
Grignard reagent can’t be prepared from:
A.

B.
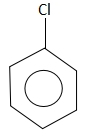
C.
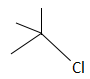
D.
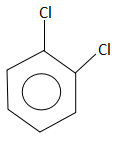




Answer
578.4k+ views
Hint: A Grignard reagent or Grignard compound is a chemical compound with the generic formula \[R - Mg - X\] , where \[X\] is a halogen and \[R\] is an organic group, normally an alkyl or aryl. Grignard compounds are popular reagents in organic synthesis for creating new carbon-carbon bonds.
Complete answer:
Grignard reagents are prepared by treating an organic halide (normally organobromine) with magnesium metal. Cyclic or acyclic ethers are required to stabilize the organomagnesium compound. Water and air, which rapidly destroy the reagent by protonolysis or oxidation, are excluded using air-free techniques. Although the reagents still need to be dry, ultrasound can allow Grignard reagents to form in wet solvents by activating the magnesium such that it consumes the water.
Grignard reagents serve as a base for protic substrates (this scheme does not show workup conditions, which typically includes water). Grignard reagents are basic and react with alcohols, phenols, etc. to give alkoxides (\[R - O - MgBr\] ).
The compound that does not take part in the formation of a Grignard reagent is:

This is so because it contains an alcoholic group which immediately reacts with the Grignard reagent. The alcoholic group is slightly acidic in nature and the hydrogen atom present on the alcohol group reacts with Grignard's reagent.
Thus, the correct option is A.
Note:
As is common for reactions involving solids and solution, the formation of Grignard reagents is often subject to an induction period. During this stage, the passivating oxide on the magnesium is removed. After this induction period, the reactions can be highly exothermic. This exothermicity must be considered when a reaction is scaled-up from laboratory to production plant. Most organohalides will work, but carbon-fluorine bonds are generally unreactive, except with specially activated magnesium.
Complete answer:
Grignard reagents are prepared by treating an organic halide (normally organobromine) with magnesium metal. Cyclic or acyclic ethers are required to stabilize the organomagnesium compound. Water and air, which rapidly destroy the reagent by protonolysis or oxidation, are excluded using air-free techniques. Although the reagents still need to be dry, ultrasound can allow Grignard reagents to form in wet solvents by activating the magnesium such that it consumes the water.
Grignard reagents serve as a base for protic substrates (this scheme does not show workup conditions, which typically includes water). Grignard reagents are basic and react with alcohols, phenols, etc. to give alkoxides (\[R - O - MgBr\] ).
The compound that does not take part in the formation of a Grignard reagent is:

This is so because it contains an alcoholic group which immediately reacts with the Grignard reagent. The alcoholic group is slightly acidic in nature and the hydrogen atom present on the alcohol group reacts with Grignard's reagent.
Thus, the correct option is A.
Note:
As is common for reactions involving solids and solution, the formation of Grignard reagents is often subject to an induction period. During this stage, the passivating oxide on the magnesium is removed. After this induction period, the reactions can be highly exothermic. This exothermicity must be considered when a reaction is scaled-up from laboratory to production plant. Most organohalides will work, but carbon-fluorine bonds are generally unreactive, except with specially activated magnesium.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




