
Helium has________ configuration.
Answer
514.8k+ views
Hint :The noble gases are a group of chemical elements with similar properties; they are all odourless, colourless, monatomic gases of very low chemical reactivity under normal conditions. Helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radioactive radon are the six naturally occurring noble gases.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Helium is known as a noble gas because it does not mix with other chemicals to form new compounds on a daily basis. Its boiling point is the lowest of all the elements. It is the universe's second most common element, after hydrogen, and has no colour or odour. When helium is exposed to an electric field, it emits a red-orange light. Helium normally doesn't react with anything else.
An atom's electron configuration is a description of how electrons are distributed among the orbital shells and subshells. The unique chemistry of the element is determined by the valence electrons, which are electrons in the outermost shell.
Helium has only two electrons, making it one of the most straightforward electron configurations to write. Around the nucleus of Helium, there are only two electrons.
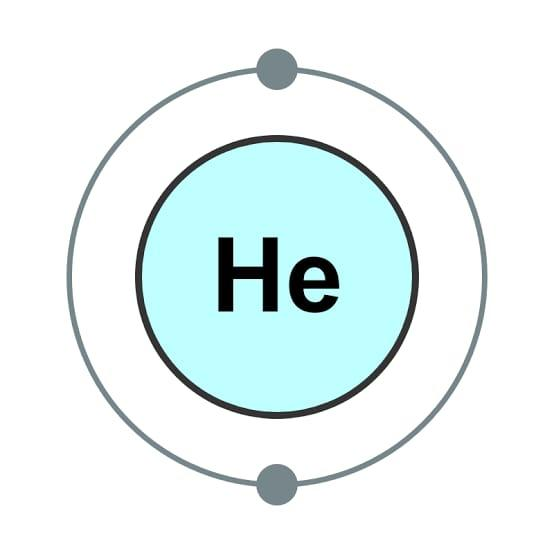
Helium has a configuration of $ 1{s^2} $ since it only has two electrons. Since the 1s orbital is already occupied by two electrons, any additional electrons will be redirected to a different energy level. Helium has a complete outer shell electron structure, which is why it is known as a Noble Gas. It will not react with other atoms because of this.
Note :
A question may arise about helium is that, Why is helium's melting point so low? As a result, the noble gas atoms have no interaction, resulting in a low boiling point. It's worth noting that intermolecular forces increase with atomic size, which is why helium has a lower boiling point than neon, which is followed by argon, and so on.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Helium is known as a noble gas because it does not mix with other chemicals to form new compounds on a daily basis. Its boiling point is the lowest of all the elements. It is the universe's second most common element, after hydrogen, and has no colour or odour. When helium is exposed to an electric field, it emits a red-orange light. Helium normally doesn't react with anything else.
An atom's electron configuration is a description of how electrons are distributed among the orbital shells and subshells. The unique chemistry of the element is determined by the valence electrons, which are electrons in the outermost shell.
Helium has only two electrons, making it one of the most straightforward electron configurations to write. Around the nucleus of Helium, there are only two electrons.

Helium has a configuration of $ 1{s^2} $ since it only has two electrons. Since the 1s orbital is already occupied by two electrons, any additional electrons will be redirected to a different energy level. Helium has a complete outer shell electron structure, which is why it is known as a Noble Gas. It will not react with other atoms because of this.
Note :
A question may arise about helium is that, Why is helium's melting point so low? As a result, the noble gas atoms have no interaction, resulting in a low boiling point. It's worth noting that intermolecular forces increase with atomic size, which is why helium has a lower boiling point than neon, which is followed by argon, and so on.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




