
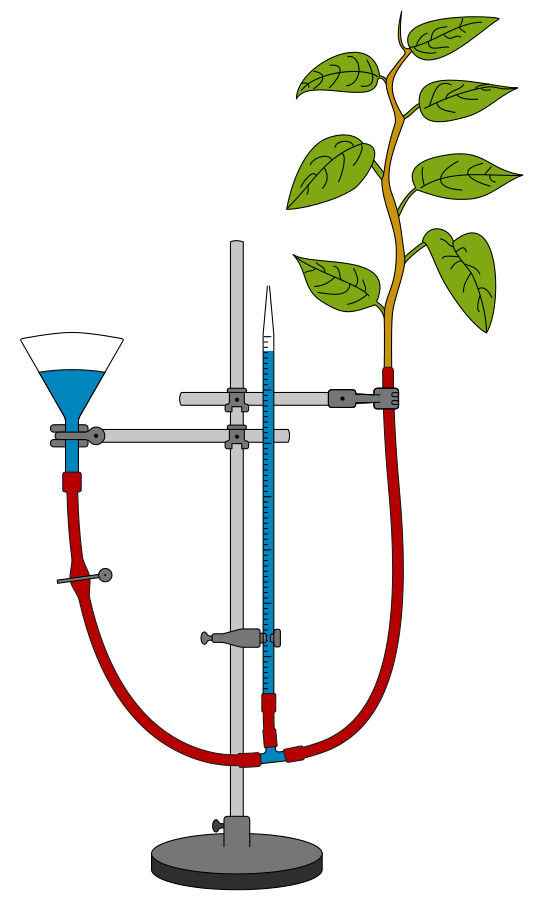
Given is the diagram of an apparatus used to study a particular phenomenon in plants:
Name the apparatus
What is it used for?
What is the role played by the air-bubble in this experiment ?
What is the use of the reservoir?
What happens to the movement of the air - bubble if apparatus is kept:
(i) in the dark ; (ii) in sunlight ; (iii) in front of a fan?

Answer
559.2k+ views
Hint: Plants absorb the water from the soil for photosynthesis. However, a large portion of this water is lost in the form of vapours as a result of transpiration. Water is carried in the upward direction through the xylem which passed it onto the leaves. Transpiration rate can be measured manually either by using any instrument or by simply calculating the distance travelled by a bubble in a capillary tube over the given time which can be a bit tedious and error prone.
Complete answer:
> The given picture depicts an instrument known as a transpirometer, also called a potometer (Greek “poto”, drunken and “metron”, to measure). This particular model is known as Ganong’s potometer.
> As the name suggests, a Potometer or transpirometer is used to study and measure the amount of water absorbed by a plant shoot during transpiration.
> The air bubble introduced into the capillary tube is used to monitor the volume of water absorbed by the plant shoot due to transpiration. As the length of the capillary tube is generally graduated the distance travelled by the lone air bubble as it moves can be directly measured to estimate the volume of transpiration loss over time.
> The reservoir monitors the number and position of the bubble. We can also add further water into the setup by replenishing the volume in the reservoir.
> Since transpiration is affected by myriad factors we can expect different results e.g.,
• In absence of light, the photosynthesis is inhibited and consequently the rate of transpiration may also decrease.
• When exposed to sunlight, the double effect of increased photosynthesis and rise in temperature induces the shoot to increase the water uptake to compensate for increased transpiration losses, so the bubble may move faster.
• The rate of transpiration is affected by the relative humidity of the plant’s environment, increasing during the dry period and reducing during the wet season. In a windy condition, the water vapours in the environment around the leaves of the shoot would be quickly lost which would force the plant to continue to transpire that yet again would increase the speed of movement of the bubble.
Note: Potometer can only measure the rate of water uptake and not the actual rate of transpiration since not all the water absorbed by the shoot would be lost. Some of it would be used in photosynthesis and while some of it would be used by the plant cells to maintain their turgidity.
Complete answer:
> The given picture depicts an instrument known as a transpirometer, also called a potometer (Greek “poto”, drunken and “metron”, to measure). This particular model is known as Ganong’s potometer.
> As the name suggests, a Potometer or transpirometer is used to study and measure the amount of water absorbed by a plant shoot during transpiration.
> The air bubble introduced into the capillary tube is used to monitor the volume of water absorbed by the plant shoot due to transpiration. As the length of the capillary tube is generally graduated the distance travelled by the lone air bubble as it moves can be directly measured to estimate the volume of transpiration loss over time.
> The reservoir monitors the number and position of the bubble. We can also add further water into the setup by replenishing the volume in the reservoir.
> Since transpiration is affected by myriad factors we can expect different results e.g.,
• In absence of light, the photosynthesis is inhibited and consequently the rate of transpiration may also decrease.
• When exposed to sunlight, the double effect of increased photosynthesis and rise in temperature induces the shoot to increase the water uptake to compensate for increased transpiration losses, so the bubble may move faster.
• The rate of transpiration is affected by the relative humidity of the plant’s environment, increasing during the dry period and reducing during the wet season. In a windy condition, the water vapours in the environment around the leaves of the shoot would be quickly lost which would force the plant to continue to transpire that yet again would increase the speed of movement of the bubble.
Note: Potometer can only measure the rate of water uptake and not the actual rate of transpiration since not all the water absorbed by the shoot would be lost. Some of it would be used in photosynthesis and while some of it would be used by the plant cells to maintain their turgidity.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




