
Heat of formation of benzene, assuming no resonance . Given that
BE(C- C)= 83kcal
BE(C=C)= 140kcal
BE(C-H) = 99kcal
Heat of atomisation of C= 170.9 kcal
Heat of atomisation of H= 104.2 kcal
Answer
559.8k+ views
Hint: Benzene is the cyclic hydrocarbon which contains six carbon and hix atoms of hydrogen in it. According to the molecular orbital theory the structure of benzene has three delocalised pi orbitals which tends to span all the six carbon atoms. But if you see the valence bond theory then it states that the benzene has two stable structures by resonance. It belongs to the aromatic hydrocarbons which are non polar molecules
Complete step-by-step answer:
The benzene has been formed by six carbon and six hydrogen atoms.
\[6C+3{{H}_{2}}\to {{C}_{6}}{{H}_{6}}\]
The structure of benzene is the following:
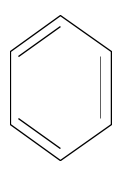
The benzene structure has three carbon carbon double bonds. The benzene structure has three carbon carbon single bonds. The benzene structure has six carbon hydrogen bonds.
So the \[\Delta H\]for the formation for products is the following:
\[\Delta H\]\[=3(C=C)+3(C-C)+6(C-H)\]\[=3(140)+3(83)+6(99)\]=1263kcal
S the for the formation of products is the following:
\[\Delta H\]=\[6(C)+3({{H}_{2}})=6(170.9)+3(104.2)=1338kcal\]
So now the \[\Delta H\]formation is :
\[\Delta {{H}_{(formation)}}=\Delta {{H}_{(reac\tan ts)}}-\Delta {{H}_{(products)}}\]
The \[\Delta {{H}_{(reac\tan ts)}}\]= 1338kcal and \[\Delta {{H}_{(products)}}\]=1263kcal
Now substituting the values in the formula we get,
\[\Delta {{H}_{(formation)}}=1338-1263=75kcal\]
So the heat of formation of the benzene is 75kcal.
Note: Benzene is a nonpolar substance which has the ability to be miscible with organic solvent and to get immiscible with water. A sooty flame is produced on the combustion of benzene. On sulphonation of benzene we get a benzene sulphuric acid. On nitration of benzene the product nitrobenzene is obtained.\[\Delta {{H}_{(formation)}}=1338-1263=75kcal\]
Complete step-by-step answer:
The benzene has been formed by six carbon and six hydrogen atoms.
\[6C+3{{H}_{2}}\to {{C}_{6}}{{H}_{6}}\]
The structure of benzene is the following:

The benzene structure has three carbon carbon double bonds. The benzene structure has three carbon carbon single bonds. The benzene structure has six carbon hydrogen bonds.
So the \[\Delta H\]for the formation for products is the following:
\[\Delta H\]\[=3(C=C)+3(C-C)+6(C-H)\]\[=3(140)+3(83)+6(99)\]=1263kcal
S the for the formation of products is the following:
\[\Delta H\]=\[6(C)+3({{H}_{2}})=6(170.9)+3(104.2)=1338kcal\]
So now the \[\Delta H\]formation is :
\[\Delta {{H}_{(formation)}}=\Delta {{H}_{(reac\tan ts)}}-\Delta {{H}_{(products)}}\]
The \[\Delta {{H}_{(reac\tan ts)}}\]= 1338kcal and \[\Delta {{H}_{(products)}}\]=1263kcal
Now substituting the values in the formula we get,
\[\Delta {{H}_{(formation)}}=1338-1263=75kcal\]
So the heat of formation of the benzene is 75kcal.
Note: Benzene is a nonpolar substance which has the ability to be miscible with organic solvent and to get immiscible with water. A sooty flame is produced on the combustion of benzene. On sulphonation of benzene we get a benzene sulphuric acid. On nitration of benzene the product nitrobenzene is obtained.\[\Delta {{H}_{(formation)}}=1338-1263=75kcal\]
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




