
What happens when Benzene is treated with chlorine in the dark in the presence of anhydrous $ FeC{l_3} $ ?
Answer
502.2k+ views
Hint: When benzene is treated with chlorine in the presence of a Lewis acid, then instead of an addition reaction taking place, a substitution reaction will take place, in which one of the chlorine atoms is replaced by one hydrogen atom from the benzene ring. The reactions usually happen at room temperature.
Complete answer:
When benzene reacts with chlorine gas in the presence of iron catalysts such as iron (III) chloride, it displaces one hydrogen from the ring as a proton. This will attach with one of the chloride ions forming hydrogen chloride. The other part of the chlorine will attach to the benzene ring leading to the formation of chlorobenzene.
This is a very useful reaction in the preparation of haloarenes and it follows the following mechanism:
Formation of $ C{l^ + } $ ion by the help of $ FeC{l_3} $ is the first step. The chlorine gas will break into $ C{l^ + } $ and $ C{l^ - } $ . The $ C{l^ - } $ is coordinated with $ FeC{l_3} $ to form $ FeCl_4^ - $ .
The $ C{l^ + } $ ion will then replace the proton from benzene to form a destabilised structure which will stabilize with the loss of a proton.
The overall reaction can be written as:
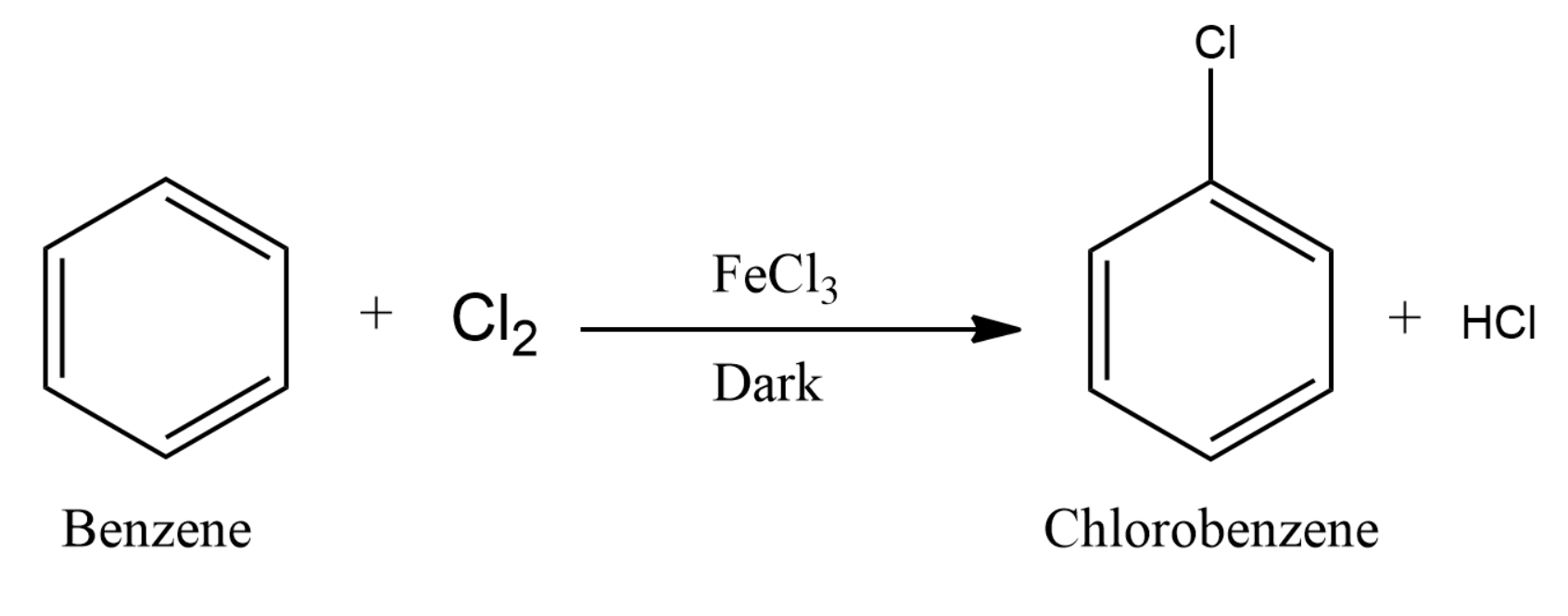
Note:
In the dark the above reaction will take place. But in the presence of sunlight but without any catalyst present, hot benzene will undergo an additional reaction with chlorine or bromine or any other reactive halogens. The ring delocalisation will be permanently broken and a chlorine or bromine atom adds on to each of the carbon atoms.
The product formed in that case will be:
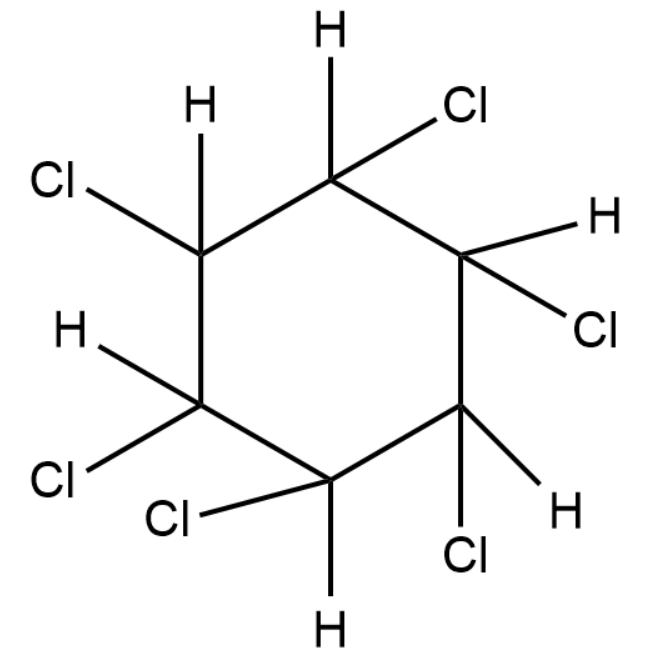
Complete answer:
When benzene reacts with chlorine gas in the presence of iron catalysts such as iron (III) chloride, it displaces one hydrogen from the ring as a proton. This will attach with one of the chloride ions forming hydrogen chloride. The other part of the chlorine will attach to the benzene ring leading to the formation of chlorobenzene.
This is a very useful reaction in the preparation of haloarenes and it follows the following mechanism:
Formation of $ C{l^ + } $ ion by the help of $ FeC{l_3} $ is the first step. The chlorine gas will break into $ C{l^ + } $ and $ C{l^ - } $ . The $ C{l^ - } $ is coordinated with $ FeC{l_3} $ to form $ FeCl_4^ - $ .
The $ C{l^ + } $ ion will then replace the proton from benzene to form a destabilised structure which will stabilize with the loss of a proton.
The overall reaction can be written as:

Note:
In the dark the above reaction will take place. But in the presence of sunlight but without any catalyst present, hot benzene will undergo an additional reaction with chlorine or bromine or any other reactive halogens. The ring delocalisation will be permanently broken and a chlorine or bromine atom adds on to each of the carbon atoms.
The product formed in that case will be:

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




