
What will happen if there are no valves in the heart?
Answer
580.8k+ views
Hint: The heart valves and the chambers are lined with endocardium. Heart valves separate the atria from the ventricles, or the ventricles from a blood vessel.
Complete Answer:
To answer this question, we have to know about the heart valves. A heart valve is a one-way valve that normally allows blood to run in only one way via the heart. The four valves are usually described in a mammalian heart that determines the pathway of blood flow through the heart. A heart valve opens or closes incumbent on differential blood pressure on each side.
The four valves in the mammalian heart are:
- The two atrioventricular (AV) valves are the mitral valve (bicuspid valve) and the tricuspid valve, which are between the upper chambers (atria) and the lower chambers (ventricles).
- The two semilunar (SL) valves are the aortic valve and the pulmonary valves that are in the arteries depart from the heart.
- The mitral valve and the aortic valve are in the left heart; the tricuspid valve and the pulmonary valve are in the right heart.
- The valves present in the heart allow the transfer of blood only in one way from atria to the ventricles from the ventricles to the pulmonary aorta. These valves inhibit any reverse flow. If there will be no valves, all the backflow will not be prevented and it will get disturbed.
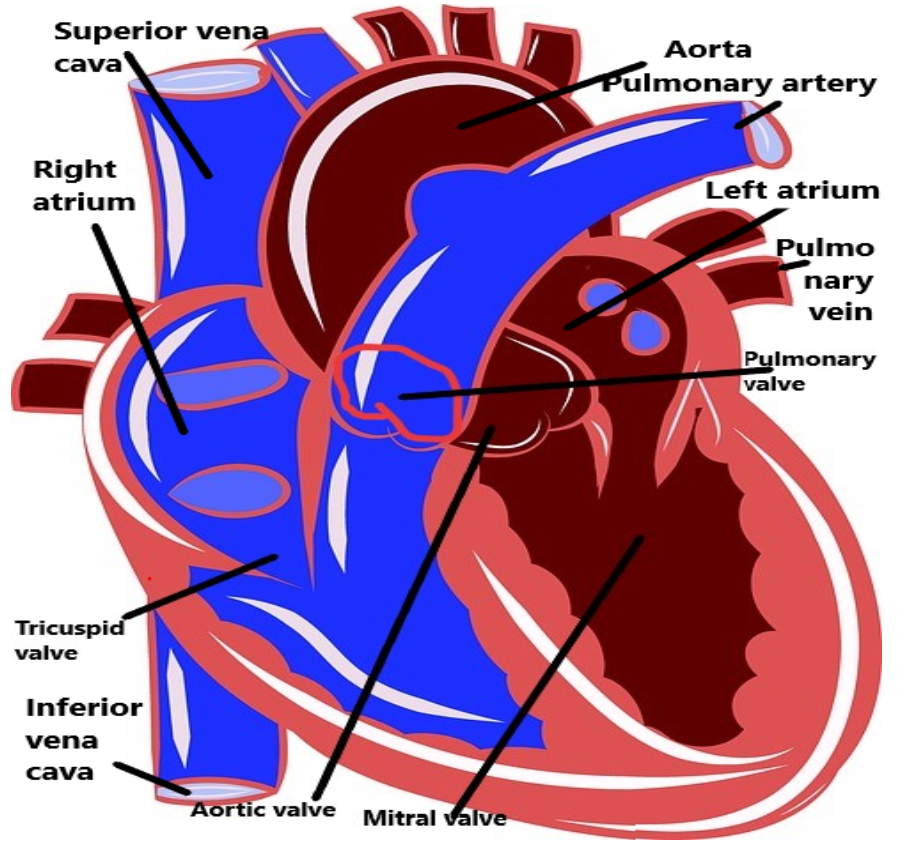
Fig- heart valves.
Note: Heart valves are situated around the fibrous rings of the cardiac skeleton. The valves include flaps known as leaflets or cusps, alike with a flutter valve or duckbill valve that are pressed open to permit blood run and which then block together to seal and stop reverse flow. The others have three but the mitral valve has two cusps. There are nodules present at the heads of the cusps which give tightness to the seal.
Complete Answer:
To answer this question, we have to know about the heart valves. A heart valve is a one-way valve that normally allows blood to run in only one way via the heart. The four valves are usually described in a mammalian heart that determines the pathway of blood flow through the heart. A heart valve opens or closes incumbent on differential blood pressure on each side.
The four valves in the mammalian heart are:
- The two atrioventricular (AV) valves are the mitral valve (bicuspid valve) and the tricuspid valve, which are between the upper chambers (atria) and the lower chambers (ventricles).
- The two semilunar (SL) valves are the aortic valve and the pulmonary valves that are in the arteries depart from the heart.
- The mitral valve and the aortic valve are in the left heart; the tricuspid valve and the pulmonary valve are in the right heart.
- The valves present in the heart allow the transfer of blood only in one way from atria to the ventricles from the ventricles to the pulmonary aorta. These valves inhibit any reverse flow. If there will be no valves, all the backflow will not be prevented and it will get disturbed.

Fig- heart valves.
Note: Heart valves are situated around the fibrous rings of the cardiac skeleton. The valves include flaps known as leaflets or cusps, alike with a flutter valve or duckbill valve that are pressed open to permit blood run and which then block together to seal and stop reverse flow. The others have three but the mitral valve has two cusps. There are nodules present at the heads of the cusps which give tightness to the seal.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




