
Give the mechanism of Beckmann rearrangement.
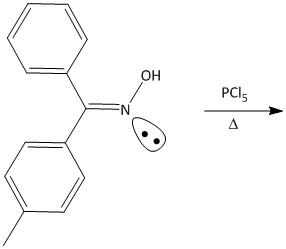
Product (A) of the above reaction is:

Answer
545.7k+ views
Hint: The Beckmann rearrangement reaction is a rearrangement reaction in which a group migrated to the \[N\] of an oxime. The group must be anti to the hydroxyl group of oxime.
Complete step by step answer:
The given reaction is an example of Beckmann rearrangement. Beckmann rearrangement was developed by German chemist Ernst Otto Beckmann. The reaction involves rearrangement of the oxime functional group to produce amide compounds.
The reaction is catalysed by an acid which can be a Brønsted acid like \[{H_2}S{O_4}\] or a Lewis acid like \[PC{l_5}\]. The reaction sometimes leads to formation of different products from the same starting material. This is because of the so called migratory aptitude of the migrating group. The better the migrating group stability the better is the migrating power.
For the given molecule, two phenyl rings are attached to the oxime double bonded carbon atom. One is benzene and the other is toluene. Out of benzene and toluene, toluene is anti to the hydroxyl group attached to the oxime nitrogen atom. Also toluene is a better migratory group than benzene considering that the stability of the corresponding toluene cation is more than benzene cation.
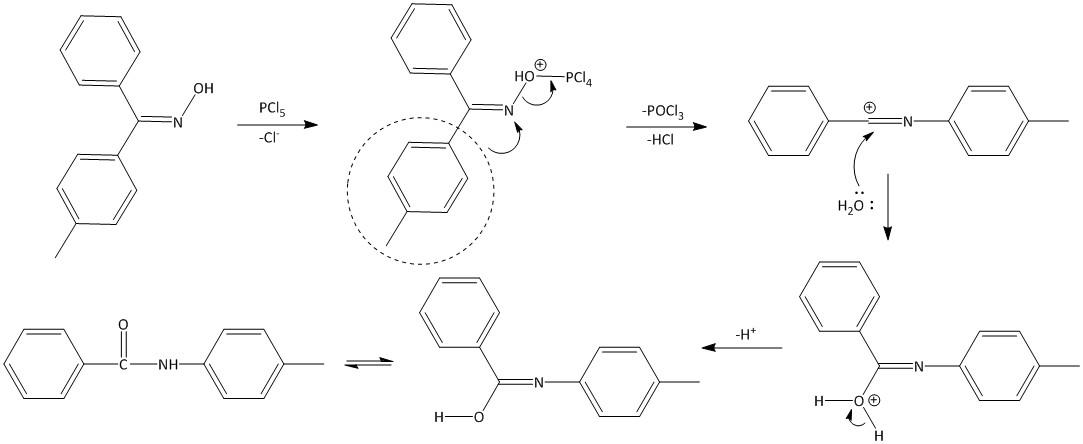
The reaction proceeds by the formation of the \[O - PC{l_4}\] complex formed by the reaction of the hydroxyl oxime and the \[PC{l_5}\]. The toluene present at the antiperiplanar orientation undergoes migration to the oxime nitrogen thereby releasing a molecule of \[POC{l_3}\] and \[HCl\] to produce an intermediate carbocation. This intermediate thus produced is unstable and is hydrolyzed by water to produce an amide. Thus the mechanism of the reaction is as follows:
Note: The reaction is very useful for the generation of lactams. In this case intramolecular rearrangement of bonds takes place to generate an amide.
Complete step by step answer:
The given reaction is an example of Beckmann rearrangement. Beckmann rearrangement was developed by German chemist Ernst Otto Beckmann. The reaction involves rearrangement of the oxime functional group to produce amide compounds.
The reaction is catalysed by an acid which can be a Brønsted acid like \[{H_2}S{O_4}\] or a Lewis acid like \[PC{l_5}\]. The reaction sometimes leads to formation of different products from the same starting material. This is because of the so called migratory aptitude of the migrating group. The better the migrating group stability the better is the migrating power.
For the given molecule, two phenyl rings are attached to the oxime double bonded carbon atom. One is benzene and the other is toluene. Out of benzene and toluene, toluene is anti to the hydroxyl group attached to the oxime nitrogen atom. Also toluene is a better migratory group than benzene considering that the stability of the corresponding toluene cation is more than benzene cation.
The reaction proceeds by the formation of the \[O - PC{l_4}\] complex formed by the reaction of the hydroxyl oxime and the \[PC{l_5}\]. The toluene present at the antiperiplanar orientation undergoes migration to the oxime nitrogen thereby releasing a molecule of \[POC{l_3}\] and \[HCl\] to produce an intermediate carbocation. This intermediate thus produced is unstable and is hydrolyzed by water to produce an amide. Thus the mechanism of the reaction is as follows:

Note: The reaction is very useful for the generation of lactams. In this case intramolecular rearrangement of bonds takes place to generate an amide.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




