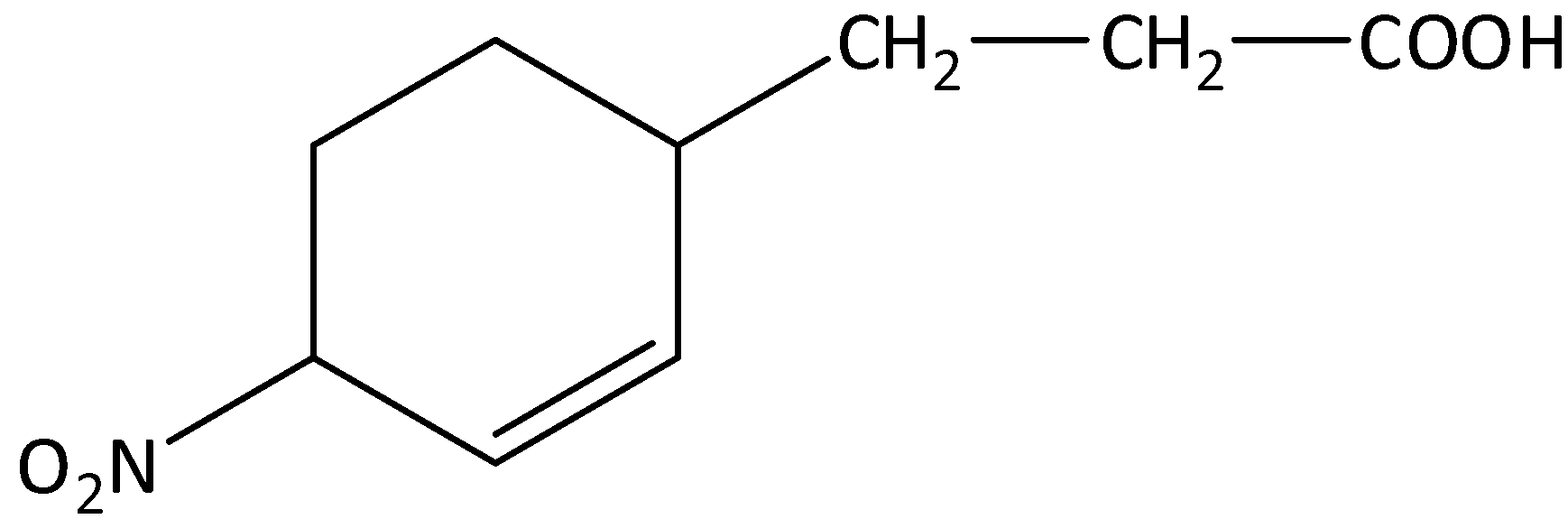
c)

d)
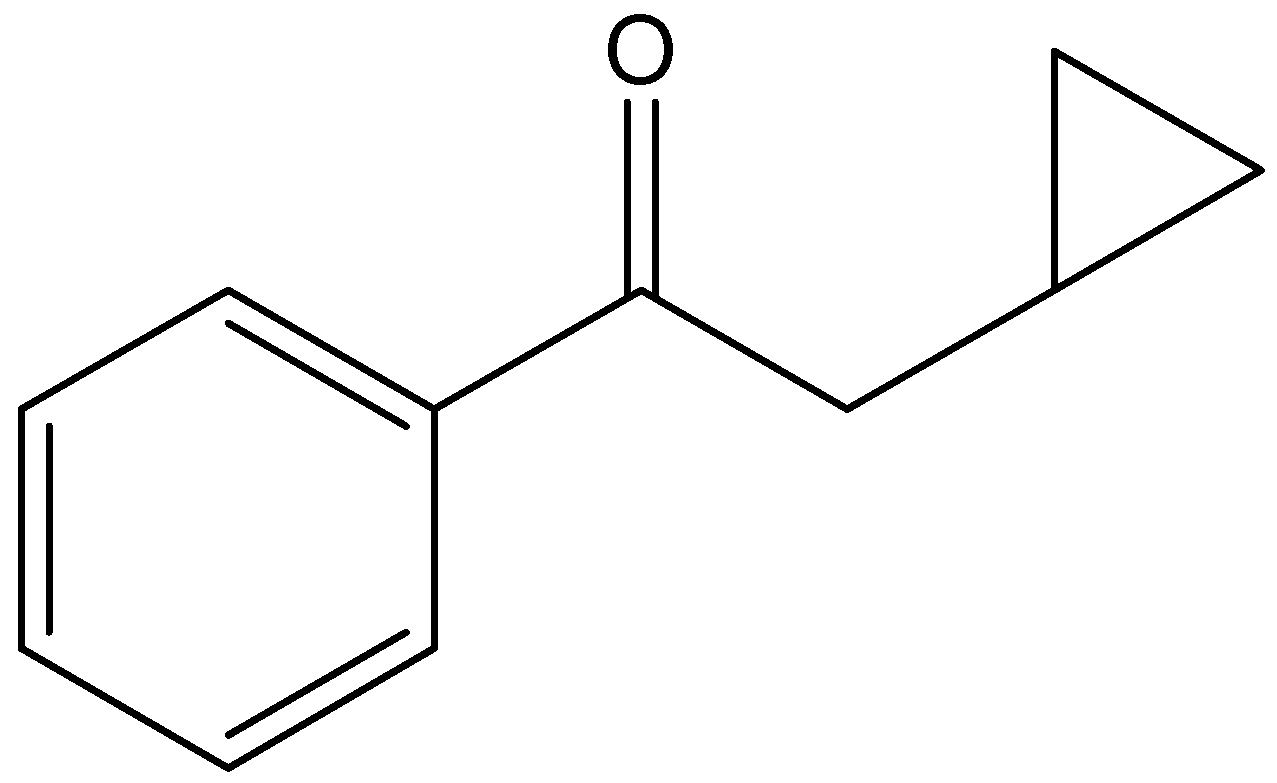




Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: We know that hydrocarbons are organic compounds that are made up of carbon and hydrogen. We can say in IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry, a number of suffixes, prefixes, and infixes are used to explain the position and type of the functional groups present in the compound. The different types of functional groups are alcohols, alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, carboxylic acids, aldehydes, ketones, amines, amides etc.
Complete answer:
a)
The given compound is,
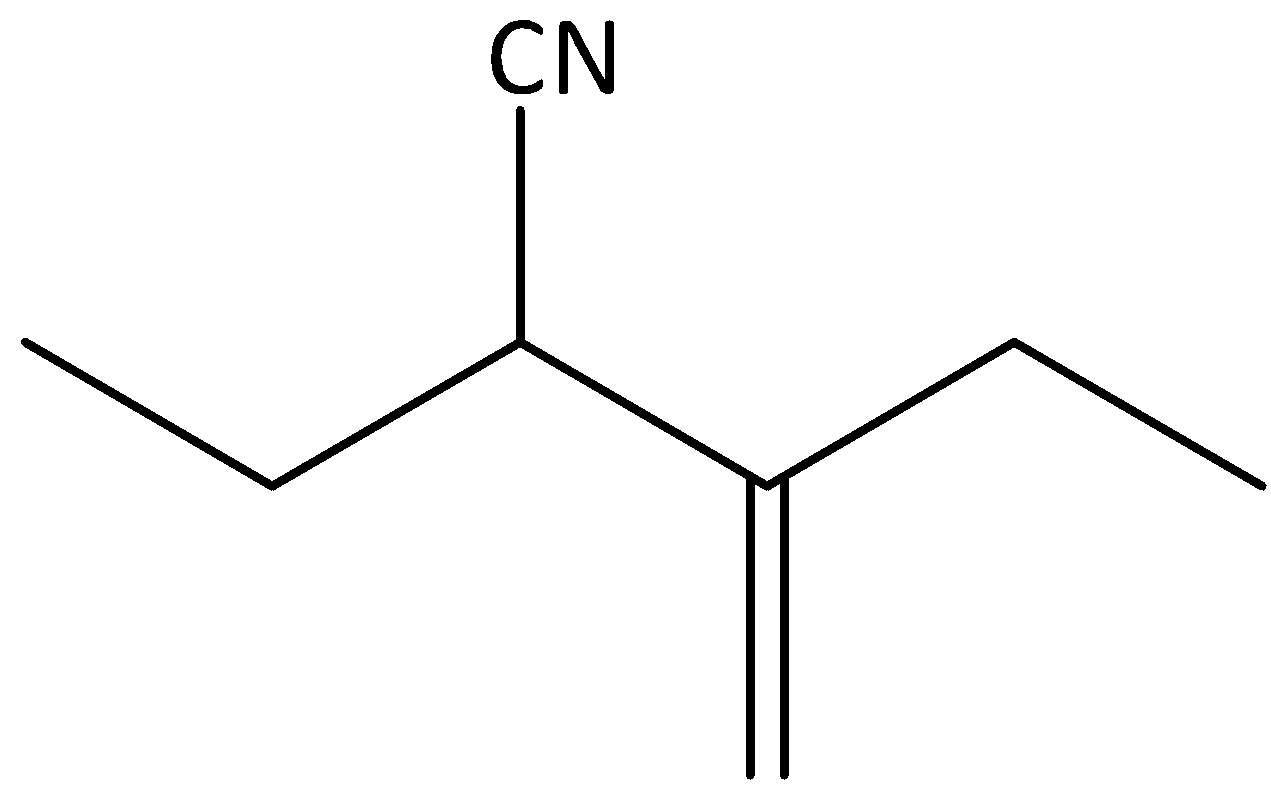
We can see that the given compound is an alkane. We know that saturated hydrocarbons are called alkanes. Each atom in an alkane exhibits the presence of four single bonds in a tetrahedral arrangement with $s{p^3}$ hybridization. The name of alkane ends with “-ane”.
Rules for naming compound:
1.We have to count the carbon atoms in the longest chain.
2.We have to identify and count the substituents.
3.We have to number the backbone carbon atoms by assigning the lowest number from the starting end.
In the given compound, the parent carbon chain is identified as pentane and we can see a substituent nitrile present in the parent chain. Therefore, the name of the parent hydrocarbon chain is pentanenitrile. We can see that ethyl substituent is present in the second carbon atom and the methylene group is attached to the third carbon atom. Therefore, the IUPAC name of the compound is 2-ethyl-3-methylpentanenitrile.
b)
The given compound is,

From the presence of the $ - COOH$ functional group present in the compound, we can say that the compound contains carboxylic acid functional groups.
IUPAC naming of Carboxylic acids:
1.We have to determine the longest continuous carbon chain consisting of the carboxyl group.
2.The carboxyl carbon is numbered as carbon-${\text{1}}$.
3.The –e ending of the parent alkane is replaced with suffix –oic acid. If they contain two carboxyl groups, we use –dioic acid as the suffix.
4.We have to name and number the substituents.
In the given compound, the parent chain is propane, and it becomes propanoic acid. The cyclohex-2-en-yl is attached to the third carbon of propanoic acid. A nitro is attached to the fourth position of cyclohex-2-en-yl ring. So, the IUPAC name of the compound is 3-(4-nitro cyclohex-2-en-yl) propanoic acid.
c)
The given compound is,
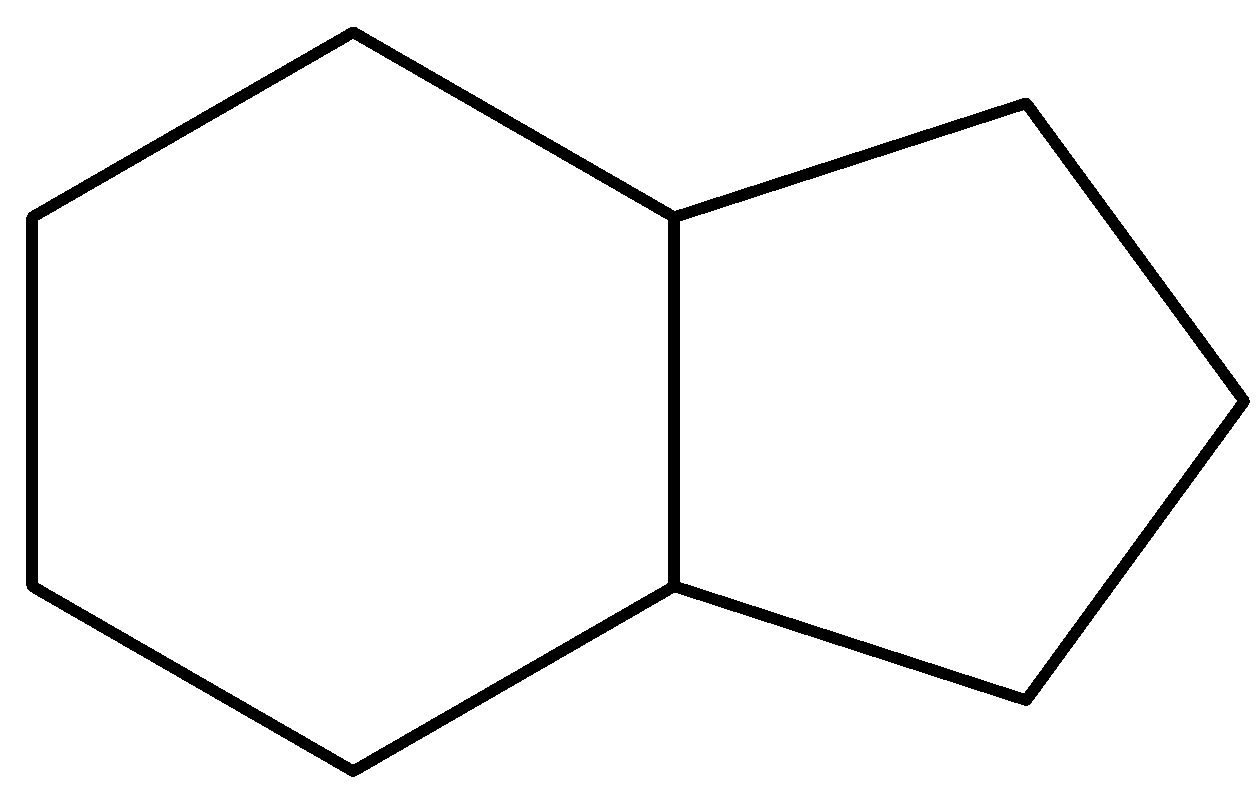
We can see that the given compound is a bicyclic compound. It contains a cyclohexane ring fused with a cyclopentane ring. The compound is trans-hydrindane with (R,R-configuration). The IUPAC name of the compound is Octahydro-1H-indene. The molecular formula of the compound is ${C_9}{H_{16}}$.
d)
The given compound is,
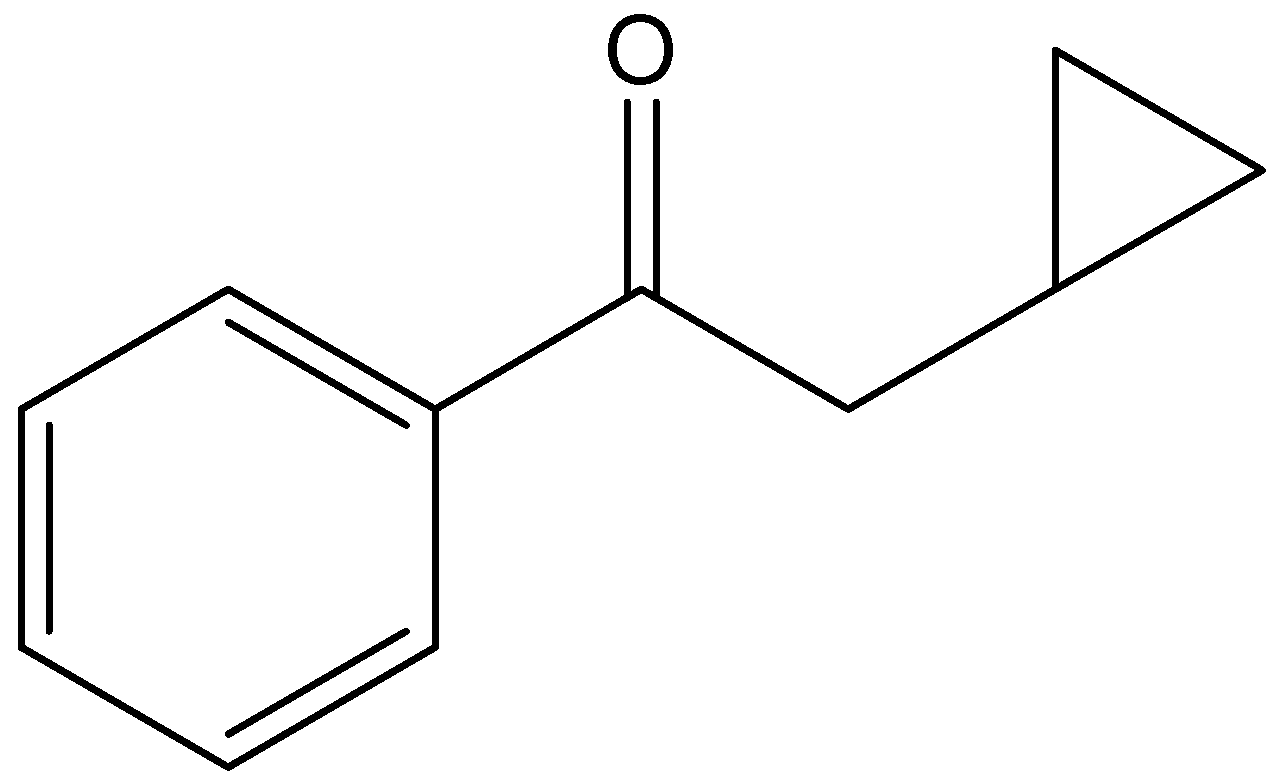
From the presence of carbonyl carbon attached with double bonded oxygen, we can say the compound contains ketone functional groups.
IUPAC nomenclature of naming ketones:
-We can determine the parent compound that is the longest carbon chain containing the carbonyl group.
-We have to replace the –e ending of the parent alkane with –one suffix of the ketone family.
-We have to number the carbon atom. The carbonyl carbon takes the lowest possible number.
In the given compound the parent carbon chain is phenylethane, since it contains ketone functional groups, the name of the parent carbon chain is phenylethanone. We can see that a cyclopropyl group is present at the second carbon of the chain. Hence, the IUPAC compound is 2-cyclopropyl-1-phenylethanone.
Note:
Some of the examples of IUPAC names of compounds of carboxylic acids are discussed below.
The structure of the compound is,
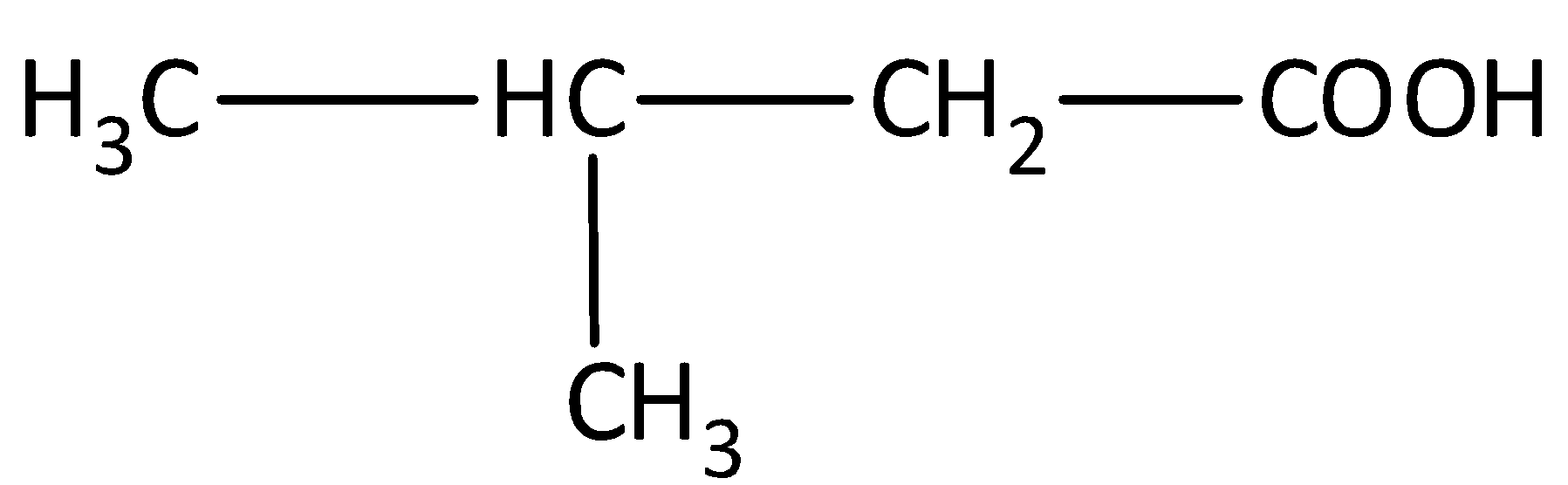
The parent carbon chain is butane. One methyl group is present as substituent in the carbon third position and the presence of carboxyl group, gives the systematic name of the compound as 3-methylbutanoic acid.
The structure of the compound is,
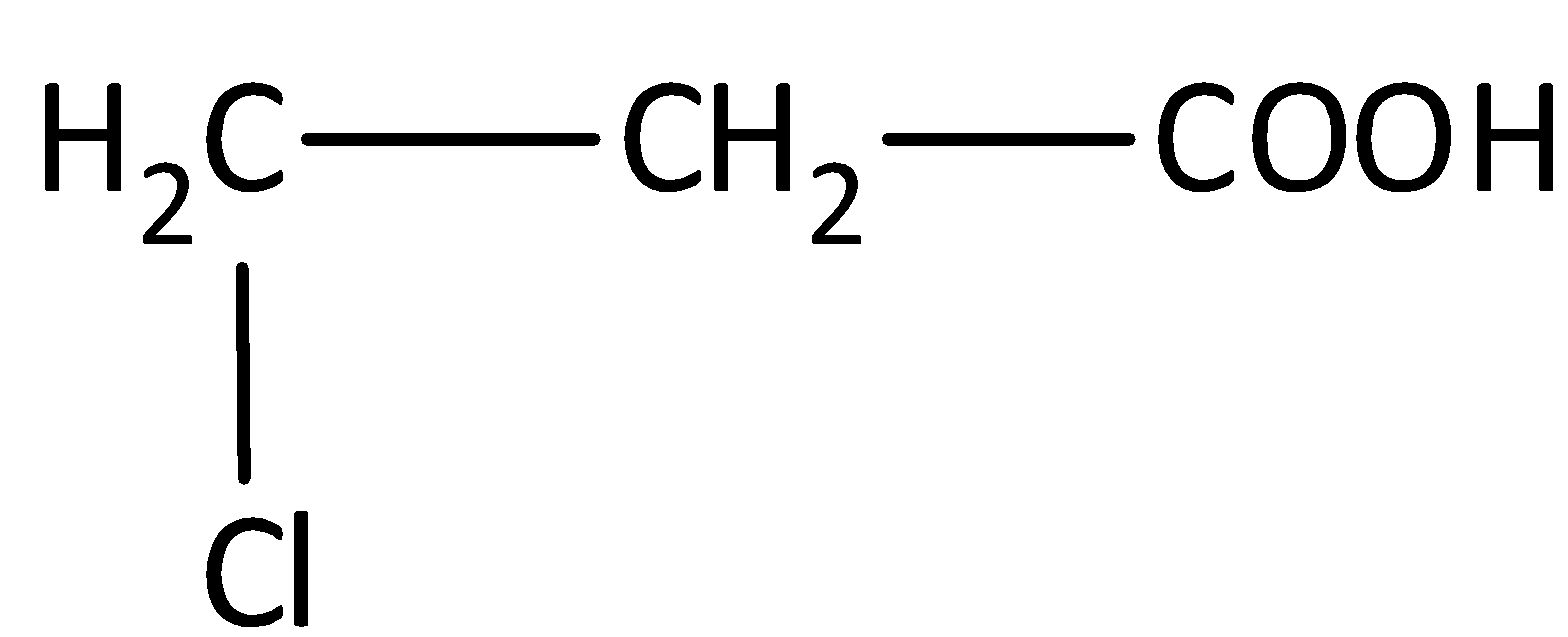
The parent carbon chain is propane. One chloro group is present as substituent in the carbon third position and the presence of carboxyl group, gives the systematic name of the compound as 3-chloropropanoic acid.
Complete answer:
a)
The given compound is,

We can see that the given compound is an alkane. We know that saturated hydrocarbons are called alkanes. Each atom in an alkane exhibits the presence of four single bonds in a tetrahedral arrangement with $s{p^3}$ hybridization. The name of alkane ends with “-ane”.
Rules for naming compound:
1.We have to count the carbon atoms in the longest chain.
2.We have to identify and count the substituents.
3.We have to number the backbone carbon atoms by assigning the lowest number from the starting end.
In the given compound, the parent carbon chain is identified as pentane and we can see a substituent nitrile present in the parent chain. Therefore, the name of the parent hydrocarbon chain is pentanenitrile. We can see that ethyl substituent is present in the second carbon atom and the methylene group is attached to the third carbon atom. Therefore, the IUPAC name of the compound is 2-ethyl-3-methylpentanenitrile.
b)
The given compound is,

From the presence of the $ - COOH$ functional group present in the compound, we can say that the compound contains carboxylic acid functional groups.
IUPAC naming of Carboxylic acids:
1.We have to determine the longest continuous carbon chain consisting of the carboxyl group.
2.The carboxyl carbon is numbered as carbon-${\text{1}}$.
3.The –e ending of the parent alkane is replaced with suffix –oic acid. If they contain two carboxyl groups, we use –dioic acid as the suffix.
4.We have to name and number the substituents.
In the given compound, the parent chain is propane, and it becomes propanoic acid. The cyclohex-2-en-yl is attached to the third carbon of propanoic acid. A nitro is attached to the fourth position of cyclohex-2-en-yl ring. So, the IUPAC name of the compound is 3-(4-nitro cyclohex-2-en-yl) propanoic acid.
c)
The given compound is,

We can see that the given compound is a bicyclic compound. It contains a cyclohexane ring fused with a cyclopentane ring. The compound is trans-hydrindane with (R,R-configuration). The IUPAC name of the compound is Octahydro-1H-indene. The molecular formula of the compound is ${C_9}{H_{16}}$.
d)
The given compound is,

From the presence of carbonyl carbon attached with double bonded oxygen, we can say the compound contains ketone functional groups.
IUPAC nomenclature of naming ketones:
-We can determine the parent compound that is the longest carbon chain containing the carbonyl group.
-We have to replace the –e ending of the parent alkane with –one suffix of the ketone family.
-We have to number the carbon atom. The carbonyl carbon takes the lowest possible number.
In the given compound the parent carbon chain is phenylethane, since it contains ketone functional groups, the name of the parent carbon chain is phenylethanone. We can see that a cyclopropyl group is present at the second carbon of the chain. Hence, the IUPAC compound is 2-cyclopropyl-1-phenylethanone.
Note:
Some of the examples of IUPAC names of compounds of carboxylic acids are discussed below.
The structure of the compound is,

The parent carbon chain is butane. One methyl group is present as substituent in the carbon third position and the presence of carboxyl group, gives the systematic name of the compound as 3-methylbutanoic acid.
The structure of the compound is,

The parent carbon chain is propane. One chloro group is present as substituent in the carbon third position and the presence of carboxyl group, gives the systematic name of the compound as 3-chloropropanoic acid.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




