
What would happen if the external field E is increasing (a) Parallel to ‘p’ and (b) anti-parallel to ‘p’?
Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: In electrostatics, dipole moment is the quantity which is denoted by ‘p’. Electric dipole is a setup of two charges in which two charges of equal magnitude are placed at a very small distance from each other. One must know the true meaning of ‘pole’. Monopole means a system of single charge. Hence the monopole of a system is the net value of charge contained within a region. When considered the system of two charges separated by some distance, it’s called electric dipole.
Formula used: $\vec F=q\vec E$
Complete step by step answer:
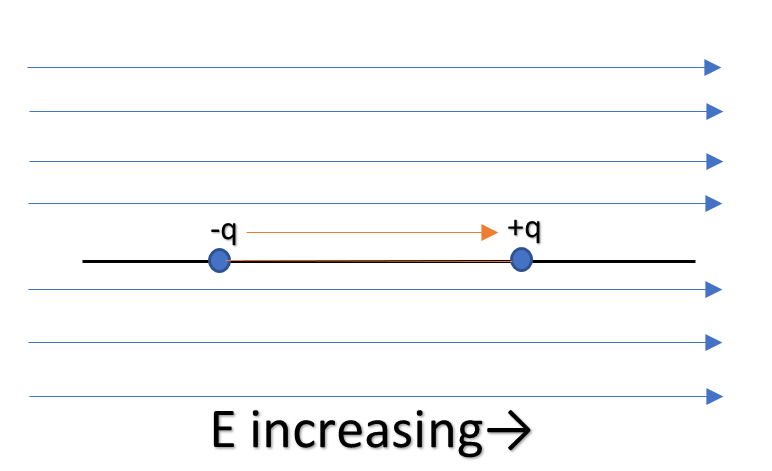
In the first case, the electric field is increasing parallel to ‘p’. Thus that means the electric field on the positive charge will be larger than that on negative charge. Hence positive charge will experience more force than negative charge. So the net force will be towards the positive charge which will cause the dipole to move in the direction of the electric field.
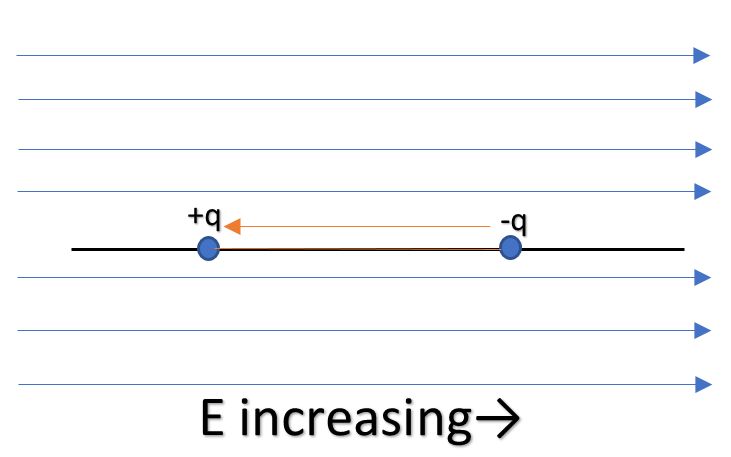
In the second case, the electric field is increasing anti-parallel to ‘p’. Thus that means the electric field on the negative charge will be larger than that on positive charge. Hence negative charge will experience more force than positive charge. So the net force will be towards the negative charge which will cause the dipole to move in the direction opposite to the direction of the electric field.
Note:
Students should not forget that the force on negative charge will be in a direction opposite to the direction of the electric field. Whereas for positive charge, it is the same as that of direction of field. Also the direction of ‘p’ i.e. dipole moment is always from negative to positive charge and along the line of joining.
Formula used: $\vec F=q\vec E$
Complete step by step answer:

In the first case, the electric field is increasing parallel to ‘p’. Thus that means the electric field on the positive charge will be larger than that on negative charge. Hence positive charge will experience more force than negative charge. So the net force will be towards the positive charge which will cause the dipole to move in the direction of the electric field.

In the second case, the electric field is increasing anti-parallel to ‘p’. Thus that means the electric field on the negative charge will be larger than that on positive charge. Hence negative charge will experience more force than positive charge. So the net force will be towards the negative charge which will cause the dipole to move in the direction opposite to the direction of the electric field.
Note:
Students should not forget that the force on negative charge will be in a direction opposite to the direction of the electric field. Whereas for positive charge, it is the same as that of direction of field. Also the direction of ‘p’ i.e. dipole moment is always from negative to positive charge and along the line of joining.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




