
Glucose has _________ optical isomers.
(A) 4
(B) 8
(C) 16
(D) 10
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: To answer this question, you must know the structure of glucose. Glucose is an aldohexose sugar-containing two chiral centres and other centres are chiral. A general formula for obtaining the maximum number of optical isomers is ${2^n}$, where n is the number of chiral centres.
Complete step by step solution:
Molecular formula of glucose is ${C_6}{H_{12}}{O_6}$. Structure of glucose is:
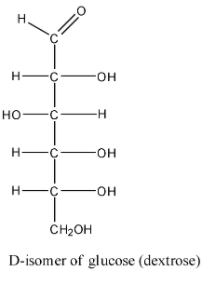
As you can see in the above structure of glucose there are six carbon atoms, hence it is an aldohexose. We usually consider glucose as D-glucose (dextrose). The D-isomer of glucose is the one whose carbon 2 is in the R configuration or has OH in the right-hand side. The mirror image of dextrose is L-glucose, having S configuration of carbon 2. Glucose contains one aldehydic carbon and five alcoholic carbons. It contains four chiral centres. A chiral centre is the one that has four different groups bonded to it in such a manner that it has a non-superimposable mirror image. Thus, in glucose, carbon 2, 3, 4 and 5 are chiral centres and carbon 1 and 6 are achiral. Now, the formula to obtain the maximum number of possible optical isomers is ${2^n}$, where n is the total number of chiral centres. Since, glucose has four chiral centres, n=4 and we get,
${2^4} = 16{\text{ }}$ optical isomers.
Hence, option (C) is correct.
Note: The 16 optical isomers of glucose are allose, altrose, galactose, glucose, gulose, idose, mannose, and tallose. The various conformations of glucopyranose rings are not considered since they are anomers rather than optical isomers.
Complete step by step solution:
Molecular formula of glucose is ${C_6}{H_{12}}{O_6}$. Structure of glucose is:

As you can see in the above structure of glucose there are six carbon atoms, hence it is an aldohexose. We usually consider glucose as D-glucose (dextrose). The D-isomer of glucose is the one whose carbon 2 is in the R configuration or has OH in the right-hand side. The mirror image of dextrose is L-glucose, having S configuration of carbon 2. Glucose contains one aldehydic carbon and five alcoholic carbons. It contains four chiral centres. A chiral centre is the one that has four different groups bonded to it in such a manner that it has a non-superimposable mirror image. Thus, in glucose, carbon 2, 3, 4 and 5 are chiral centres and carbon 1 and 6 are achiral. Now, the formula to obtain the maximum number of possible optical isomers is ${2^n}$, where n is the total number of chiral centres. Since, glucose has four chiral centres, n=4 and we get,
${2^4} = 16{\text{ }}$ optical isomers.
Hence, option (C) is correct.
Note: The 16 optical isomers of glucose are allose, altrose, galactose, glucose, gulose, idose, mannose, and tallose. The various conformations of glucopyranose rings are not considered since they are anomers rather than optical isomers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




