
The final image formed by a compound microscope is inverted:
A) True
B) False
Answer
593.1k+ views
Hint: This problem can be solved by recalling the ray diagram for the formation of an image by a compound microscope. A compound microscope consists of two convex lenses that work in unison to form a magnified image of an object.
Complete step by step answer:
A compound microscope is an optical instrument that is used to form an enlarged or magnified image of a very small object. The microscope achieves this task by the use of two convex lenses that work in unison. Hence, the microscope is called compound, as it consists of two lenses.
Let us draw the ray diagram of the formation of an image by a compound microscope.
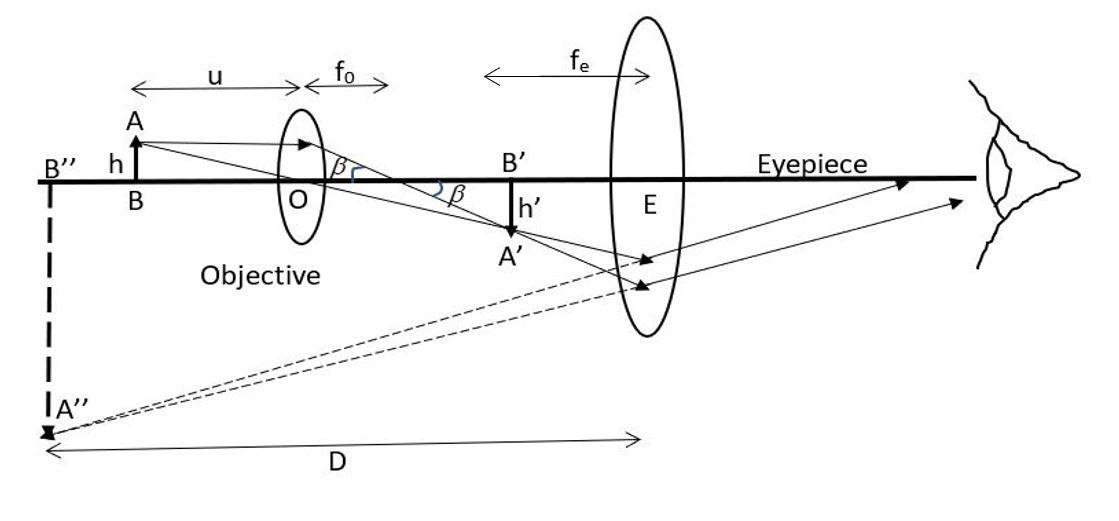
As can be seen from the above ray diagram, the first convex lens, or the objective forms a real and inverted image of the object. This image falls within the focal length of the second convex lens – the eyepiece and acts as the object for it. Since, for the eyepiece, the object is within its focal length it forms a virtual and erect image of the object. Now, since the object for the eyepiece is nothing but the inverted image of the object formed by the objective, the erect final image of the inverted intermediate image will mean that the final image is actually inverted with respect to the object as is evident from the above ray diagram.
Therefore, the final image formed by a compound microscope is inverted.
Therefore, the correct answer is A) True.
Note:
Students should not get confused between the ray diagrams of the astronomical telescope and compound microscope thought both of them are similar. For an astronomical telescope, the rays from an object are said to come from infinity and the telescope magnifies the angle subtended by the object on the eye whereas the compound microscope magnifies the size of the image with respect to the object. For an astronomical telescope, the objective is larger than the eyepiece in diameter whereas for a compound microscope, it is the opposite.
Complete step by step answer:
A compound microscope is an optical instrument that is used to form an enlarged or magnified image of a very small object. The microscope achieves this task by the use of two convex lenses that work in unison. Hence, the microscope is called compound, as it consists of two lenses.
Let us draw the ray diagram of the formation of an image by a compound microscope.

As can be seen from the above ray diagram, the first convex lens, or the objective forms a real and inverted image of the object. This image falls within the focal length of the second convex lens – the eyepiece and acts as the object for it. Since, for the eyepiece, the object is within its focal length it forms a virtual and erect image of the object. Now, since the object for the eyepiece is nothing but the inverted image of the object formed by the objective, the erect final image of the inverted intermediate image will mean that the final image is actually inverted with respect to the object as is evident from the above ray diagram.
Therefore, the final image formed by a compound microscope is inverted.
Therefore, the correct answer is A) True.
Note:
Students should not get confused between the ray diagrams of the astronomical telescope and compound microscope thought both of them are similar. For an astronomical telescope, the rays from an object are said to come from infinity and the telescope magnifies the angle subtended by the object on the eye whereas the compound microscope magnifies the size of the image with respect to the object. For an astronomical telescope, the objective is larger than the eyepiece in diameter whereas for a compound microscope, it is the opposite.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




