
Here is the diagram of Prothallus. Identify A, B, and C.
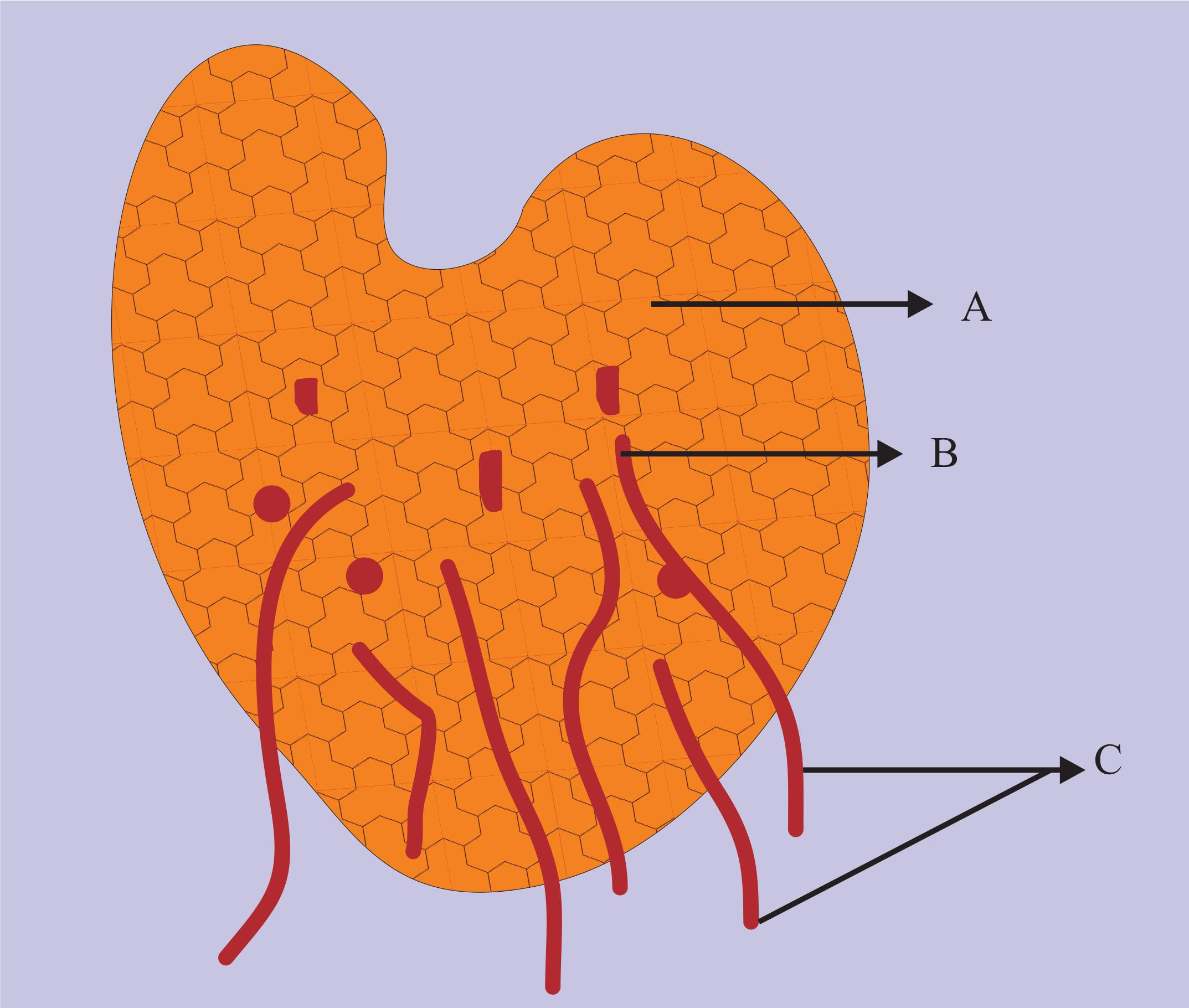
(A)A- archegonia, B- antheridia, C- rhizoids
(B)A-antheridia, B- archegonia, C- rhizoids
(C)A-antheridia, B- archegonia, C- roots
(D)A-antheridia, B- archegonia, C- roots

Answer
567.3k+ views
Hint: It is usually the gametophyte stage in the life of a fern or other pteridophyte. Occasionally the term is additionally wont to describe the young gametophyte of a liverwort or sphagnum also. Appearance varies quite a lot between species. Some are green and lead photosynthesis while others are colorless and support themselves underground as saprotrophs.
Complete answer:
Prothallus may be a free-living gametophyte of pteridophytes that roll in the hay organs. A young sporophytic plant body is developed by prothallus from inside the feminine reproductive organ.
A represents archegonia. It is a female sex organ. These are flask-shaped structures that are partially embedded within the prothallus. Four rows of cells are available in the rounded neck of archegonium.
B represents antheridia. It is a male sex organ. These are small hemispherical structures. They have a three-celled coat which encases 32-48 sperm mother cells.
C represents rhizoids. These are root-like structures.
Additional information
The prothallus develops from a germinating spore. It is a fleeting and subtle heart-molded structure regularly 2–5 millimeters wide, with an assortment of rhizoids (root-like hairs) developing underneath, and consequently the sex organs: archegonium (female) and antheridium (male). Appearance fluctuates a considerable amount between species. Some are green and direct photosynthesis while others are colorless and support themselves underground as saprotrophs.
Spore-bearing plants, similar to all plants, experience a day to day existence pattern of the shift of ages. The completely developed sporophyte, which is generally alluded to as the greenery, delivers genetically interesting spores in the sori by meiosis. The haploid spores from the sporophyte and grow by mitosis, given the best possible conditions, into the gametophyte stage, the prothallus.
So the correct answer is ‘ A- archegonia, B- antheridia, C- rhizoids’.
Note: The prothallus develops independently for several weeks; it grows sex organs that produce ova (archegonia) and flagellated sperm (antheridia). The sperm can swim to the ova for fertilization to frame a diploid zygote which isolates by mitosis to shape a multicellular sporophyte. In the early stages of growth, the sporophyte grows out of the prothallus, counting on it for the water system and nutrition, but develops into a replacement independent fern, which will create new spores which will develop into new prothallia, and so on, hence finishing the existing pattern of the creature.
Complete answer:
Prothallus may be a free-living gametophyte of pteridophytes that roll in the hay organs. A young sporophytic plant body is developed by prothallus from inside the feminine reproductive organ.
A represents archegonia. It is a female sex organ. These are flask-shaped structures that are partially embedded within the prothallus. Four rows of cells are available in the rounded neck of archegonium.
B represents antheridia. It is a male sex organ. These are small hemispherical structures. They have a three-celled coat which encases 32-48 sperm mother cells.
C represents rhizoids. These are root-like structures.
Additional information
The prothallus develops from a germinating spore. It is a fleeting and subtle heart-molded structure regularly 2–5 millimeters wide, with an assortment of rhizoids (root-like hairs) developing underneath, and consequently the sex organs: archegonium (female) and antheridium (male). Appearance fluctuates a considerable amount between species. Some are green and direct photosynthesis while others are colorless and support themselves underground as saprotrophs.
Spore-bearing plants, similar to all plants, experience a day to day existence pattern of the shift of ages. The completely developed sporophyte, which is generally alluded to as the greenery, delivers genetically interesting spores in the sori by meiosis. The haploid spores from the sporophyte and grow by mitosis, given the best possible conditions, into the gametophyte stage, the prothallus.
So the correct answer is ‘ A- archegonia, B- antheridia, C- rhizoids’.
Note: The prothallus develops independently for several weeks; it grows sex organs that produce ova (archegonia) and flagellated sperm (antheridia). The sperm can swim to the ova for fertilization to frame a diploid zygote which isolates by mitosis to shape a multicellular sporophyte. In the early stages of growth, the sporophyte grows out of the prothallus, counting on it for the water system and nutrition, but develops into a replacement independent fern, which will create new spores which will develop into new prothallia, and so on, hence finishing the existing pattern of the creature.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




