
Given,${{He}}_{{2}}^{{{ + 2}}}$ ion is more stable than ${{H}}{{{e}}_{{2}}}$ molecule. Explain.
Answer
518.7k+ views
Hint: Helium is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert monatomic gas that belongs to the noble gas section of the periodic table. It has the lowest boiling point of all the elements. In the observable universe, helium is the second lightest and most abundant element.
Complete answer:
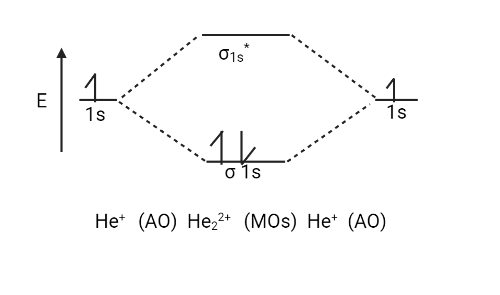
There are only two valence electrons in the ${{He}}_{{2}}^{{{ + 2}}}$ ion (two from each He atom minus two for the $ + 2$ charge). The molecular orbital diagram can now be filled in.
The two electrons occupy the bonding $\left( {{{\sigma 1s}}} \right)$ orbital, which is the lowest energy molecular orbital, resulting in an $\left( {{{\sigma 1s}}} \right)$ $2$ electron configuration. So, the bond order is
${{ = }}\,\dfrac{{{1}}}{{{2}}}\left[ {{{{N}}_{{b}}}\,{{ - }}\,{{{N}}_{{a}}}} \right]\,\,{{ = }}\,\dfrac{{\left( {{{2}}\,{{ - }}\,{{0}}} \right)}}{{{2}}}\,{{ = }}\,\dfrac{{{2}}}{{{2}}}\,{{ = }}\,{{1}}$
As a result, ${{He}}_{{2}}^{{{ + 2}}}$ is expected to contain a single ${{He}}\,\,{{ - }}\,{{He}}$ bond. As a result, it should be a stable species.
Let us take a look at the ${{H}}{{{e}}_{{2}}}$ molecules, which are made up of two ${{He}}$ atoms with the ${{1}}{{{s}}^{{2}}}$ electronic configuration.
Both the ${{\sigma 1s}}$ bonding and $\left( {{{\sigma *1s}}} \right)$ antibonding orbitals must contain two electrons with a total of four valence electrons. This results in an electronic configuration of \[{\left( {{{\sigma 1s}}} \right)^{{2}}}{\left( {{{\sigma 1s}}} \right)^{{2}}}\].
So, the bond order is
Bond order ${{ = }}\,\dfrac{{{1}}}{{{2}}}\left[ {{{{N}}_{{b}}}\,{{ - }}\,{{{N}}_{{a}}}} \right]\,\,{{ = }}\,\dfrac{{\left( {{{2}}\,{{ - }}\,2} \right)}}{{{2}}}\,{{ = }}\,0$
The ${{H}}{{{e}}_{{2}}}$ molecule has no net covalent bond, indicating that it is not a stable species.
Note:
Cryogenics (the largest single use, accounting for about a quarter of production) uses liquid helium to cool superconducting magnets, with MRI scanners being the most popular commercial use.
Inhaling a small amount of helium temporarily alters the timbre and quality of the human voice, just as it does for any gas whose density varies from that of air.
Complete answer:
There are only two valence electrons in the ${{He}}_{{2}}^{{{ + 2}}}$ ion (two from each He atom minus two for the $ + 2$ charge). The molecular orbital diagram can now be filled in.
The two electrons occupy the bonding $\left( {{{\sigma 1s}}} \right)$ orbital, which is the lowest energy molecular orbital, resulting in an $\left( {{{\sigma 1s}}} \right)$ $2$ electron configuration. So, the bond order is
${{ = }}\,\dfrac{{{1}}}{{{2}}}\left[ {{{{N}}_{{b}}}\,{{ - }}\,{{{N}}_{{a}}}} \right]\,\,{{ = }}\,\dfrac{{\left( {{{2}}\,{{ - }}\,{{0}}} \right)}}{{{2}}}\,{{ = }}\,\dfrac{{{2}}}{{{2}}}\,{{ = }}\,{{1}}$
As a result, ${{He}}_{{2}}^{{{ + 2}}}$ is expected to contain a single ${{He}}\,\,{{ - }}\,{{He}}$ bond. As a result, it should be a stable species.
Let us take a look at the ${{H}}{{{e}}_{{2}}}$ molecules, which are made up of two ${{He}}$ atoms with the ${{1}}{{{s}}^{{2}}}$ electronic configuration.
Both the ${{\sigma 1s}}$ bonding and $\left( {{{\sigma *1s}}} \right)$ antibonding orbitals must contain two electrons with a total of four valence electrons. This results in an electronic configuration of \[{\left( {{{\sigma 1s}}} \right)^{{2}}}{\left( {{{\sigma 1s}}} \right)^{{2}}}\].
So, the bond order is
Bond order ${{ = }}\,\dfrac{{{1}}}{{{2}}}\left[ {{{{N}}_{{b}}}\,{{ - }}\,{{{N}}_{{a}}}} \right]\,\,{{ = }}\,\dfrac{{\left( {{{2}}\,{{ - }}\,2} \right)}}{{{2}}}\,{{ = }}\,0$
The ${{H}}{{{e}}_{{2}}}$ molecule has no net covalent bond, indicating that it is not a stable species.

Note:
Cryogenics (the largest single use, accounting for about a quarter of production) uses liquid helium to cool superconducting magnets, with MRI scanners being the most popular commercial use.
Inhaling a small amount of helium temporarily alters the timbre and quality of the human voice, just as it does for any gas whose density varies from that of air.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




