
Glucose on oxidation with bromine water yields gluconic acid. This reaction confirms the presence of:
A. Six carbon atoms linked in straight chain
B. Secondary alcoholic groups in glucose
C. Aldehyde groups in glucose
D. Primary alcoholic groups in glucose.
Answer
525.8k+ views
Hint: Think about which kind of carbohydrate glucose is. Draw the structure of glucose and gluconic acid and write the reaction taking place. We know bromine water is a mild oxidizing agent so use this idea and then compare reactant and product and note the difference between the two structures.
Complete step by step answer:
Glucose is a simple sugar and a monosaccharide. It has the chemical formula, \[{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{O}_{6}}\].
The structure of glucose is represented below.
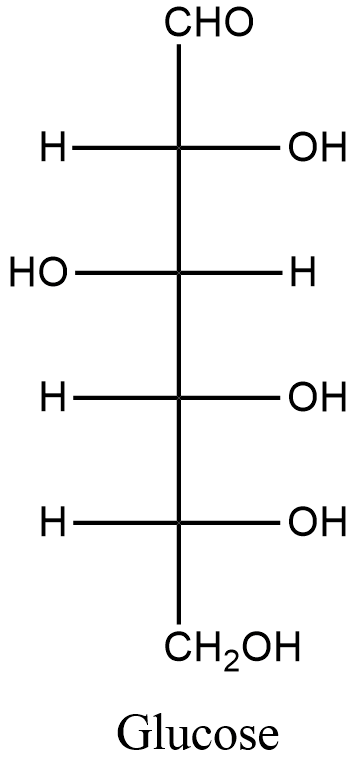
Now, we will know about gluconic acid. Gluconic acid is with molecular formula \[{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{O}_{7}}\]. We find gluconic acid occurs naturally in fruit, honey, and wine. The structure is represented below:
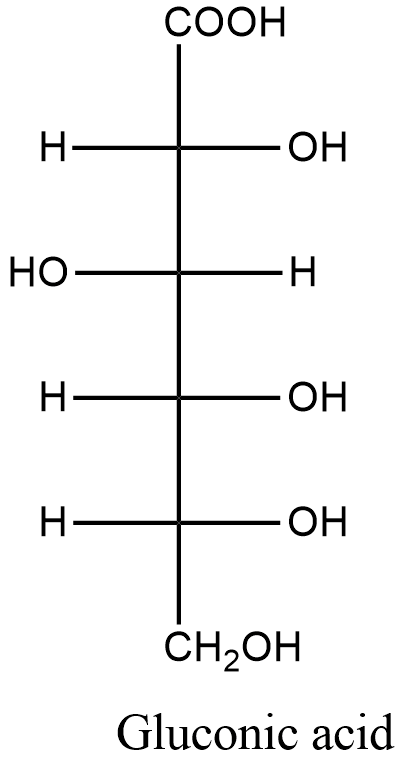
Let’s take a look at the question. Glucose undergoes an oxidation reaction to give gluconic acid in the presence of bromine water solution. Bromine water is a mild oxidizing agent which selectively oxidizes aldehyde to carboxylic acid only. It doesn’t oxidize alcohol or ketone.
The reaction of glucose with bromine water to form gluconic acid is shown below.
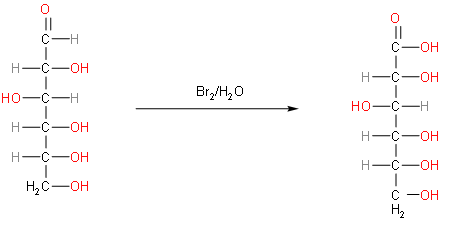
So, by observing the reaction we can say that glucose is converted to gluconic acid. From the given option we can say that, option C is correct because glucose has an aldehyde group present. We can confirm this option by observing the structure of glucose. An aldehyde group is present on C-1 carbon which is converted to acid.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Bromine water test is one of the tests used to distinguish between glucose and fructose because only glucose gets oxidized in the presence of bromine water and fructose remains as it is. Unsaturated compounds also react with bromine water and undergo addition reactions and the colour of bromine water is decolourized. Saturated compounds don’t react with bromine water and the colour of bromine water remains the same. For example, ethene reacts with bromine water to give 1,2-dibromoethane. Aniline or phenylamine reacts with bromine water to give a white precipitate is formed along with decolourisation of bromine water.
Complete step by step answer:
Glucose is a simple sugar and a monosaccharide. It has the chemical formula, \[{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{O}_{6}}\].
The structure of glucose is represented below.

Now, we will know about gluconic acid. Gluconic acid is with molecular formula \[{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{O}_{7}}\]. We find gluconic acid occurs naturally in fruit, honey, and wine. The structure is represented below:

Let’s take a look at the question. Glucose undergoes an oxidation reaction to give gluconic acid in the presence of bromine water solution. Bromine water is a mild oxidizing agent which selectively oxidizes aldehyde to carboxylic acid only. It doesn’t oxidize alcohol or ketone.
The reaction of glucose with bromine water to form gluconic acid is shown below.

So, by observing the reaction we can say that glucose is converted to gluconic acid. From the given option we can say that, option C is correct because glucose has an aldehyde group present. We can confirm this option by observing the structure of glucose. An aldehyde group is present on C-1 carbon which is converted to acid.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Bromine water test is one of the tests used to distinguish between glucose and fructose because only glucose gets oxidized in the presence of bromine water and fructose remains as it is. Unsaturated compounds also react with bromine water and undergo addition reactions and the colour of bromine water is decolourized. Saturated compounds don’t react with bromine water and the colour of bromine water remains the same. For example, ethene reacts with bromine water to give 1,2-dibromoethane. Aniline or phenylamine reacts with bromine water to give a white precipitate is formed along with decolourisation of bromine water.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




