
GUG specifies amino acid valine. However, when functioning as initiation codon it specifies _____________.
(A) Methionine
(B) Valine
(C) Lysine
(D) Isoleucine
Answer
545.1k+ views
Hint: Initiation codon codes for that amino acid which is found in meat, fish, and dairy products, and it plays an important role in many cell functions. It is even used in preventing liver damage in acetaminophen (Tylenol) poisoning.
Complete answer:
The initiation codon is known to be the first codon of the messenger RNA (mRNA) transcript which is translated with the help of a ribosome. The beginning codon always codes for methionine in eukaryotes and Archaea and an N-formylmethionine (fMet) in bacteria, mitochondria, and plastids. The foremost common start codon is AUG (i.e., ATG within the corresponding DNA sequence).
The start codon is usually preceded by a 5' untranslated region (5' UTR). In prokaryotes, this includes the ribosome binding site.
Redundancy within the genetic code means most amino acids are specified by more than one mRNA codon, for instance, the amino acid phenylalanine (Phe) is specified by the codons UUU and UUC, and therefore the amino acid leucine (Leu) is specified by the codons CUU, CUC, CUA, and CUG. Methionine is specified by the codon AUG, which is additionally referred to as the start codon. Consequently, methionine is known to be the first amino acid to dock within the ribosome during the synthesis of proteins. Tryptophan is exclusive because it's the sole amino acid specified by one codon. The remaining 19 amino acids are specified by between two and 6 codons each. The three codons i.e UAA, UAG, and UGA are the stop codons that signal the termination of translation.
So, the correct answer is ‘Methionine’.
Note:
The three-letter nature of codons means the four nucleotides found in mRNA — A, U, G, and C — can produce a complete of 64 different combinations. of those 64 codons, 61 represent amino acids, and therefore the remaining three represent stop signals, which trigger the top of protein synthesis. Because there are only 20 different types of amino acids but 64 possible codons, most amino acids are indicated by more than one codon.
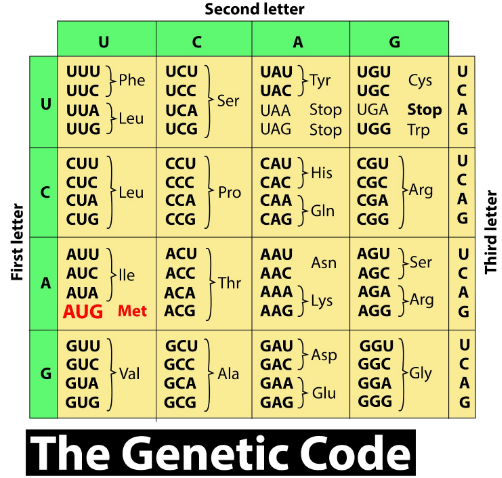
Complete answer:
The initiation codon is known to be the first codon of the messenger RNA (mRNA) transcript which is translated with the help of a ribosome. The beginning codon always codes for methionine in eukaryotes and Archaea and an N-formylmethionine (fMet) in bacteria, mitochondria, and plastids. The foremost common start codon is AUG (i.e., ATG within the corresponding DNA sequence).
The start codon is usually preceded by a 5' untranslated region (5' UTR). In prokaryotes, this includes the ribosome binding site.
Redundancy within the genetic code means most amino acids are specified by more than one mRNA codon, for instance, the amino acid phenylalanine (Phe) is specified by the codons UUU and UUC, and therefore the amino acid leucine (Leu) is specified by the codons CUU, CUC, CUA, and CUG. Methionine is specified by the codon AUG, which is additionally referred to as the start codon. Consequently, methionine is known to be the first amino acid to dock within the ribosome during the synthesis of proteins. Tryptophan is exclusive because it's the sole amino acid specified by one codon. The remaining 19 amino acids are specified by between two and 6 codons each. The three codons i.e UAA, UAG, and UGA are the stop codons that signal the termination of translation.
So, the correct answer is ‘Methionine’.
Note:
The three-letter nature of codons means the four nucleotides found in mRNA — A, U, G, and C — can produce a complete of 64 different combinations. of those 64 codons, 61 represent amino acids, and therefore the remaining three represent stop signals, which trigger the top of protein synthesis. Because there are only 20 different types of amino acids but 64 possible codons, most amino acids are indicated by more than one codon.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




