
When glucose reacts with bromine water, the main product is:
A.An acetic acid
B.saccharin acid
C.glyceraldehyde
D.gluconic acid
Answer
581.7k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, we must understand two important things: the class of compounds to which aldotriose belongs to, and the required specifications for forming an aldotriose. The empirical formula of carbohydrate comes from the fact that a carbohydrate is a biomolecule consists of carbon(C), hydrogen(H), and oxygen(O) atoms, with a hydrogen-oxygen atom ratio of \[2:1\] and the ratio of carbon to hydrogen to oxygen is \[1:2:1\] . So we can refer to it as carbon water or hydrates of carbon and represent it as \[{(C{H_2}O)_n}\] , where n can be any number greater than 3.
Complete step by step answer:
Aldotriose can be defined as monosaccharides which contain 3 carbon atoms. Now you may be wondering what a monosaccharide is? To answer this question, we can say that a monosaccharide is a polyhydroxy aldehyde or a polyhydroxy ketone, which contains three or more carbon atoms. The commonly assigned term ‘monosaccharide’ represents a single unit, sans the glycosidic connections to other such units. These include a wide variety of compounds like ketoses, diketoses, aldohexoses, aldoses, dial doses, and deoxy sugars.
we must first understand the molecular structures of glucose shown below.
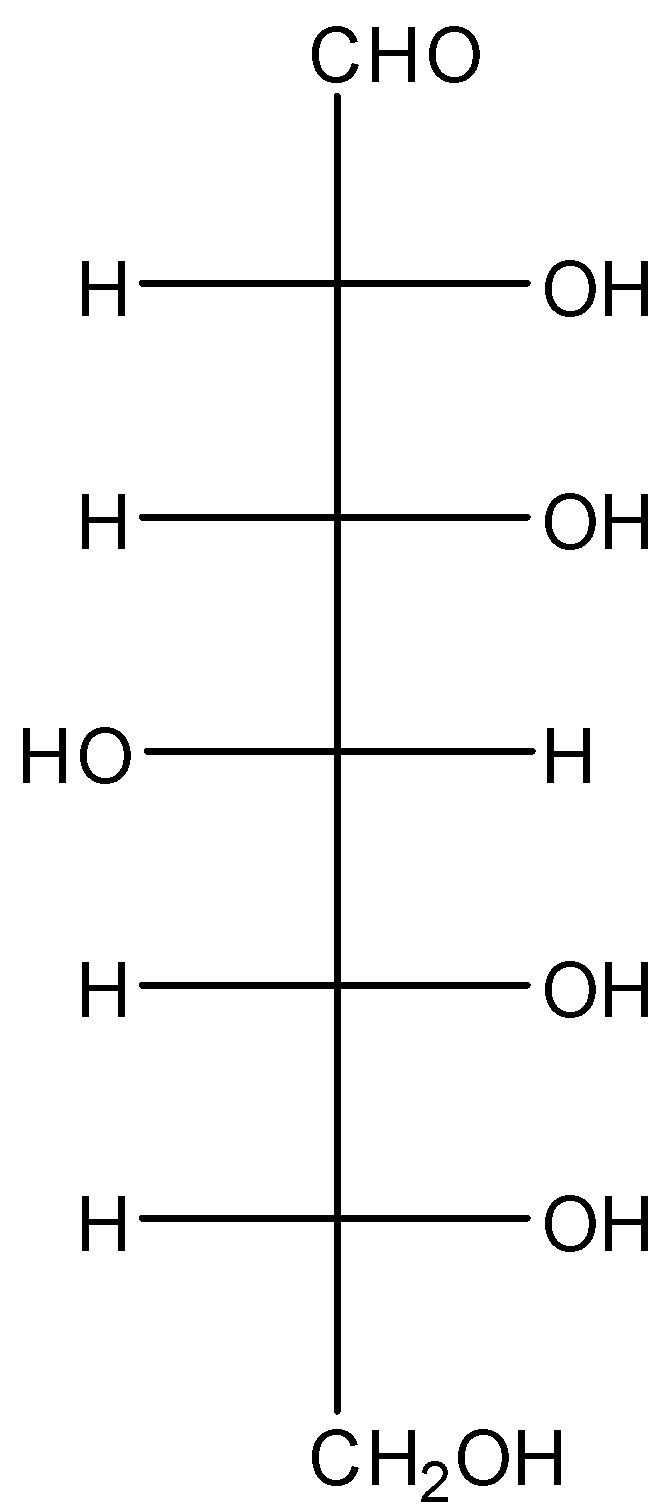
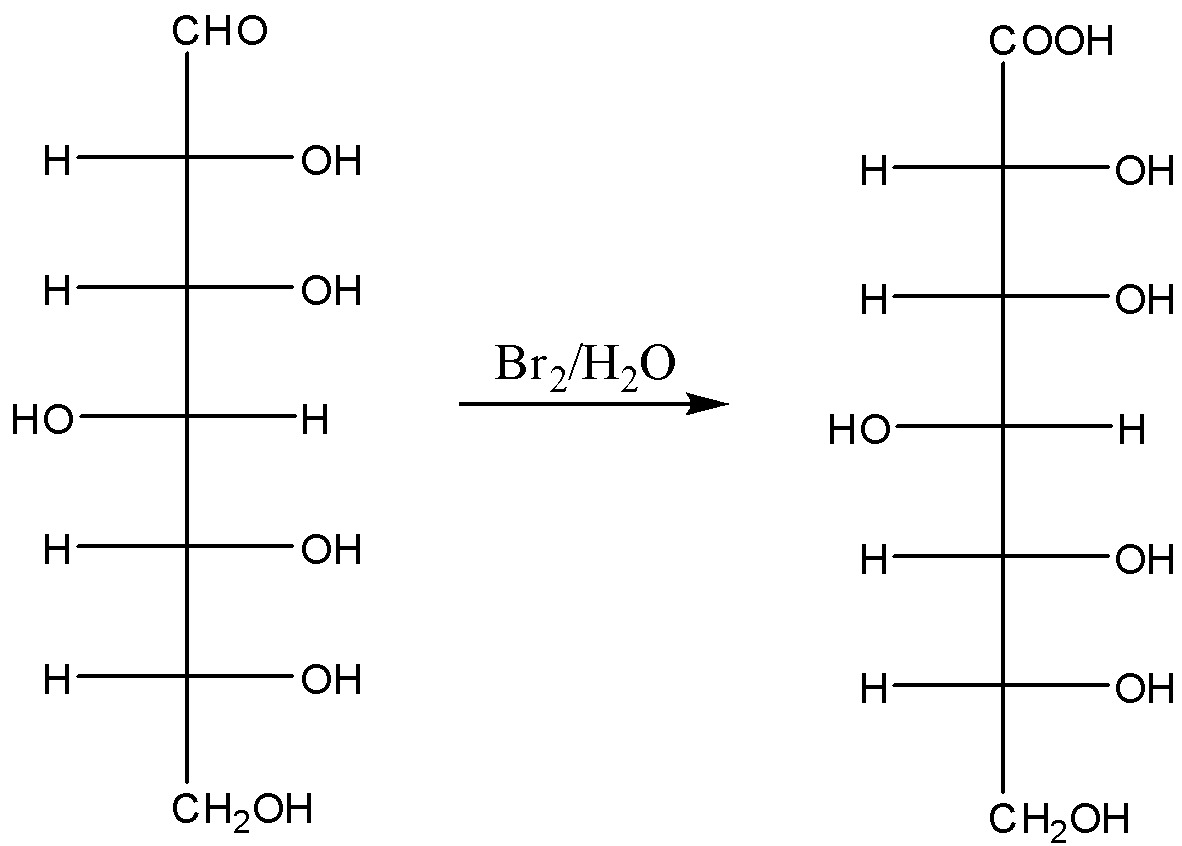
Now in presence of bromine water oxidation of glucose takes place. In this case oxidation of the aldehyde group takes place. As a result, it will convert into a carboxylic acid. The compound is known as gluconic acid, the reaction is shown below,
So, the correct answer is, D.
Additional information:
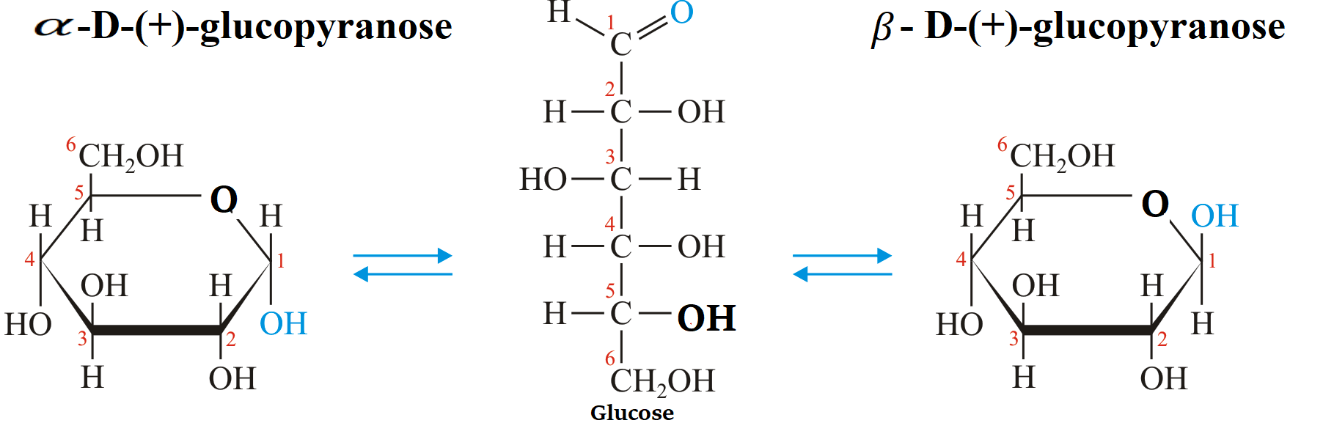
Sugars in chemistry are described by using Haworth’s formula. The pyran and furan heterocyclic rings are resembled by pyranose and furanose oxide rings, having one of the positions occupied by oxide.
Pyranose is used to depict saccharides that are six-membered rings which have five carbon atoms and one oxygen atom in it. There can be other external carbons in the ring as substitutes.
To draw the structures of \[\alpha - D - ( + ) - \] glucopyranose and \[\beta - D - ( + ) - \] glucopyranose, a simple six-membered pyranose ring having five carbon atoms and one oxygen atom is drawn first. These structures were first suggested by Haworth and we call them Haworth projection formulae.
In the pyranose ring, \[C{H_2}OH\] the group is added at the terminal, placed above the plane of the hexagon ring always. Groups that are present on the left-hand side in Fischer projection are placed above the plane of the ring and placed all the groups of the right hand below the plane of the ring.
Note:Glucose is one of the most important carbohydrates having a structural formula Therefore, the general formula can also be written as \[{C_n}{({H_2}O)_n}\] . This formula explains the meaning of the term ‘carbohydrate’ i.e. the components are carbon for carbo and water for hydrate. The simplest carbohydrate thus formed by putting n as 1 is glucose, \[{C_6}{H_{12}}{O_6}\] .
Complete step by step answer:
Aldotriose can be defined as monosaccharides which contain 3 carbon atoms. Now you may be wondering what a monosaccharide is? To answer this question, we can say that a monosaccharide is a polyhydroxy aldehyde or a polyhydroxy ketone, which contains three or more carbon atoms. The commonly assigned term ‘monosaccharide’ represents a single unit, sans the glycosidic connections to other such units. These include a wide variety of compounds like ketoses, diketoses, aldohexoses, aldoses, dial doses, and deoxy sugars.
we must first understand the molecular structures of glucose shown below.

Now in presence of bromine water oxidation of glucose takes place. In this case oxidation of the aldehyde group takes place. As a result, it will convert into a carboxylic acid. The compound is known as gluconic acid, the reaction is shown below,

So, the correct answer is, D.
Additional information:
Sugars in chemistry are described by using Haworth’s formula. The pyran and furan heterocyclic rings are resembled by pyranose and furanose oxide rings, having one of the positions occupied by oxide.
Pyranose is used to depict saccharides that are six-membered rings which have five carbon atoms and one oxygen atom in it. There can be other external carbons in the ring as substitutes.
To draw the structures of \[\alpha - D - ( + ) - \] glucopyranose and \[\beta - D - ( + ) - \] glucopyranose, a simple six-membered pyranose ring having five carbon atoms and one oxygen atom is drawn first. These structures were first suggested by Haworth and we call them Haworth projection formulae.
In the pyranose ring, \[C{H_2}OH\] the group is added at the terminal, placed above the plane of the hexagon ring always. Groups that are present on the left-hand side in Fischer projection are placed above the plane of the ring and placed all the groups of the right hand below the plane of the ring.

Note:Glucose is one of the most important carbohydrates having a structural formula Therefore, the general formula can also be written as \[{C_n}{({H_2}O)_n}\] . This formula explains the meaning of the term ‘carbohydrate’ i.e. the components are carbon for carbo and water for hydrate. The simplest carbohydrate thus formed by putting n as 1 is glucose, \[{C_6}{H_{12}}{O_6}\] .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




