
Glycosidic bond exists in DNA molecule between
(A) Sugar and phosphate
(B) Any two nitrogen bases
(C) Sugar and a nitrogen base
(DPurines and pyrimidines
Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint: Glycosidic bond exists in DNA molecules to form a nucleoside. A nucleoside is made up of two molecules only. One molecule is of 5 carbon and another molecule helps in the bonding of nucleic acid together.
Complete step by step answer:
A glycosidic bond exists in the DNA molecule between sugar and nitrogen base. The glycosidic bond is formed by the nitrogen-carbon linkage between the 9' nitrogen of purine bases or 1' nitrogen of pyrimidine bases and the 1' carbon of the sugar group.
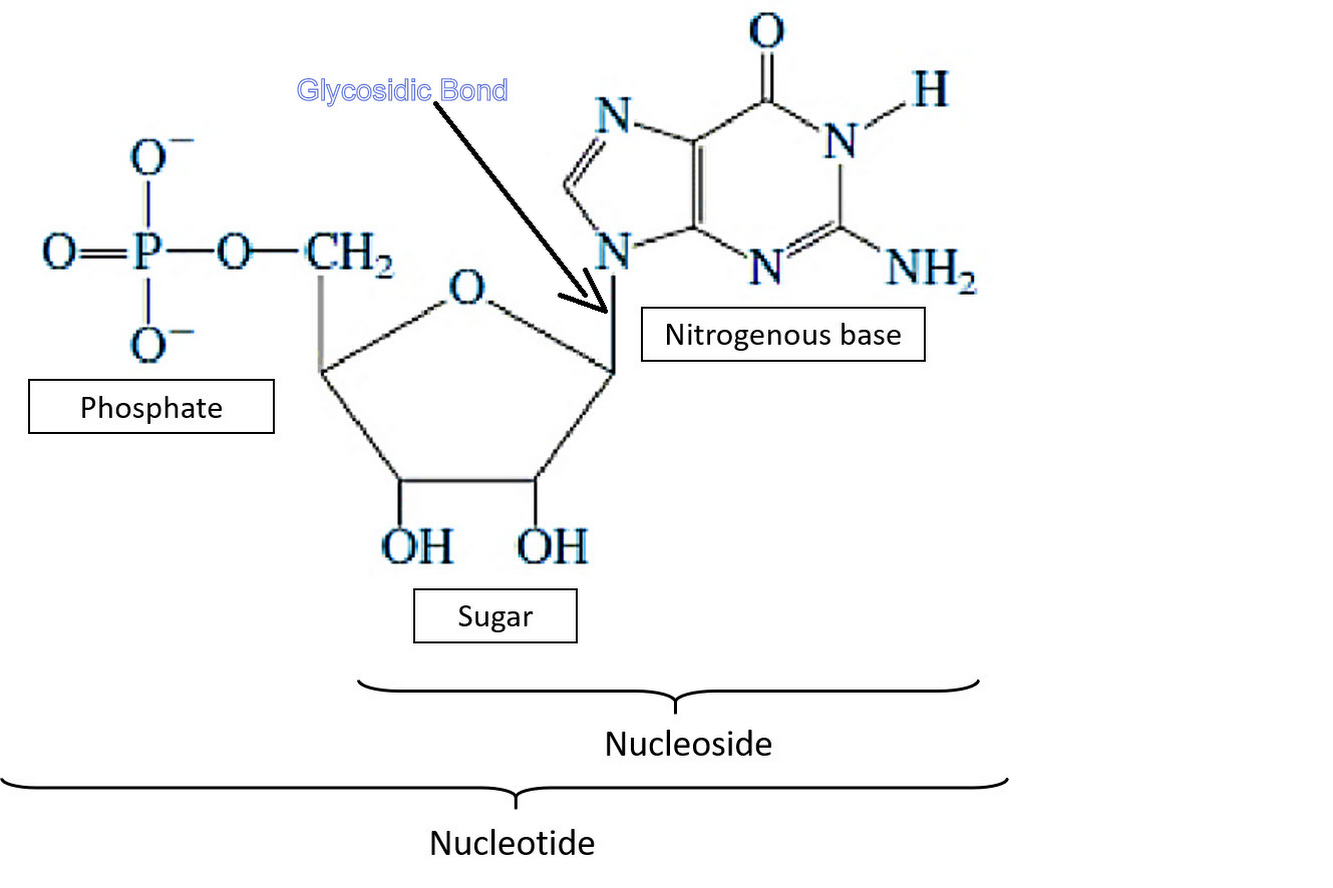
Sugar present in DNA is deoxyribose. DNA is a nucleic acid which is made up of nucleotides. Nucleotides are the monomers that are made up of three components i.e a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. On the other side, a nucleoside is a molecule or polymer consisting of only sugar and a nitrogenous base. These sugar molecules, nitrogenous bases, and phosphate groups have to be joined together with the help of bonding. The bond present between sugar and nitrogen base is the glycosidic bond which is also known as N-glycosidic linkage.
The bond which joins or connects the phosphate group with the sugar molecule is known as a phosphodiester bond.
So, the correct answer is ‘(C) Sugar and nitrogen base’.
Note: Four nitrogenous bases present in DNA are adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine These nitrogenous bases of an opposite strand of DNA binds with the help of hydrogen bonding. Purine always binds with a pyrimidine. Adenine and Guanine are purine and Thymine and Cytosine are pyrimidine.
Adenine always forms a hydrogen bond with thymine and guanine makes hydrogen bonds with cytosine. Adenine form two hydrogen bonds with thymine and guanine forms three hydrogen bonds with cytosine.
Complete step by step answer:
A glycosidic bond exists in the DNA molecule between sugar and nitrogen base. The glycosidic bond is formed by the nitrogen-carbon linkage between the 9' nitrogen of purine bases or 1' nitrogen of pyrimidine bases and the 1' carbon of the sugar group.

Sugar present in DNA is deoxyribose. DNA is a nucleic acid which is made up of nucleotides. Nucleotides are the monomers that are made up of three components i.e a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. On the other side, a nucleoside is a molecule or polymer consisting of only sugar and a nitrogenous base. These sugar molecules, nitrogenous bases, and phosphate groups have to be joined together with the help of bonding. The bond present between sugar and nitrogen base is the glycosidic bond which is also known as N-glycosidic linkage.
The bond which joins or connects the phosphate group with the sugar molecule is known as a phosphodiester bond.
So, the correct answer is ‘(C) Sugar and nitrogen base’.
Note: Four nitrogenous bases present in DNA are adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine These nitrogenous bases of an opposite strand of DNA binds with the help of hydrogen bonding. Purine always binds with a pyrimidine. Adenine and Guanine are purine and Thymine and Cytosine are pyrimidine.
Adenine always forms a hydrogen bond with thymine and guanine makes hydrogen bonds with cytosine. Adenine form two hydrogen bonds with thymine and guanine forms three hydrogen bonds with cytosine.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




