
What happens when diborane reacts with Lewis bases?
A.It forms boron trihydride $\left( {{\text{B}}{{\text{H}}_3}} \right)$ due to cleavage.
B.It undergoes cleavage to give borane adduct ${\text{B}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{L}}$ (where L = Lewis base).
C.It oxidised to give ${{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$
D.It does not react with Lewis bases.
Answer
585k+ views
Hint: The Lewis base is a species having filled an orbital and an electron lone pair. The lone pair is not involved in bonding but it forms a dative bond with a Lewis acid.
The structure of diborane consists of boron and hydrogen. It has two borane atoms and four hydrogen atoms. The formula for diborane is ${{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}$.
Complete step by step answer:
The reaction of diborane with Lewis base is as follows:
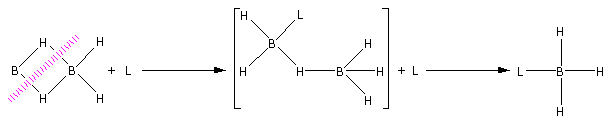
Diborane on reaction with Lewis base (L) undergoes cleavage to give borane adduct ${\text{B}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{L}}$.
Consider the reaction of diborane with ammonia,
${\text{3}}{{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}} + 6{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_3} \to 2{{\text{B}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{N}}_3}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}{\text{ + 12}}{{\text{H}}_2}$
Thus, ${{\text{B}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{N}}_3}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}$ is a borane adduct. ${{\text{B}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{N}}_3}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}$ is known as borazine. This reaction takes place at an elevated temperature ${180^ \circ } - {190^ \circ }{\text{C}}$.
So, the correct answer is Option B.
Additional Information:
The cleavage of diborane does not form boron trihydride.
Diborane on burning in air gives ${{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$. The reaction is as follows:${{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{6}}} + 3{{\text{O}}_2} \to {{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}} + 3{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}$.
Common properties of diborane are:
Diborane is colorless.
At room temperature, diborane is highly flammable. It is generally flammable in air.
It is a sweet smelling gas.
It hydrolyses in water and produces boric acid and hydrogen gas.
Note:
Examples of Lewis bases are:
1.Lone pair donors: ${\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{,}}\,{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O, O}}{{\text{H}}^ - },{\text{ CH}}_3^ - $.
2.Simple anions: ${{\text{H}}^ - },{\text{ }}{{\text{F}}^ - }$.
3.Complex anions: ${\text{SO}}_4^{2 - },{\text{ PO}}_4^{3 - }$.
$\pi $-systems rich in electron: ethyne, benzene.
The structure of diborane consists of boron and hydrogen. It has two borane atoms and four hydrogen atoms. The formula for diborane is ${{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}$.
Complete step by step answer:
The reaction of diborane with Lewis base is as follows:

Diborane on reaction with Lewis base (L) undergoes cleavage to give borane adduct ${\text{B}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{L}}$.
Consider the reaction of diborane with ammonia,
${\text{3}}{{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}} + 6{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_3} \to 2{{\text{B}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{N}}_3}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}{\text{ + 12}}{{\text{H}}_2}$
Thus, ${{\text{B}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{N}}_3}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}$ is a borane adduct. ${{\text{B}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{N}}_3}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}$ is known as borazine. This reaction takes place at an elevated temperature ${180^ \circ } - {190^ \circ }{\text{C}}$.
So, the correct answer is Option B.
Additional Information:
The cleavage of diborane does not form boron trihydride.
Diborane on burning in air gives ${{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$. The reaction is as follows:${{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{6}}} + 3{{\text{O}}_2} \to {{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}} + 3{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}$.
Common properties of diborane are:
Diborane is colorless.
At room temperature, diborane is highly flammable. It is generally flammable in air.
It is a sweet smelling gas.
It hydrolyses in water and produces boric acid and hydrogen gas.
Note:
Examples of Lewis bases are:
1.Lone pair donors: ${\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{,}}\,{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O, O}}{{\text{H}}^ - },{\text{ CH}}_3^ - $.
2.Simple anions: ${{\text{H}}^ - },{\text{ }}{{\text{F}}^ - }$.
3.Complex anions: ${\text{SO}}_4^{2 - },{\text{ PO}}_4^{3 - }$.
$\pi $-systems rich in electron: ethyne, benzene.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




