
Hoffmann's bromamide reaction is to convert:
(A) Acid to alcohol
(B) Alcohol to acid
(C) Amide to Amine
(D) Amine to amide
Answer
592.2k+ views
Hint: The Hoffmann's Bromamide reaction uses a halogen, a base, water and heat for it to take place. Amines are the functional group which are a derivative of ammonia but one or more hydrogen are replaced by an alkyl group or an aryl group. Amide is a functional group that has a carbonyl attached to a nitrogen atom.
Complete answer step by step: Hoffmann Bromamide reaction mechanism is a reaction that is used to convert a primary amide into a primary amine with one less carbon. This reaction uses an alkali as a strong base which attacks the amide which leads to the deprotonation and generation of an anion.
The Hoffmann' Bromamide reaction can be written as follows:
$RCON{ H }_{ 2 }\quad +\quad B{ r }_{ 2 }\quad +\quad 4NaOH\quad \rightarrow \quad R-N{ H }_{ 2\quad }\quad +\quad N{ a }_{ 2 }C{ O }_{ 3 }\quad +\quad 2NaBr\quad +\quad 2{ H }_{ 2 }O$
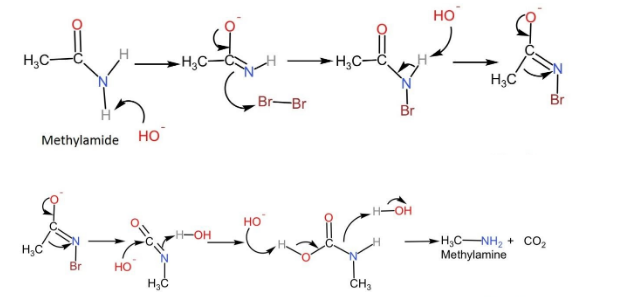
The reaction proceeds with the attack of a strong base on the amide, which leads to deprotonation and generating an anion.
The anion formed reacts with the bromine to form N-bromamide and this reaction is known as $\alpha$-substitution reaction.
Then deprotonation of bromamide molecules takes place to form bromamide anion.
This anion undergoes rearrangement such that the R group which was attached to the carbonyl carbon migrates to nitrogen. Simultaneously the bromide ion leaves the compound forming isocyanate.
Water molecules get added to isocyanate to form carbamic acid.
Finally, this carbamic acid releases carbon dioxide, leading to the formation of primary amine.
Note: Deprotonation refers to the removal/transfer of a proton from a bronsted lowry acid in an acid base reaction. This forms the conjugate base of that acid which was deprotonated.
Complete answer step by step: Hoffmann Bromamide reaction mechanism is a reaction that is used to convert a primary amide into a primary amine with one less carbon. This reaction uses an alkali as a strong base which attacks the amide which leads to the deprotonation and generation of an anion.
The Hoffmann' Bromamide reaction can be written as follows:
$RCON{ H }_{ 2 }\quad +\quad B{ r }_{ 2 }\quad +\quad 4NaOH\quad \rightarrow \quad R-N{ H }_{ 2\quad }\quad +\quad N{ a }_{ 2 }C{ O }_{ 3 }\quad +\quad 2NaBr\quad +\quad 2{ H }_{ 2 }O$

The reaction proceeds with the attack of a strong base on the amide, which leads to deprotonation and generating an anion.
The anion formed reacts with the bromine to form N-bromamide and this reaction is known as $\alpha$-substitution reaction.
Then deprotonation of bromamide molecules takes place to form bromamide anion.
This anion undergoes rearrangement such that the R group which was attached to the carbonyl carbon migrates to nitrogen. Simultaneously the bromide ion leaves the compound forming isocyanate.
Water molecules get added to isocyanate to form carbamic acid.
Finally, this carbamic acid releases carbon dioxide, leading to the formation of primary amine.
Note: Deprotonation refers to the removal/transfer of a proton from a bronsted lowry acid in an acid base reaction. This forms the conjugate base of that acid which was deprotonated.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




