
Give the relation between focal length and radius of curvature.
Answer
568.2k+ views
Hint: The focal length (f) is the distance between the centre of the lens to the principal foci or the point of focus. The radius of the mirror from which the mirror was cut is known as the radius of curvature (R). Here we derive a relation between the focal length and the radius of curvature with the help of a ray diagram.
Complete step by step answer:
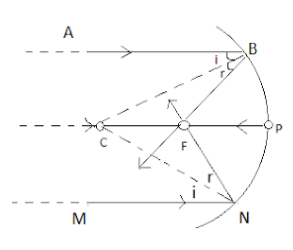
Let us consider that a ray of light AB is parallel to the principal axis and is incident on the spherical mirror.
After reflection, the ray AB passes through the point Focus F on the principal axis CP.
Also, BC is the normal to the spherical mirror at point B.
According to the law of reflection – Angle of incident is always equal to the angle of reflection.
$
\therefore \angle i = \angle r \\
\Rightarrow \angle ABC = \angle CBF{\text{ }}......{\text{(1)}} \\
$
Also, we know that lines AB and CP are parallel to each other.
Therefore, by using the property of the parallel lines- we get alternate angles equal.
$\angle ABC = \angle BCP{\text{ }}.....{\text{(2)}}$
By using equations $(1){\text{ and (2)}}$ we can say that $\Delta BCF$ is an isosceles triangle.
$ \Rightarrow BF = CF{\text{ }}....{\text{(3)}}$
The aperture of the mirror being very small, the point B would be very close to point P.
$ \Rightarrow BF = PF{\text{ }}....{\text{(4)}}$
By using equations $(3){\text{ and (4)}}$
Since the left hand side of both the equations are equal and same, we can write both its right hand side equal.
$ \Rightarrow CF = PF$
Since we have point F on the line PC, we can write PF has the sum of PF and CF.
$PC = PF + CF$
Also, PF and CF both are equal.
$ \Rightarrow PC = 2PF$
Now, by definition we have PF equal to focal length and PC equal to the radius of the curvature.
We can write above equation as-
$R = 2f$
It implies that the radius of curvature is twice the focal length.
Note:
Always remember the basic properties of the parallel lines and its transversal. Refer different angles formed by two parallel lines. Follow the law of the reflection which states that when the ray of light reflects on the surface, the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Know the difference between the law of refraction which is also known as Snell’s law which is based on the refractive index.
Complete step by step answer:

Let us consider that a ray of light AB is parallel to the principal axis and is incident on the spherical mirror.
After reflection, the ray AB passes through the point Focus F on the principal axis CP.
Also, BC is the normal to the spherical mirror at point B.
According to the law of reflection – Angle of incident is always equal to the angle of reflection.
$
\therefore \angle i = \angle r \\
\Rightarrow \angle ABC = \angle CBF{\text{ }}......{\text{(1)}} \\
$
Also, we know that lines AB and CP are parallel to each other.
Therefore, by using the property of the parallel lines- we get alternate angles equal.
$\angle ABC = \angle BCP{\text{ }}.....{\text{(2)}}$
By using equations $(1){\text{ and (2)}}$ we can say that $\Delta BCF$ is an isosceles triangle.
$ \Rightarrow BF = CF{\text{ }}....{\text{(3)}}$
The aperture of the mirror being very small, the point B would be very close to point P.
$ \Rightarrow BF = PF{\text{ }}....{\text{(4)}}$
By using equations $(3){\text{ and (4)}}$
Since the left hand side of both the equations are equal and same, we can write both its right hand side equal.
$ \Rightarrow CF = PF$
Since we have point F on the line PC, we can write PF has the sum of PF and CF.
$PC = PF + CF$
Also, PF and CF both are equal.
$ \Rightarrow PC = 2PF$
Now, by definition we have PF equal to focal length and PC equal to the radius of the curvature.
We can write above equation as-
$R = 2f$
It implies that the radius of curvature is twice the focal length.
Note:
Always remember the basic properties of the parallel lines and its transversal. Refer different angles formed by two parallel lines. Follow the law of the reflection which states that when the ray of light reflects on the surface, the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Know the difference between the law of refraction which is also known as Snell’s law which is based on the refractive index.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




