
How many isomers does ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{13}}Br$ have?
Answer
524.4k+ views
Hint: To determine the isomers of a molecule, we first need to know what are isomers. Molecules that have different arrangements but the same molecular formula are known as isomers. The concept of the existence of isomers is known as isomerism.
Complete answer:
We know that isomers are molecules having different shapes but identical formulas. Isomers don't need to have similar physical or chemical properties.
Now, there are two types of isomers.
1. Structural Isomers: When the atoms in the molecules are bonded differently, they are known as structural isomers or constitutional isomers.
2. Stereoisomers: When the position of the atoms in molecules differ but have the same bonds, they are known as stereoisomers or spatial isomers.
When a molecule cannot be superimposed upon its mirror image, the molecule is called a chiral atom. The mirror images of the chiral molecules are known as enantiomers. A chiral atom is bonded to distinct ligands.
Now, in ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{13}}Br$, 1 hydrogen atom is substituted from the hexane parent chain with bromine to form bromohexane.
Isomers of ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{13}}Br$
With hexane parent chain:
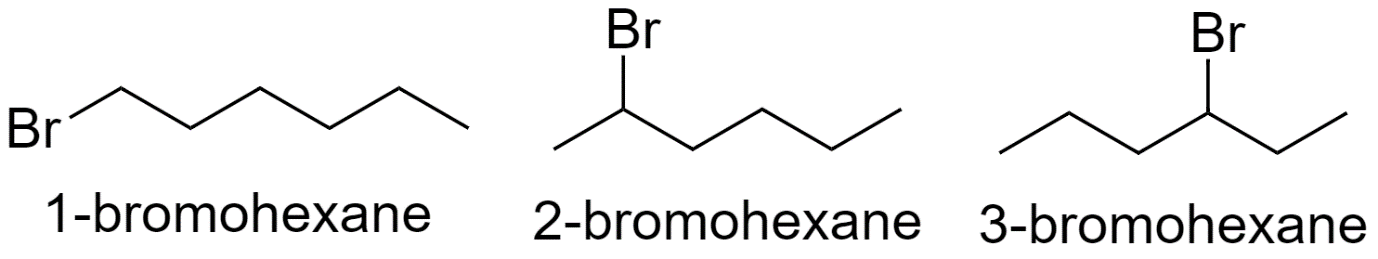
With pentane parent chain and 1 methyl substituent:
a) When methyl group is substituted on the 2nd carbon atom.
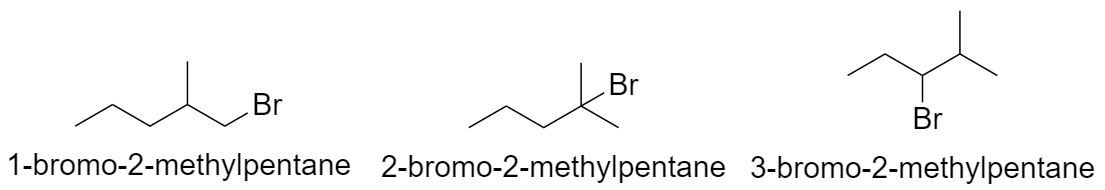
b) When methyl group is substituted on the 3rd carbon atom.
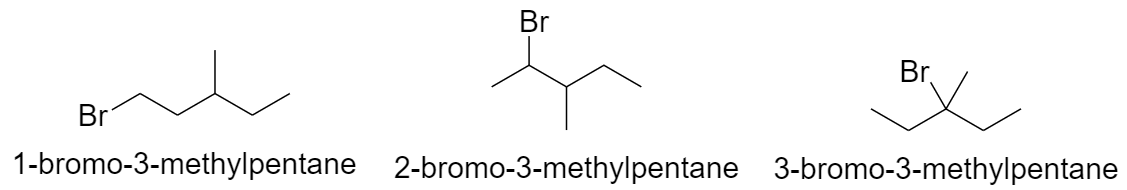
c) When methyl group is substituted on the 4th carbon atom.
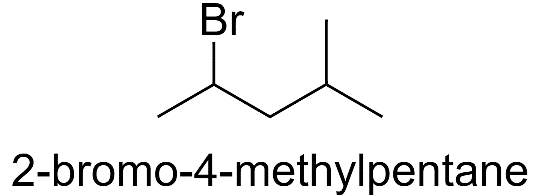
With butane parent chain and 2 methyl substituents:
a) When both the methyl groups are substituted on the 2nd carbon atom.
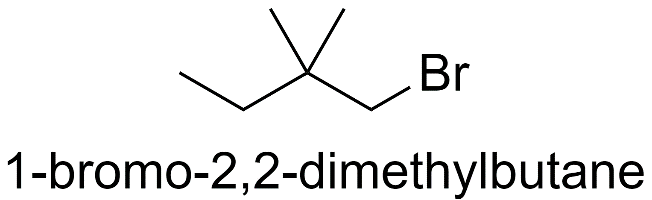
b) When both the methyl groups are substituted on the 3rd carbon atom.
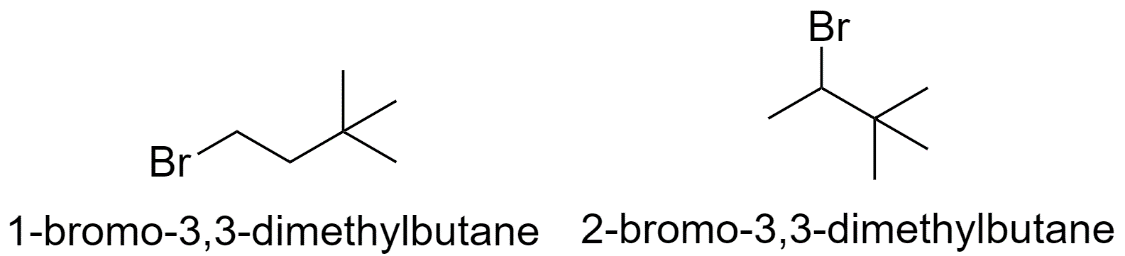
c) When the methyl groups are substituted on the 2nd and the 3rd carbon atom.
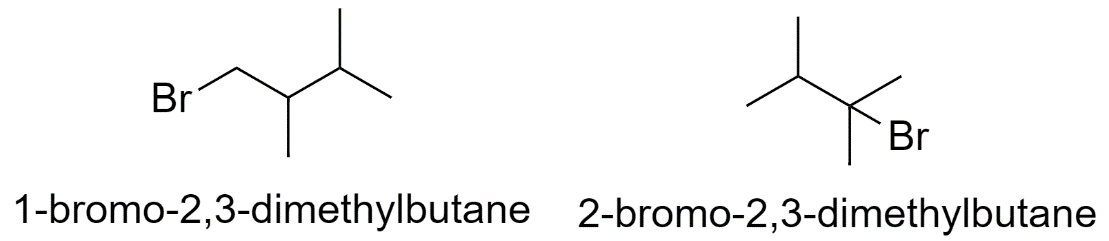
Hence there are a total of 15 structural isomers of bromohexane.
Stereoisomers
Now, if a molecule has n chiral centers, its possible stereoisomers will be ${{2}^{n}}$.
These 8 structural isomers of bromohexane have 1 chiral center. So, each of these will have 2 optical isomers.
1) 2-bromohexane
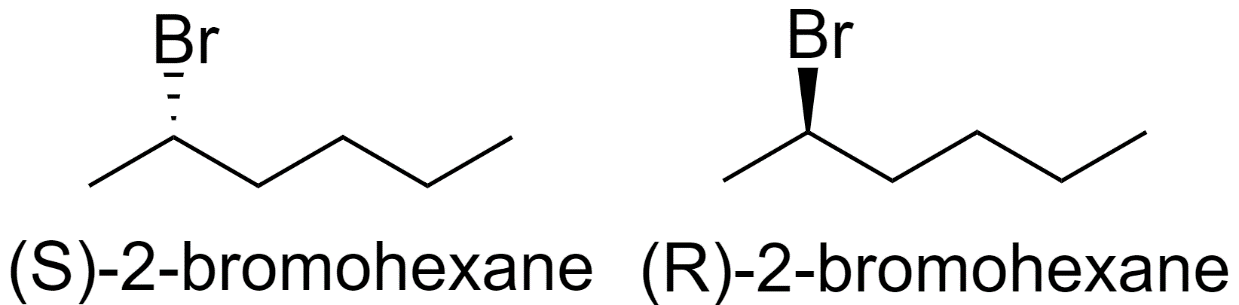
2) 3-bromohexane
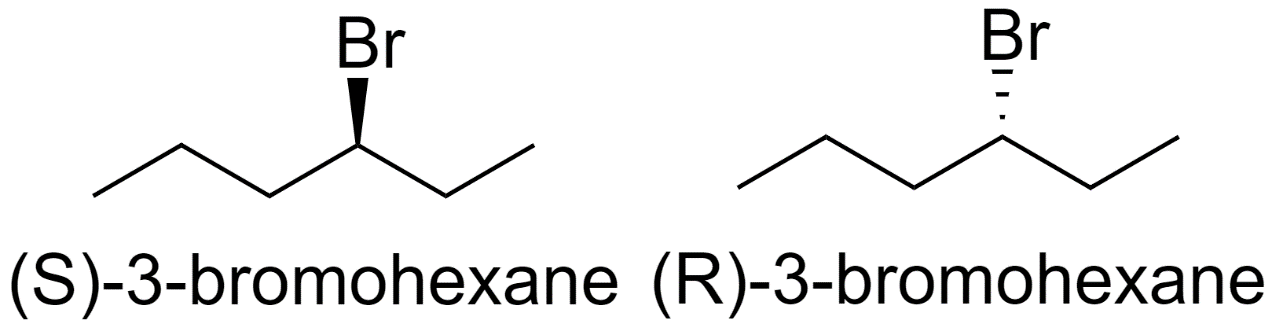
3) 1-bromo-2-methylpentane
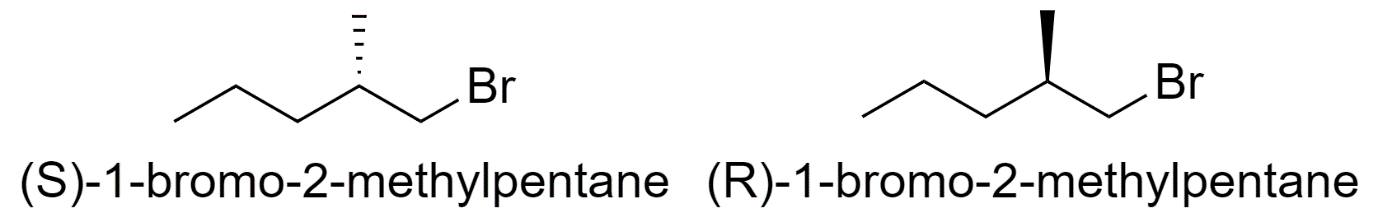
4) 3-bromo-2-methylpentane
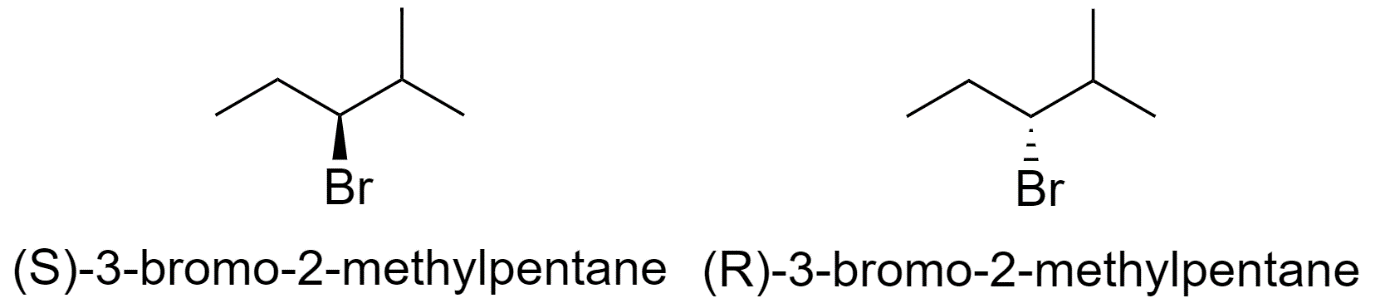
5) 1-bromo-3-methylpentane
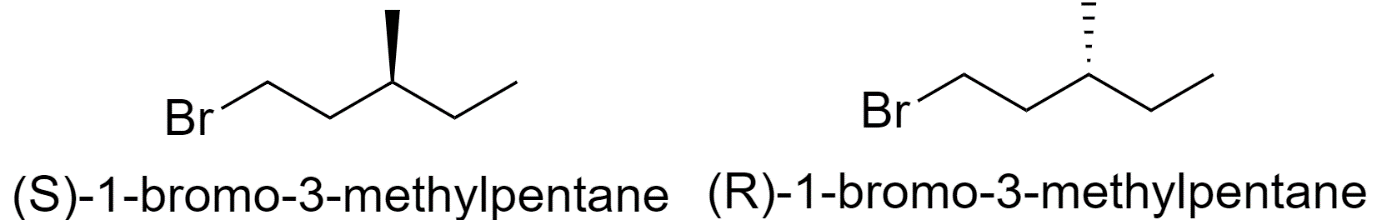
6) 2-bromo-4-methylpentane
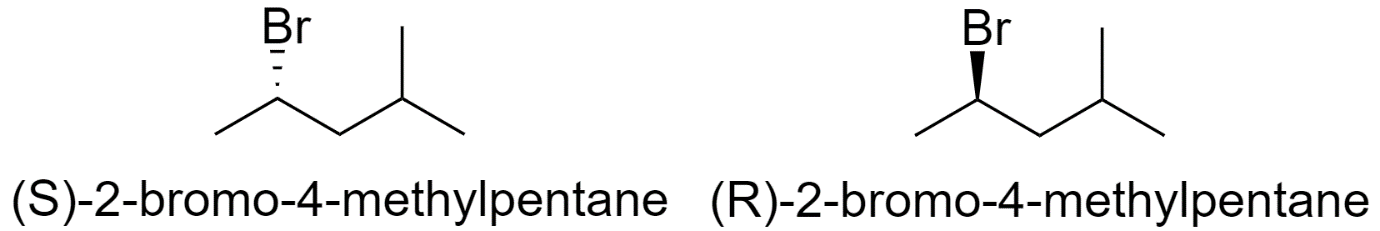
7) 2-bromo-3,3-dimethylbutane
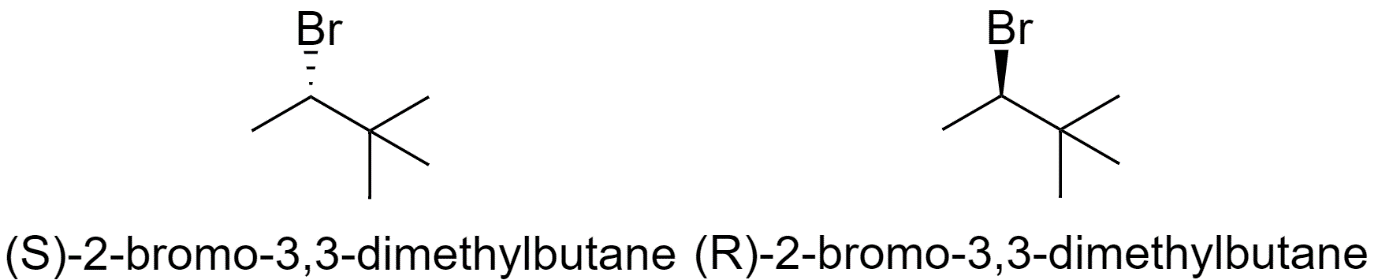
8) 1-bromo-2,3-dimethylbutane
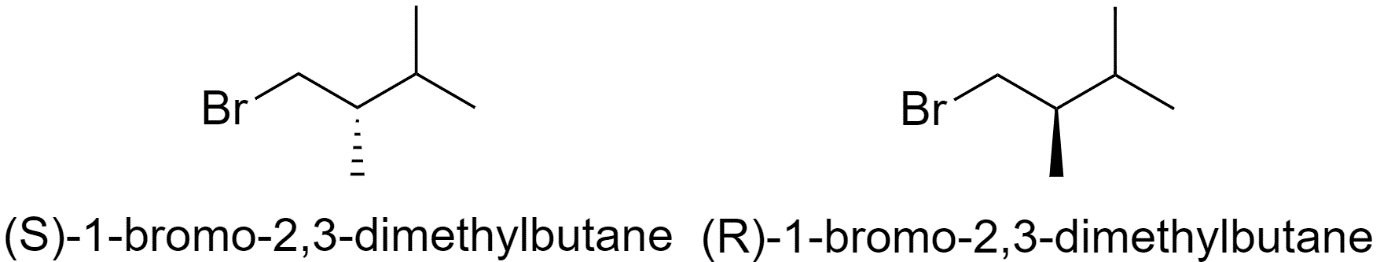
One structural isomer of bromohexane has 2 chiral centers. So, it will have 4 optical isomers.
2-bromo-3-methylpentane
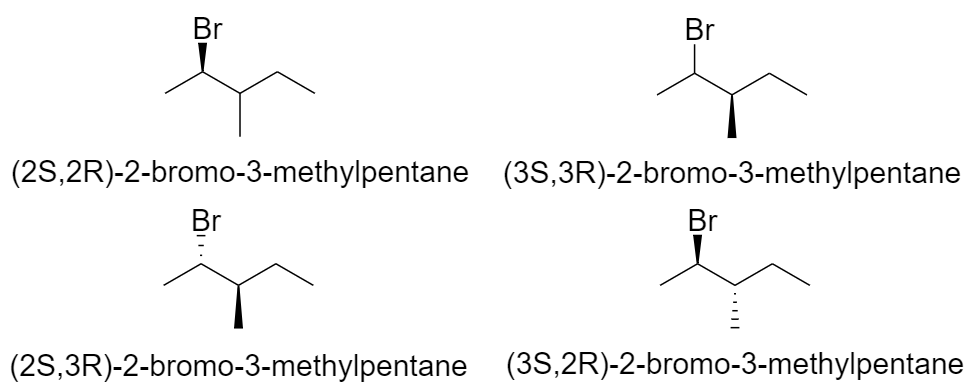
Hence there are a total of 20 optical isomers of 9 structural isomers of bromohexane.
So, the total number of isomers of bromohexane ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{13}}Br$ is 26.
Note:
It should be noted that while writing the isomers of a compound, one must include all the structural isomers like skeletal isomers, positional isomers, and the functional isomers, and the stereoisomers of these molecules, if any, including enantiomers, diastereomers, cis-trans isomers, conformers, etc.
Complete answer:
We know that isomers are molecules having different shapes but identical formulas. Isomers don't need to have similar physical or chemical properties.
Now, there are two types of isomers.
1. Structural Isomers: When the atoms in the molecules are bonded differently, they are known as structural isomers or constitutional isomers.
2. Stereoisomers: When the position of the atoms in molecules differ but have the same bonds, they are known as stereoisomers or spatial isomers.
When a molecule cannot be superimposed upon its mirror image, the molecule is called a chiral atom. The mirror images of the chiral molecules are known as enantiomers. A chiral atom is bonded to distinct ligands.
Now, in ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{13}}Br$, 1 hydrogen atom is substituted from the hexane parent chain with bromine to form bromohexane.
Isomers of ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{13}}Br$
With hexane parent chain:

With pentane parent chain and 1 methyl substituent:
a) When methyl group is substituted on the 2nd carbon atom.

b) When methyl group is substituted on the 3rd carbon atom.

c) When methyl group is substituted on the 4th carbon atom.

With butane parent chain and 2 methyl substituents:
a) When both the methyl groups are substituted on the 2nd carbon atom.

b) When both the methyl groups are substituted on the 3rd carbon atom.

c) When the methyl groups are substituted on the 2nd and the 3rd carbon atom.

Hence there are a total of 15 structural isomers of bromohexane.
Stereoisomers
Now, if a molecule has n chiral centers, its possible stereoisomers will be ${{2}^{n}}$.
These 8 structural isomers of bromohexane have 1 chiral center. So, each of these will have 2 optical isomers.
1) 2-bromohexane

2) 3-bromohexane

3) 1-bromo-2-methylpentane

4) 3-bromo-2-methylpentane

5) 1-bromo-3-methylpentane

6) 2-bromo-4-methylpentane

7) 2-bromo-3,3-dimethylbutane

8) 1-bromo-2,3-dimethylbutane

One structural isomer of bromohexane has 2 chiral centers. So, it will have 4 optical isomers.
2-bromo-3-methylpentane

Hence there are a total of 20 optical isomers of 9 structural isomers of bromohexane.
So, the total number of isomers of bromohexane ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{13}}Br$ is 26.
Note:
It should be noted that while writing the isomers of a compound, one must include all the structural isomers like skeletal isomers, positional isomers, and the functional isomers, and the stereoisomers of these molecules, if any, including enantiomers, diastereomers, cis-trans isomers, conformers, etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




