
Histone octamer contains-
a. Eight types of histones
b. Eight histones of four different types
c. Five Histones
d. Six types of histones
Answer
588k+ views
Hint: A histone octamer is the protein intricate found at the center of a nucleosome core particle. Each histone consists of both an N-terminal tail and a C-terminal histone-fold. Both of these main components interact with DNA in their method through a chain of weak interactions, involving hydrogen bonds and salt bridges.
Complete answer:
A histone octamer is the eight protein complex present at the center of a nucleosome central particle. It is composed of two copies of each of the four core histone proteins (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4). The octamer joins when a tetramer, involving two copies of both H3 and H4, complexes with two H2A/H2B dimers.
In eukaryotes, DNA association is much more complex and is carried out by a set of positively charged basic proteins called histones. Histones are opulent in the basic amino acids that remain lysines and arginines with charged side chains.
There are five kinds of histone proteins i.e., H1, H2A, H2B, H3and H4. Four of them arise in pairs to yield histone octamer or nu-body. A histone octamer involves eight proteins of four diverse kinds i.e., two copies of each H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. The negatively charged DNA is covered around the positively charged histone octamer to form an assembly called a nucleosome.
Hence, the correct answer is option (B).
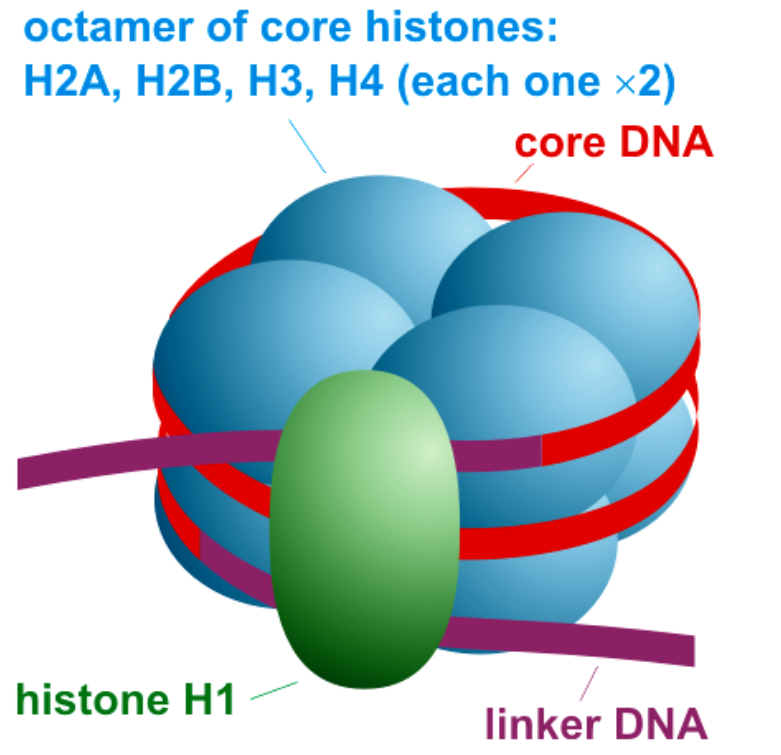
Note: The core histones are identified by the occurrence of a structurally conserved motif known as histone-fold domain and the active histone-fold extensions, named histone tails. They greatly regulate nucleosome stability and hence play a foremost role in defining the chromatin complex order structures. The histone fold is composed of three $\alpha $-helices (${\alpha _1}$, ${\alpha _2}$, and ${\alpha _3}$) linked by short loops L1 and L2. These loops facilitate heterodimeric interactions among the core histones.
Complete answer:
A histone octamer is the eight protein complex present at the center of a nucleosome central particle. It is composed of two copies of each of the four core histone proteins (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4). The octamer joins when a tetramer, involving two copies of both H3 and H4, complexes with two H2A/H2B dimers.
In eukaryotes, DNA association is much more complex and is carried out by a set of positively charged basic proteins called histones. Histones are opulent in the basic amino acids that remain lysines and arginines with charged side chains.
There are five kinds of histone proteins i.e., H1, H2A, H2B, H3and H4. Four of them arise in pairs to yield histone octamer or nu-body. A histone octamer involves eight proteins of four diverse kinds i.e., two copies of each H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. The negatively charged DNA is covered around the positively charged histone octamer to form an assembly called a nucleosome.
Hence, the correct answer is option (B).

Note: The core histones are identified by the occurrence of a structurally conserved motif known as histone-fold domain and the active histone-fold extensions, named histone tails. They greatly regulate nucleosome stability and hence play a foremost role in defining the chromatin complex order structures. The histone fold is composed of three $\alpha $-helices (${\alpha _1}$, ${\alpha _2}$, and ${\alpha _3}$) linked by short loops L1 and L2. These loops facilitate heterodimeric interactions among the core histones.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




