
Given an account of artificial chromosomes in the transfer of genetic material.
Answer
576k+ views
Hint: Genetic content which codes for the desired property (known as the gene of interest) is transferred to the host (organisms where the gene of interest is expressed) using these chromosomes. They are applied in the creation of GMOs and gene therapy.
Complete step by step answer:
For the transfer of genetic material, small extra-chromosomal structures are used known as artificial chromosomes. Artificial chromosomes are human- made and some common examples are yeast artificial chromosomes (YAC) and bacterial artificial chromosomes (BAC). The human artificial chromosomes known as HAC is also a significant human creation in recombinant technology. They are commonly called vectors in recombinant technology, where these artificial chromosomes are used for the transfer of desired genetic material to the desired host.
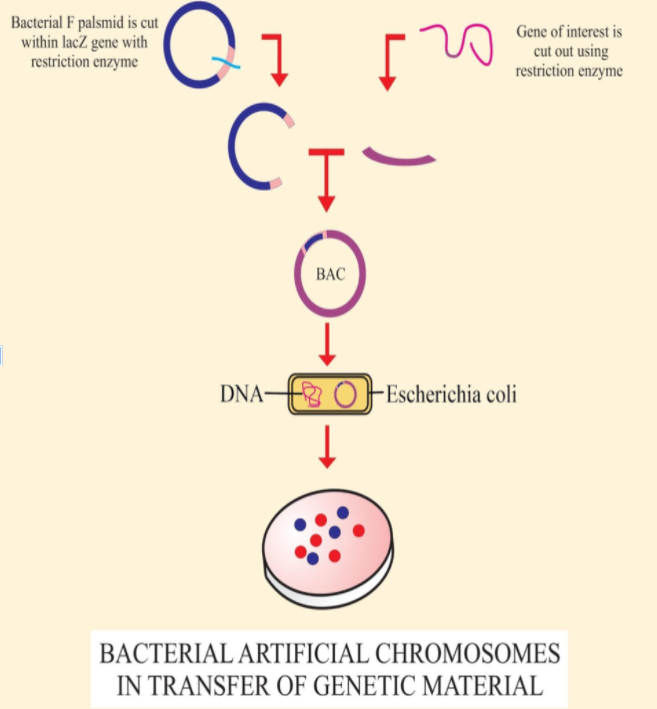
These vectors play a key role in the formation of genetically modified organisms, where the gene of interest is transferred using these vectors. These organisms are used in many industries such as dairy, pharmaceutical, etc. For example, the insulin for diabetic patients was first extracted from other animals such as pigs and horses, which later got shifted to micro- organisms where the gene which codes for human insulin was transferred to the microorganisms using vectors. The insulin synthesized this way is less immunogenic than the animal extracted insulin.
Note:
- Artificial chromosomes are used in gene therapy, where diseases can't be cured since the genetic material is altered or faulty, can be fixed using artificial chromosomes.
- GMO vegetables and plants are banned in many countries as they raise the question of turning hazardous to the consumers.
- Artificial chromosomes are used in many industries currently, as the production of desired materials using microorganisms is cost- efficient and less time- consuming.
Complete step by step answer:
For the transfer of genetic material, small extra-chromosomal structures are used known as artificial chromosomes. Artificial chromosomes are human- made and some common examples are yeast artificial chromosomes (YAC) and bacterial artificial chromosomes (BAC). The human artificial chromosomes known as HAC is also a significant human creation in recombinant technology. They are commonly called vectors in recombinant technology, where these artificial chromosomes are used for the transfer of desired genetic material to the desired host.

These vectors play a key role in the formation of genetically modified organisms, where the gene of interest is transferred using these vectors. These organisms are used in many industries such as dairy, pharmaceutical, etc. For example, the insulin for diabetic patients was first extracted from other animals such as pigs and horses, which later got shifted to micro- organisms where the gene which codes for human insulin was transferred to the microorganisms using vectors. The insulin synthesized this way is less immunogenic than the animal extracted insulin.
Note:
- Artificial chromosomes are used in gene therapy, where diseases can't be cured since the genetic material is altered or faulty, can be fixed using artificial chromosomes.
- GMO vegetables and plants are banned in many countries as they raise the question of turning hazardous to the consumers.
- Artificial chromosomes are used in many industries currently, as the production of desired materials using microorganisms is cost- efficient and less time- consuming.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




