
Give the structural formula and IUPAC names of the following compounds
(a) Malonic acid
(b) Succinic acid.
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint:Malonic acid and succinic acid are dicarboxylic acids belonging to a homologous group, that is, compounds which differ only by a $ - C{H_2}$ group and molecular mass of $14$. Malonic acid is the second member of this series while succinic acid is the third member.
Complete step by step answer:
Both malonic acid and succinic acid belong to dicarboxylic acids, meaning that they have two carboxylic acid ($ - COOH$) groups in their structure. They are also members of a homologous series, which are compounds which differ only by a $ - C{H_2}$ group and molecular mass of $14$. The first member of this series is oxalic acid, which has only two $ - COOH$ groups. Malonic acid being the next member, has a $ - C{H_2}$ group in between the two carboxylic acid groups, while succinic acid, the next member, has two $ - C{H_2}$ groups. With this information, we can draw their structure as follows:
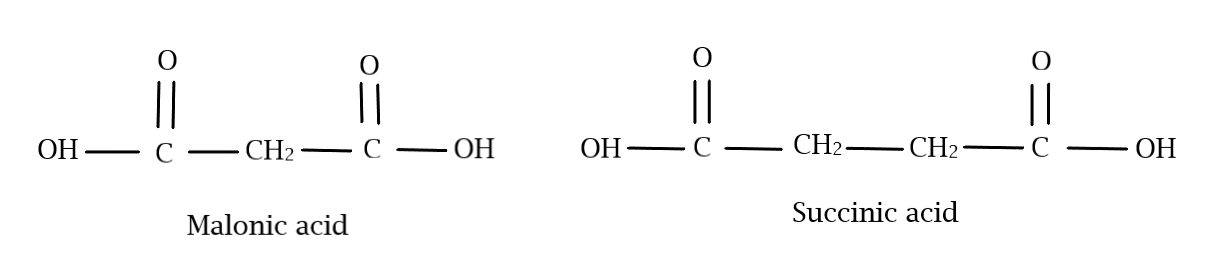
For the IUPAC name of malonic acid, let us start counting the carbon atoms from the left. We have 3 carbon atoms and two carboxylic acid groups on the first and third carbon atoms. For the three carbon atoms, we have to include “propane” and to account for the two carboxylic acids, we include “dioic acid” with the numbers at which they are present written at the beginning. Hence the IUPAC name is:
$1,3$ – propanedioic acid
For the IUPAC name of succinic acid, let us start counting the carbon atoms from the left. We have 4 carbon atoms and two carboxylic acid groups on the first and fourth carbon atoms. For the four carbon atoms, we have to include “butane” and to account for the two carboxylic acids, we include “dioic acid” with the numbers at which they are present written at the beginning. Hence the IUPAC name is:
$1,4$ – butanedioic acid
Note:
While writing IUPAC name, numbering of carbon atoms should begin from the closest carbon atom to the functional group. Here as both the compounds are symmetric (same groups of atoms on either side of a line drawn through the middle of the compound) and contain the same functional group, we can start numbering from any side and still get the same answer. When two or more functional groups are present, numbering should be done according to the series of preference of functional groups.
Complete step by step answer:
Both malonic acid and succinic acid belong to dicarboxylic acids, meaning that they have two carboxylic acid ($ - COOH$) groups in their structure. They are also members of a homologous series, which are compounds which differ only by a $ - C{H_2}$ group and molecular mass of $14$. The first member of this series is oxalic acid, which has only two $ - COOH$ groups. Malonic acid being the next member, has a $ - C{H_2}$ group in between the two carboxylic acid groups, while succinic acid, the next member, has two $ - C{H_2}$ groups. With this information, we can draw their structure as follows:
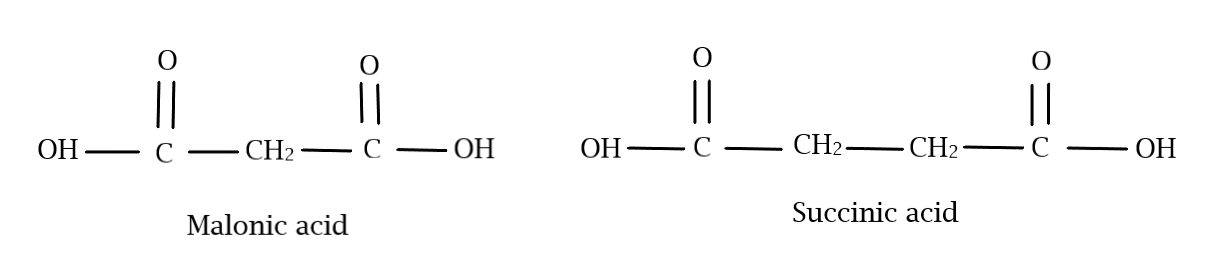
For the IUPAC name of malonic acid, let us start counting the carbon atoms from the left. We have 3 carbon atoms and two carboxylic acid groups on the first and third carbon atoms. For the three carbon atoms, we have to include “propane” and to account for the two carboxylic acids, we include “dioic acid” with the numbers at which they are present written at the beginning. Hence the IUPAC name is:
$1,3$ – propanedioic acid
For the IUPAC name of succinic acid, let us start counting the carbon atoms from the left. We have 4 carbon atoms and two carboxylic acid groups on the first and fourth carbon atoms. For the four carbon atoms, we have to include “butane” and to account for the two carboxylic acids, we include “dioic acid” with the numbers at which they are present written at the beginning. Hence the IUPAC name is:
$1,4$ – butanedioic acid
Note:
While writing IUPAC name, numbering of carbon atoms should begin from the closest carbon atom to the functional group. Here as both the compounds are symmetric (same groups of atoms on either side of a line drawn through the middle of the compound) and contain the same functional group, we can start numbering from any side and still get the same answer. When two or more functional groups are present, numbering should be done according to the series of preference of functional groups.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




