
Hormogonia are the vegetatively reproducing structure of
(a) Ulothrix
(b) Spirogyra
(c) Oscillatoria
(d) Chlamydomonas
Answer
568.5k+ views
Hint: They are a genus of filamentous cyanobacterium which is known as after the oscillation in its movement. Filaments within the colonies could slide back and forth against one another till the entire mass is reorganized to its light.
Complete answer:
Oscillatoria is an organism that reproduces by fragmentation. Oscillatoria forms long filaments of cells which may force an entry of fragments called hormogonia. The hormogonia can grow into a replacement, longer filament.
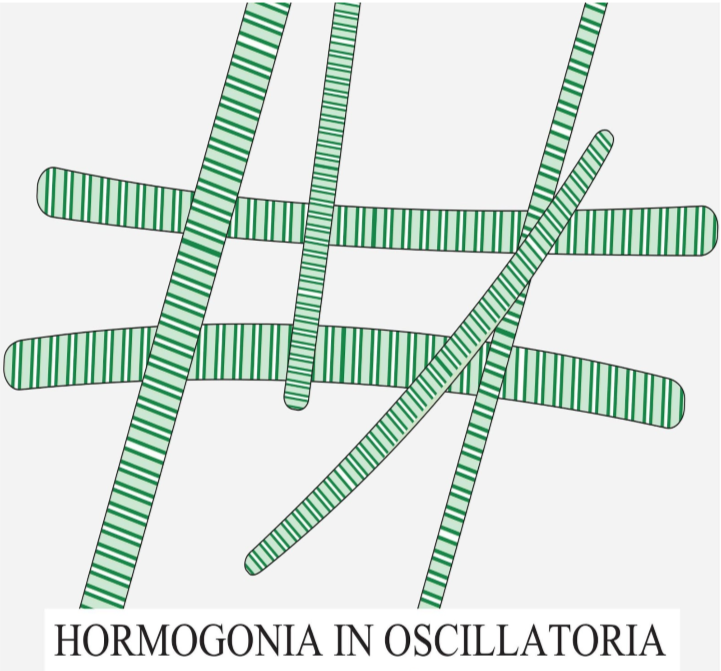
Oscillatoria uses photosynthesis to survive and reproduce. Each filament of oscillatoria consists of a trichome which is formed from rows of cells. The tip of the trichome oscillates sort of like a pendulum. In reproduction, it occurs through vegetative means only. Basically, the filament splits up into a variety of fragments known as homogonia. Each hormogonium contains one or more cells and grows into a filament by cellular division in one direction.
Additional information: Hormogonium discrimination is important for the event of nitrogen-fixing plant cyanobacteria symbioses, especially in between cyanobacteria of the genus Nostoc and their hosts. In reaction to a hormogonium- persuading part released by plant hosts, cyanobacterial symbionts distinguished into hormogonia then de-discrimination back to vegetative cells following around 96 hours. Hopefully, they need to manage to succeed in the plant host by this point. The bacteria afterward differentiate specialized nitrogen-fixing cells known as heterocysts and enter into a functioning symbiosis with the plant.
So, the correct answer is ‘(c) Oscillatoria’.
Note: Oscillatoria is the subject of research into the natural production of butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT), an antioxidant, food additive, and industrial chemical. Depending on species, Hormogonia are often many micrometers long and may travel as fast as 11 μm/s. They move through gliding motility, needing a wet-able surface or a viscous substrate, like agar for motility.
Complete answer:
Oscillatoria is an organism that reproduces by fragmentation. Oscillatoria forms long filaments of cells which may force an entry of fragments called hormogonia. The hormogonia can grow into a replacement, longer filament.

Oscillatoria uses photosynthesis to survive and reproduce. Each filament of oscillatoria consists of a trichome which is formed from rows of cells. The tip of the trichome oscillates sort of like a pendulum. In reproduction, it occurs through vegetative means only. Basically, the filament splits up into a variety of fragments known as homogonia. Each hormogonium contains one or more cells and grows into a filament by cellular division in one direction.
Additional information: Hormogonium discrimination is important for the event of nitrogen-fixing plant cyanobacteria symbioses, especially in between cyanobacteria of the genus Nostoc and their hosts. In reaction to a hormogonium- persuading part released by plant hosts, cyanobacterial symbionts distinguished into hormogonia then de-discrimination back to vegetative cells following around 96 hours. Hopefully, they need to manage to succeed in the plant host by this point. The bacteria afterward differentiate specialized nitrogen-fixing cells known as heterocysts and enter into a functioning symbiosis with the plant.
So, the correct answer is ‘(c) Oscillatoria’.
Note: Oscillatoria is the subject of research into the natural production of butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT), an antioxidant, food additive, and industrial chemical. Depending on species, Hormogonia are often many micrometers long and may travel as fast as 11 μm/s. They move through gliding motility, needing a wet-able surface or a viscous substrate, like agar for motility.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




