
How is glucose related with fructose?
(A)Functional group isomerism
(B)Rotamers
(C)Position isomerism
(D)Geometrical isomerism
Answer
594.9k+ views
Hint: Both glucose and fructose have the same molecular formula but glucose is an aldohexose also known as dextrose and has 5 hydroxyl groups attached to it and an aldehydic group, while fructose is a ketohexose sugar having 5 hydroxy groups and a ketone group at second carbon position.
Complete step by step answer:
-First let us all see both glucose and fructose individually.
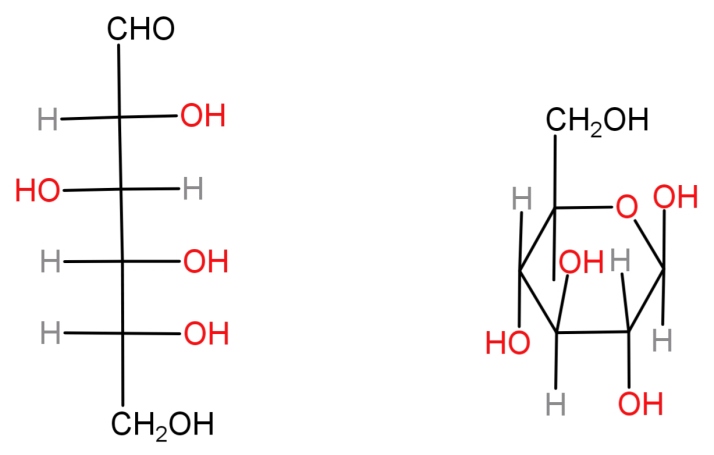
-Glucose: It is an aldohexose sugar also known as dextrose. It is a monosaccharide and forms the monomer of many large carbohydrates including cellulose and starch.
It’s molecular formula is: ${C_6}{H_{12}}{O_6}$ . In its open chain structure 5 carbons are attached to hydroxyl groups (-OH) while terminal carbon forms an aldehyde. But usually glucose is found as a six membered cyclic structure called pyranose structure (α and β forms). Both these structures are shown below:
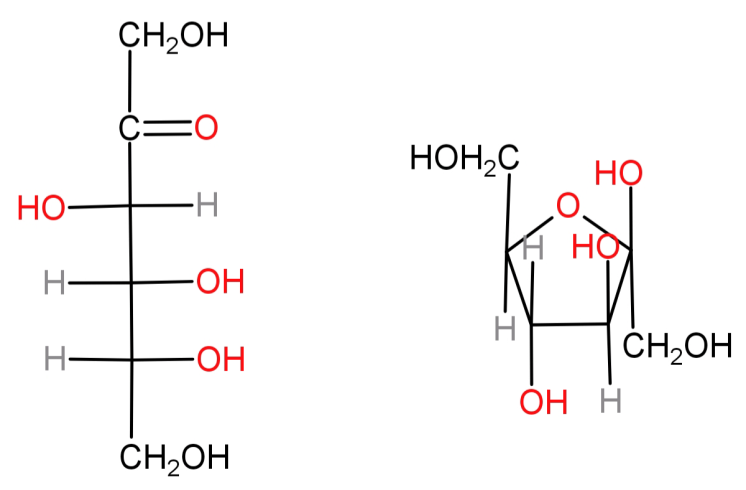
-Fructose: It is a ketohexose sugar. Even it is a monosaccharide and is usually found as a monomer attached to glucose forming sucrose. It is a natural monosaccharide usually found in honey, fruits and vegetables.
It’s molecular formula is: ${C_6}{H_{12}}{O_6}$ . In its open chain structure the carbon at position 2 has a ketone functional group and the rest are attached to a hydroxyl group (-OH). It is also usually found in its 5 membered cyclic form known as furanose (α and β forms). Both these structures are shown below:
-Above we saw that both glucose and fructose have the same molecular formula but different functional groups (glucose has aldehyde while fructose has ketone). Hence both of them will be functional group isomers.
-They cannot be rotamers because rotamers are any set of conformers that arise from restricted rotation around a single bond. This is not the case here.
-They cannot be position isomers because positional isomerism requires both of them to have the same functional group.
-In geometrical isomerism the compounds have the same number and types of bonds between those atoms, but differ only in the geometries for those atoms. Glucose and fructose do not have the same type of bonds (due to presence of different functional groups) and hence they cannot be geometrical isomers.
So, the correct option is: (A) functional group isomerism.
Note: Just by seeing the same molecular formulas do not think glucose and fructose to be positional isomerism because for this they need to have the same functional group as well. Since their functional groups are different they cannot be position isomers.
Complete step by step answer:
-First let us all see both glucose and fructose individually.
-Glucose: It is an aldohexose sugar also known as dextrose. It is a monosaccharide and forms the monomer of many large carbohydrates including cellulose and starch.
It’s molecular formula is: ${C_6}{H_{12}}{O_6}$ . In its open chain structure 5 carbons are attached to hydroxyl groups (-OH) while terminal carbon forms an aldehyde. But usually glucose is found as a six membered cyclic structure called pyranose structure (α and β forms). Both these structures are shown below:

-Fructose: It is a ketohexose sugar. Even it is a monosaccharide and is usually found as a monomer attached to glucose forming sucrose. It is a natural monosaccharide usually found in honey, fruits and vegetables.
It’s molecular formula is: ${C_6}{H_{12}}{O_6}$ . In its open chain structure the carbon at position 2 has a ketone functional group and the rest are attached to a hydroxyl group (-OH). It is also usually found in its 5 membered cyclic form known as furanose (α and β forms). Both these structures are shown below:

-Above we saw that both glucose and fructose have the same molecular formula but different functional groups (glucose has aldehyde while fructose has ketone). Hence both of them will be functional group isomers.
-They cannot be rotamers because rotamers are any set of conformers that arise from restricted rotation around a single bond. This is not the case here.
-They cannot be position isomers because positional isomerism requires both of them to have the same functional group.
-In geometrical isomerism the compounds have the same number and types of bonds between those atoms, but differ only in the geometries for those atoms. Glucose and fructose do not have the same type of bonds (due to presence of different functional groups) and hence they cannot be geometrical isomers.
So, the correct option is: (A) functional group isomerism.
Note: Just by seeing the same molecular formulas do not think glucose and fructose to be positional isomerism because for this they need to have the same functional group as well. Since their functional groups are different they cannot be position isomers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




