
Give three examples of materials that refract light rays. What happens to the speed of light when they enter these materials?
Answer
497.4k+ views
Hint: Refractive index is the ratio of sine of angle of incidence to the sine of angle of refraction. The mathematical expression is $\mu = \dfrac{{\sin i}}{{\sin r}}$ .
Refractive index can also be given as the ratio of speed of light in vacuum to the speed of light in the medium. The mathematical expression is given as $\mu = \dfrac{c}{v}$ where c is the speed of light in air and v is the velocity of the light in the medium.
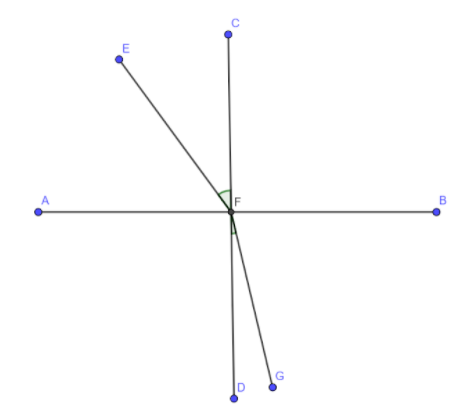
Here EF is the incident ray and FG is the refracted ray while CD is the normal.
Complete step by step solution:
We know that the refractive index is given as the ratio of speed of light in vacuum to the speed of light in the medium. The mathematical expression is given as $\mu = \dfrac{c}{v}$ where c is the speed of light in air and v is the velocity of the light in the medium.
Now since the refractive indices of different materials are different and are never equal to 1 except when the medium is air itself, the light would refract in all mediums.
Some examples of such mediums are: Glass, Water, Oil.
The speed of light changes when it enters these mediums.
This depends on the refractive index of the medium. If the medium is denser than the previous medium, then the rays would refract towards the normal. Else the rays would bend away from the normal.
Note:
When we mention the term denser here, it has a different meaning than the mass density of materials and must be carefully noted for sound concepts. Here denser means that the material is optically denser than the other medium. It has more ability to bend the incident rays towards the normal.
Refractive index can also be given as the ratio of speed of light in vacuum to the speed of light in the medium. The mathematical expression is given as $\mu = \dfrac{c}{v}$ where c is the speed of light in air and v is the velocity of the light in the medium.

Here EF is the incident ray and FG is the refracted ray while CD is the normal.
Complete step by step solution:
We know that the refractive index is given as the ratio of speed of light in vacuum to the speed of light in the medium. The mathematical expression is given as $\mu = \dfrac{c}{v}$ where c is the speed of light in air and v is the velocity of the light in the medium.
Now since the refractive indices of different materials are different and are never equal to 1 except when the medium is air itself, the light would refract in all mediums.
Some examples of such mediums are: Glass, Water, Oil.
The speed of light changes when it enters these mediums.
This depends on the refractive index of the medium. If the medium is denser than the previous medium, then the rays would refract towards the normal. Else the rays would bend away from the normal.
Note:
When we mention the term denser here, it has a different meaning than the mass density of materials and must be carefully noted for sound concepts. Here denser means that the material is optically denser than the other medium. It has more ability to bend the incident rays towards the normal.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




