
Why do Helium, Neon and Argon have zero valency?
Answer
548.7k+ views
Hint: Valency of an element can be defined as the capacity of that atom/element to form bonds with other atoms in a compound. Valency is calculated with the help of Valence electrons of the element. These valence electrons are present in the outermost shell.
Complete step by step answer:
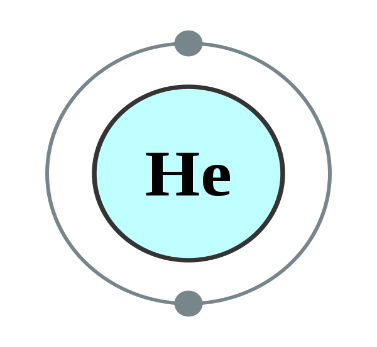
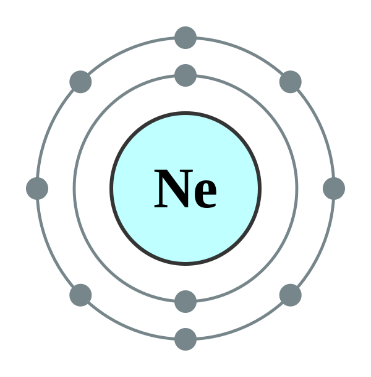
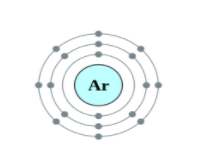
Helium, Neon and Argon are the elements that are present in the Group \[18\] of the modern periodic table. All the members of this family exist in gas form and are called noble gases. They show low chemical reactivity due to their stable electronic configuration, Hence, they are also known as inert gases. Due to this, they also do not form molecules so easily and mostly exist as monatomic gases. The valence shell of these elements is completely filled i.e. the duplet in case of helium and the octet in case of others. The general electronic configuration of these elements is given as $n{s^2}n{p^6}$. This configuration is also called as noble gas configuration. Hence, Due to their fully filled valence shell these gases shows the inert behavior. In the process of bond formation, they neither gain nor lose an electron as a result of this they do not participate in formation of new molecules. Therefore, the valency of group \[18\] is considered $0$. Hence, we can say that Helium, Neon and Argon have zero valency.
Note:
Inert gas configuration means that the octet of the element is complete i.e. there are $8$ electrons in the valence shell. In case of helium, it is a duplate i.e. $2$ electrons are present in the valence shell. The ionization enthalpies of these gases decreases down the group due to the increase in atomic size.
Complete step by step answer:
Helium, Neon and Argon are the elements that are present in the Group \[18\] of the modern periodic table. All the members of this family exist in gas form and are called noble gases. They show low chemical reactivity due to their stable electronic configuration, Hence, they are also known as inert gases. Due to this, they also do not form molecules so easily and mostly exist as monatomic gases. The valence shell of these elements is completely filled i.e. the duplet in case of helium and the octet in case of others. The general electronic configuration of these elements is given as $n{s^2}n{p^6}$. This configuration is also called as noble gas configuration. Hence, Due to their fully filled valence shell these gases shows the inert behavior. In the process of bond formation, they neither gain nor lose an electron as a result of this they do not participate in formation of new molecules. Therefore, the valency of group \[18\] is considered $0$. Hence, we can say that Helium, Neon and Argon have zero valency.



Note:
Inert gas configuration means that the octet of the element is complete i.e. there are $8$ electrons in the valence shell. In case of helium, it is a duplate i.e. $2$ electrons are present in the valence shell. The ionization enthalpies of these gases decreases down the group due to the increase in atomic size.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




