
How many vertices does a Cone have?
Answer
517.2k+ views
Hint: In order to the given question, to know the number of vertices of a cone, first we will explain the vertices and then we will talk about the cone and its properties, and then we will also discuss on the shape of cone.
Complete step by step solution:
A vertices is a point where two or more edges intersect
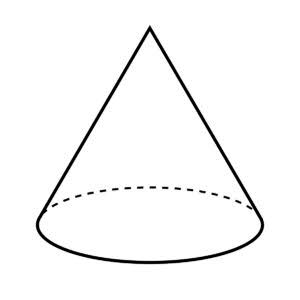
A cone is a three-dimensional geometric shape that narrows smoothly from a flat base (usually circular) to a point called the apex or vertex (which forms an axis to the base's centre). The cone can also be described as a pyramid with a circular cross-section, as opposed to a pyramid with a triangular cross-section.
A cone has one vertex.
Additional information:
A circular cone is another name for these cones. A cone is made up of line segments, half-lines, or lines that link a common point, the apex, to all of the points on a base that are not in the same plane as the apex. The base may be a circle, any one-dimensional quadratic form in the plane, any closed one-dimensional figure, or any of the above plus all the enclosed points, depending on the author.
The lateral surface of a solid object is defined as the boundary created by these lines or partial lines; if the lateral surface is unbounded, it is referred to as a conical surface.
This is a cone with:
$\bullet$ 2 faces (1 curved, 1 circle)
$\bullet$ 1 corner
$\bullet$ 1 curved edge
Note:
Now, one question arises here: Is Cone a Pyramid? So, a cone is a typical pyramid-like figure with a circle or other closed curve as the base rather than a polygon. A cone has a curved lateral surface rather than multiple triangular sides, but both a cone and a pyramid have the same volume.
Complete step by step solution:
A vertices is a point where two or more edges intersect
A cone is a three-dimensional geometric shape that narrows smoothly from a flat base (usually circular) to a point called the apex or vertex (which forms an axis to the base's centre). The cone can also be described as a pyramid with a circular cross-section, as opposed to a pyramid with a triangular cross-section.
A cone has one vertex.

Additional information:
A circular cone is another name for these cones. A cone is made up of line segments, half-lines, or lines that link a common point, the apex, to all of the points on a base that are not in the same plane as the apex. The base may be a circle, any one-dimensional quadratic form in the plane, any closed one-dimensional figure, or any of the above plus all the enclosed points, depending on the author.
The lateral surface of a solid object is defined as the boundary created by these lines or partial lines; if the lateral surface is unbounded, it is referred to as a conical surface.
This is a cone with:
$\bullet$ 2 faces (1 curved, 1 circle)
$\bullet$ 1 corner
$\bullet$ 1 curved edge
Note:
Now, one question arises here: Is Cone a Pyramid? So, a cone is a typical pyramid-like figure with a circle or other closed curve as the base rather than a polygon. A cone has a curved lateral surface rather than multiple triangular sides, but both a cone and a pyramid have the same volume.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Find the mode and median of the data 13 16 12 14 1-class-9-maths-CBSE

What were the main changes brought about by the Bolsheviks class 9 social science CBSE

What is the theme or message of the poem The road not class 9 english CBSE

What are the major achievements of the UNO class 9 social science CBSE

Explain the importance of pH in everyday life class 9 chemistry CBSE

Differentiate between parenchyma collenchyma and sclerenchyma class 9 biology CBSE




