
How Lysosomes are formed?
Answer
537.9k+ views
Hint: A lysosome is a membrane-bound organelle that is involved with various cell processes and helps in the breakdown of excess, worn-out cell parts. It is the suicidal cell organelles of the cell. They are formed by the endomembrane organelle that helps in packaging.
Complete answer:
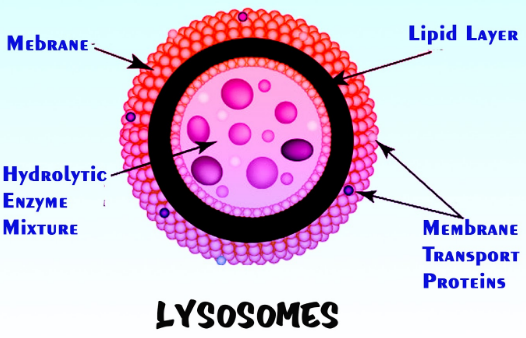
Lysosomes are membrane-enclosed compartments crammed with hydrolytic enzymes that are used for the controlled intracellular digestion of macromolecules. They contain around 40 types of hydrolytic synthetic compounds, including proteases, glycosidases, nucleases, lipases, phosphatases, phospholipases, and sulfatases.
Lysosomes digest several different kinds of molecules. They can digest food molecules that enter the cell into more modest pieces if an endocytic vesicle (a vesicle that carries particles into the cell) wires with them. They are formed by the Golgi bodies when they transport in the form of small vesicles. Lysosomes are formed by budding off of the Golgi body, and therefore the hydrolytic enzymes within them are formed within the endoplasmic reticulum. The catalysts are labeled with the atom mannose-6-phosphate, shipped to the Golgi body in vesicles, at that point bundled into the lysosomes.
They can likewise perform autophagy, which is the devastation of inappropriately working organelles. In addition, lysosomes have a task in phagocytosis, which is when a cell engulfs a molecule so as to interrupt it down; it's also referred to as “cell eating”. For example, the white blood cells called phagocytes ingest invading bacteria in order to break it down and destroy it, and the bacteria are enclosed by a vesicle that lysosomes fuse with. These lysosomes then break down the bacteria.
The food material enters into the food vacuole through the plasma membrane by the process of endocytosis and the lysosome consisting of active hydrolytic enzyme moves away from the plasma membrane. The lysosome fusing with the food vacuole and the hydrolytic enzymes enter into the food vacuole and the hydrolytic enzymes digest the food particles. It consists of more than 60 different enzymes and has 50 membrane proteins. The enzymes get synthesized in the rough endoplasmic reticulum and are exported to the Golgi apparatus for recruitment by the complex composed of proteins. They fuse with the larger acidic vesicles and are destined for lysosomes which are specifically tagged with the molecule and are properly sorted into the acidified vesicles.
Note:
Lysosomes are generally very small, ranging in size from 0.1-0.5 µm, though they can reach up to 1.2 µm. They have an easy structure; they're spheres made from a lipid bilayer that encloses fluid that contains a spread of hydrolytic enzymes. The lipids that structure the bilayer are phospholipids, which are molecules that have hydrophilic phosphate group heads, a glycerol molecule, and hydrophobic carboxylic acid tails.
Complete answer:
Lysosomes are membrane-enclosed compartments crammed with hydrolytic enzymes that are used for the controlled intracellular digestion of macromolecules. They contain around 40 types of hydrolytic synthetic compounds, including proteases, glycosidases, nucleases, lipases, phosphatases, phospholipases, and sulfatases.
Lysosomes digest several different kinds of molecules. They can digest food molecules that enter the cell into more modest pieces if an endocytic vesicle (a vesicle that carries particles into the cell) wires with them. They are formed by the Golgi bodies when they transport in the form of small vesicles. Lysosomes are formed by budding off of the Golgi body, and therefore the hydrolytic enzymes within them are formed within the endoplasmic reticulum. The catalysts are labeled with the atom mannose-6-phosphate, shipped to the Golgi body in vesicles, at that point bundled into the lysosomes.
They can likewise perform autophagy, which is the devastation of inappropriately working organelles. In addition, lysosomes have a task in phagocytosis, which is when a cell engulfs a molecule so as to interrupt it down; it's also referred to as “cell eating”. For example, the white blood cells called phagocytes ingest invading bacteria in order to break it down and destroy it, and the bacteria are enclosed by a vesicle that lysosomes fuse with. These lysosomes then break down the bacteria.
The food material enters into the food vacuole through the plasma membrane by the process of endocytosis and the lysosome consisting of active hydrolytic enzyme moves away from the plasma membrane. The lysosome fusing with the food vacuole and the hydrolytic enzymes enter into the food vacuole and the hydrolytic enzymes digest the food particles. It consists of more than 60 different enzymes and has 50 membrane proteins. The enzymes get synthesized in the rough endoplasmic reticulum and are exported to the Golgi apparatus for recruitment by the complex composed of proteins. They fuse with the larger acidic vesicles and are destined for lysosomes which are specifically tagged with the molecule and are properly sorted into the acidified vesicles.
Note:
Lysosomes are generally very small, ranging in size from 0.1-0.5 µm, though they can reach up to 1.2 µm. They have an easy structure; they're spheres made from a lipid bilayer that encloses fluid that contains a spread of hydrolytic enzymes. The lipids that structure the bilayer are phospholipids, which are molecules that have hydrophilic phosphate group heads, a glycerol molecule, and hydrophobic carboxylic acid tails.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




