
What happens in meiosis during oogenesis?
Answer
501.3k+ views
Hint: Oogenesis is defined as the process of formation of a mature female gamete by reductional division. It is different from the meiosis that occurs in spermatogenesis at one basic feature, i.e., in spermatogenesis all the 4 cells formed get transformed into gametes; but in oogenesis, there is formation of polar bodies.
Complete answer:
The meiosis in case of oogenesis is described as follows:
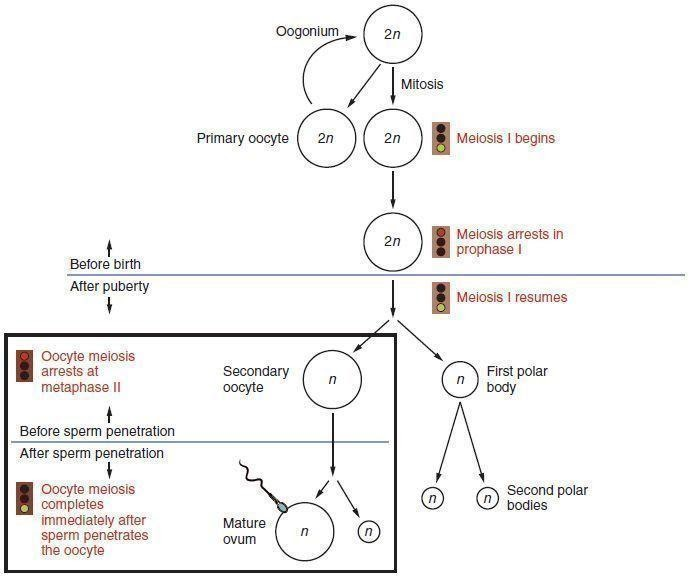
The oogonial cells undergo the first meiotic division to form the primary oocyte and the first polar body. This is actually a kind of cell division where unequal cytokinesis is observed. One cell gets a larger fraction of the cytoplasm and gets converted into a primary oocyte, and the other one gets converted into a polar body, which later degenerates.
This typical unequal cytokinesis occurs due to the fact that the ovum needs to retain much of the cytoplasm in order to have enough nutrients to nourish the ovum during the early stages of development.
The primary oocyte then undergoes the second meiotic division to release the secondary oocyte and another polar body (2nd polar body). The first polar body also undergoes meiosis-II to release another two small polar bodies.
All the polar bodies eventually degenerate. Thus, from oogenesis, a mature oogonium releases a mature egg or ovum and three polar bodies.
Note:
The point to be noted here is that oogenesis starts itself during birth but gets arrested during the diplotene phase of meiosis-I. Later during puberty, the cycle is again released and continues further. Thus, it is evident that no more oogonium formation occurs after birth.
In human beings from one primary oocyte, a single ovum and two polar bodies are formed. The ovum is released from the ovary in the secondary oocyte stage after the release of the 1st polar body.
Complete answer:
The meiosis in case of oogenesis is described as follows:

The oogonial cells undergo the first meiotic division to form the primary oocyte and the first polar body. This is actually a kind of cell division where unequal cytokinesis is observed. One cell gets a larger fraction of the cytoplasm and gets converted into a primary oocyte, and the other one gets converted into a polar body, which later degenerates.
This typical unequal cytokinesis occurs due to the fact that the ovum needs to retain much of the cytoplasm in order to have enough nutrients to nourish the ovum during the early stages of development.
The primary oocyte then undergoes the second meiotic division to release the secondary oocyte and another polar body (2nd polar body). The first polar body also undergoes meiosis-II to release another two small polar bodies.
All the polar bodies eventually degenerate. Thus, from oogenesis, a mature oogonium releases a mature egg or ovum and three polar bodies.
Note:
The point to be noted here is that oogenesis starts itself during birth but gets arrested during the diplotene phase of meiosis-I. Later during puberty, the cycle is again released and continues further. Thus, it is evident that no more oogonium formation occurs after birth.
In human beings from one primary oocyte, a single ovum and two polar bodies are formed. The ovum is released from the ovary in the secondary oocyte stage after the release of the 1st polar body.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




