
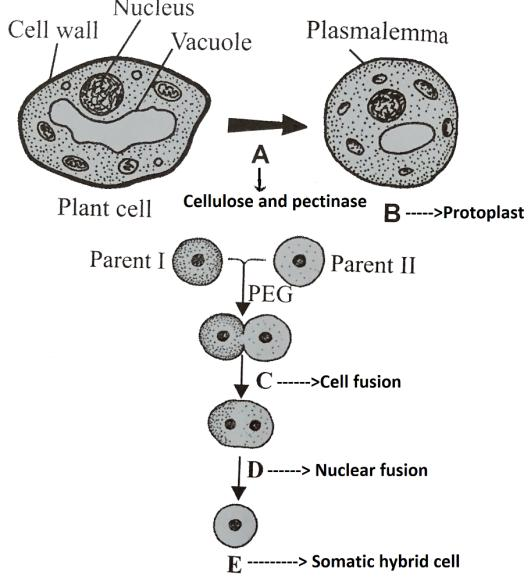
Given below is the flowchart showing the process of somatic hybridisation. Identify A, B, C, D and E
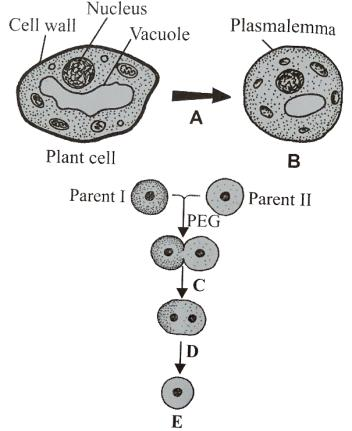
A) A-Cell fusion, B-Nuclear fusion, C-Cellulose and pectinase, D-Protoplast, E-Somatic hybrid cell
B) A-Cellulose and pectinase, B-Protoplast, C-Cell fusion, D-Nuclear fusion, E-Somatic hybrid cell
C) A-Protoplast, B-Nuclear fusion, C-Somatic hybrid cell, D-Cellulose and pectinase, E-Cell fusion
D) A-Cellulose and pectinase, B-Protoplast, C-Nuclear fusion, D-Cell fusion, E-Somatic hybrid cell

Answer
508.8k+ views
Hint: Somatic hybridization is a technique that allows for protoplast fusion, which allows for modification of the cellular genome. It's a type of plant genetic alteration in which two different species of plants are fused together to create a new hybrid plant with both of its traits. Pomato, for example, is a somatic hybrid created by fusing the protoplasts of tomato and potato.
One of the requirements for successful somatic hybridization is protoplast regeneration. Several attempts at protoplast fusion have been conducted among Fagopyrum species, with the maximum success achieved in plant regeneration from protoplasts in common buckwheat.
Complete explanation:
Option A: Cell fusion is a crucial biological process that occurs when numerous uninucleate cells join together to produce a multinucleate cell called a syncytium. Cell fusion occurs during myoblast differentiation, osteoblast differentiation, and trophoblast development, as well as embryogenesis and morphogenesis.
So, option A is not correct.
Option B: We isolate naked protoplasts through somatic hybridisation by digesting their cell walls with digesting enzymes. The separated protoplasts then merged to generate a hybrid protoplast, which grew to become a new plant.
So, option B is correct.
Option C: Pectinase is a polymer present in plant cell walls that is broken down by the enzyme pectinase. Pectolyase, pectozyme, and polygalacturonase, one of the most studied and commonly used commercial pectinases, are examples of pectic enzymes.
So, option C is not correct.
Option D: By dissolving their cell membranes with digesting enzymes, we isolate bare protoplasts through somatic hybridisation. After then, the distinct protoplasts joined to form a hybrid protoplast, which developed into a new plant.
So, option D is not correct.
Therefore, Option B is the correct answer.
Note:
Somatic hybridization involves the following steps:
Single cells extracted from selected plants.
Using enzymes like pectinase and cellulase, the fusing cell's cell wall is removed. These enzymes break down the cell wall, exposing the protoplast.
Under aseptic circumstances, the isolated protoplasts of selected Parents are united to produce hybrid protoplasts on a specific nutritional medium. The use of polyethylene glycol (PEG) or a brief high voltage electric current might cause this fusion.
The hybrid protoplasts are grown in nutrient media, where they regenerate cell walls and begin to divide to form new plantlets.
One of the requirements for successful somatic hybridization is protoplast regeneration. Several attempts at protoplast fusion have been conducted among Fagopyrum species, with the maximum success achieved in plant regeneration from protoplasts in common buckwheat.
Complete explanation:
Option A: Cell fusion is a crucial biological process that occurs when numerous uninucleate cells join together to produce a multinucleate cell called a syncytium. Cell fusion occurs during myoblast differentiation, osteoblast differentiation, and trophoblast development, as well as embryogenesis and morphogenesis.
So, option A is not correct.
Option B: We isolate naked protoplasts through somatic hybridisation by digesting their cell walls with digesting enzymes. The separated protoplasts then merged to generate a hybrid protoplast, which grew to become a new plant.
So, option B is correct.
Option C: Pectinase is a polymer present in plant cell walls that is broken down by the enzyme pectinase. Pectolyase, pectozyme, and polygalacturonase, one of the most studied and commonly used commercial pectinases, are examples of pectic enzymes.
So, option C is not correct.
Option D: By dissolving their cell membranes with digesting enzymes, we isolate bare protoplasts through somatic hybridisation. After then, the distinct protoplasts joined to form a hybrid protoplast, which developed into a new plant.
So, option D is not correct.
Therefore, Option B is the correct answer.

Note:
Somatic hybridization involves the following steps:
Single cells extracted from selected plants.
Using enzymes like pectinase and cellulase, the fusing cell's cell wall is removed. These enzymes break down the cell wall, exposing the protoplast.
Under aseptic circumstances, the isolated protoplasts of selected Parents are united to produce hybrid protoplasts on a specific nutritional medium. The use of polyethylene glycol (PEG) or a brief high voltage electric current might cause this fusion.
The hybrid protoplasts are grown in nutrient media, where they regenerate cell walls and begin to divide to form new plantlets.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




